Abstract
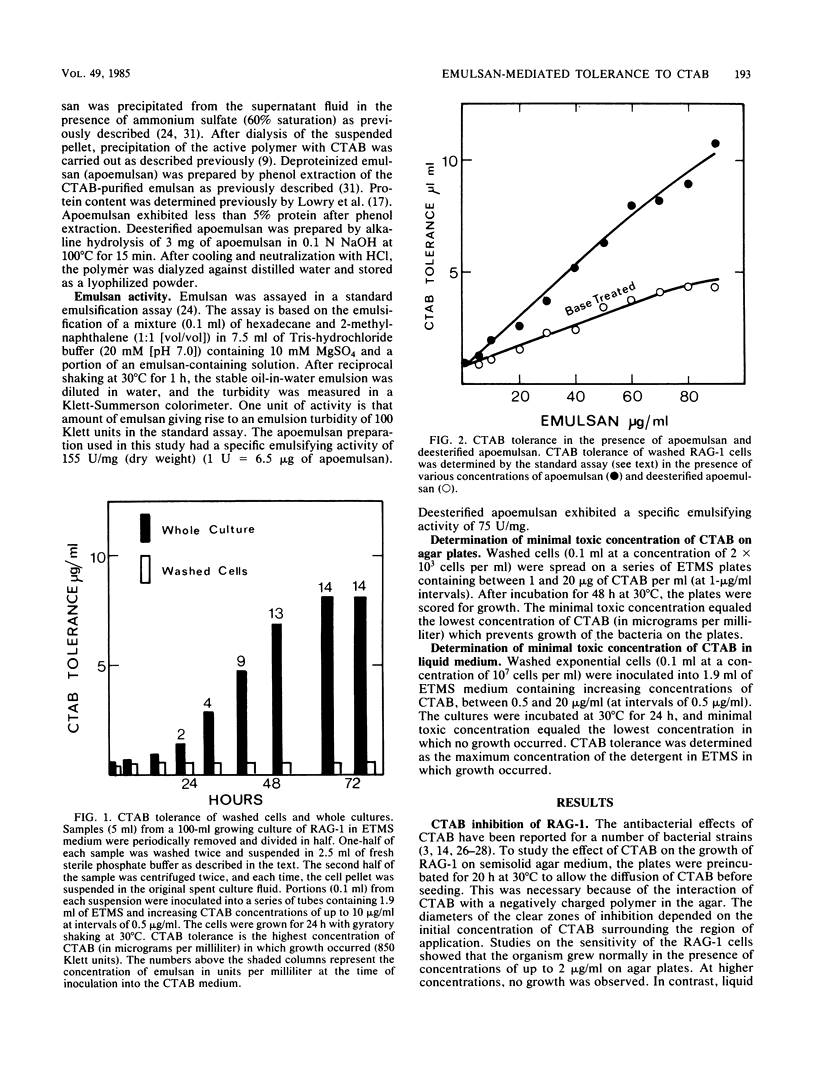
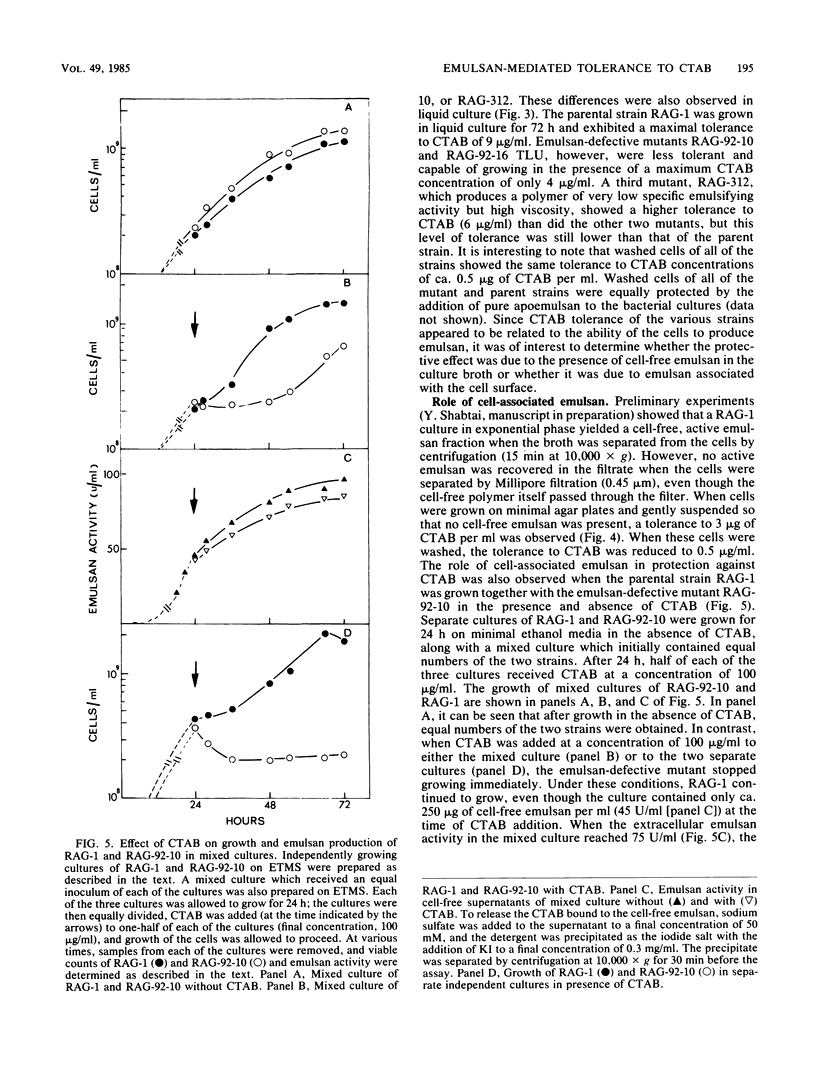
Emulsan, the polyanionic heteropolysaccharide bioemulsifier produced by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus RAG-1, was found to enhance the tolerance of RAG-1 cells to the toxic effects of the cationic detergent cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB). Emulsan-mediated tolerance was obtained with the purified deproteinated apoemulsan; ca. 9 micrograms of apoemulsan neutralized 1 microgram of CTAB. Deesterified apoemulsan was only half as effective in protecting the cells from CTAB toxicity. Tolerance was also mediated by the cell-associated emulsan minicapsule. Mutants lacking this capsule were more sensitive to CTAB than the corresponding parent. The growth of mutants and parent cells in mixed-culture experiments demonstrated that the cell-associated polymer mediates CTAB tolerance in the early stages of growth. Once sufficient cell-free polymer has been released into the aqueous medium (ca. 0.5 micrograms/ml), this extracellular emulsan also plays a role in CTAB tolerance.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer E. A., Rosenberg E., Gutnick D. The isolation of cell surface mutants of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus RAG-1. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Dec;127(2):295–300. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belsky I., Gutnick D. L., Rosenberg E. Emulsifier of Arthrobacter RAG-1: determination of emulsifier-bound fatty acids. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 1;101(1):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Irvin R. T., Cheng K. J. The role of bacterial surface structures in pathogenesis. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1981;8(4):303–338. doi: 10.3109/10408418109085082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman S., Shabtai Y., Rubinovitz C., Rosenberg E., Gutnick D. L. Emulsan in Acinetobacter calcoaceticus RAG-1: Distribution of Cell-Free and Cell-Associated Cross-Reacting Material. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):165–170. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.165-170.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Fyfe J. A. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa and cystic fibrosis: resistance of the mucoid from to carbenicillin, flucloxacillin and tobramycin and the isolation of mucoid variants in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 May;4(3):233–240. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R. Mucoid strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the influence of culture medium on the stability of mucus production. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Nov;8(4):513–522. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-4-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutnick D. L., Rosenberg E. Oil tankers and pollution: a microbiological approach. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:379–396. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines O., Bayer E. A., Gutnick D. L. Localization of emulsan-like polymers associated with the cell surface of acinetobacter calcoaceticus. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):893–905. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.893-905.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines O., Gutnick D. Specific binding of a bacteriophage at a hydrocarbon-water interface. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):179–183. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.179-183.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisfeld A., Rosenberg E., Gutnick D. Microbial degradation of crude oil: factors affecting the dispersion in sea water by mixed and pure cultures. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Sep;24(3):363–368. doi: 10.1128/am.24.3.363-368.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg E., Perry A., Gibson D. T., Gutnick D. L. Emulsifier of Arthrobacter RAG-1: specificity of hydrocarbon substrate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):409–413. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.409-413.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg E., Zuckerberg A., Rubinovitz C., Gutnick D. L. Emulsifier of Arthrobacter RAG-1: isolation and emulsifying properties. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):402–408. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.402-408.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinovitz C., Gutnick D. L., Rosenberg E. Emulsan production by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus in the presence of chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):126–132. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.126-132.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. J., HORNE R. W., COSSLETT V. E. Electron microscopy of bacteria treated with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 May;5(2):405–407. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-2-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. J. The adsorption of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide by bacteria, its action in releasing cellular constituents and its bactericidal effects. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 May;5(2):391–404. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-2-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulitzur S., Shilo M. Effect of Prymnesium parvum toxin, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide and sodium dodecyl sulphate on bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Aug;62(3):363–370. doi: 10.1099/00221287-62-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerberg A., Diver A., Peeri Z., Gutnick D. L., Rosenberg E. Emulsifier of Arthrobacter RAG-1: chemical and physical properties. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):414–420. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.414-420.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


