Abstract
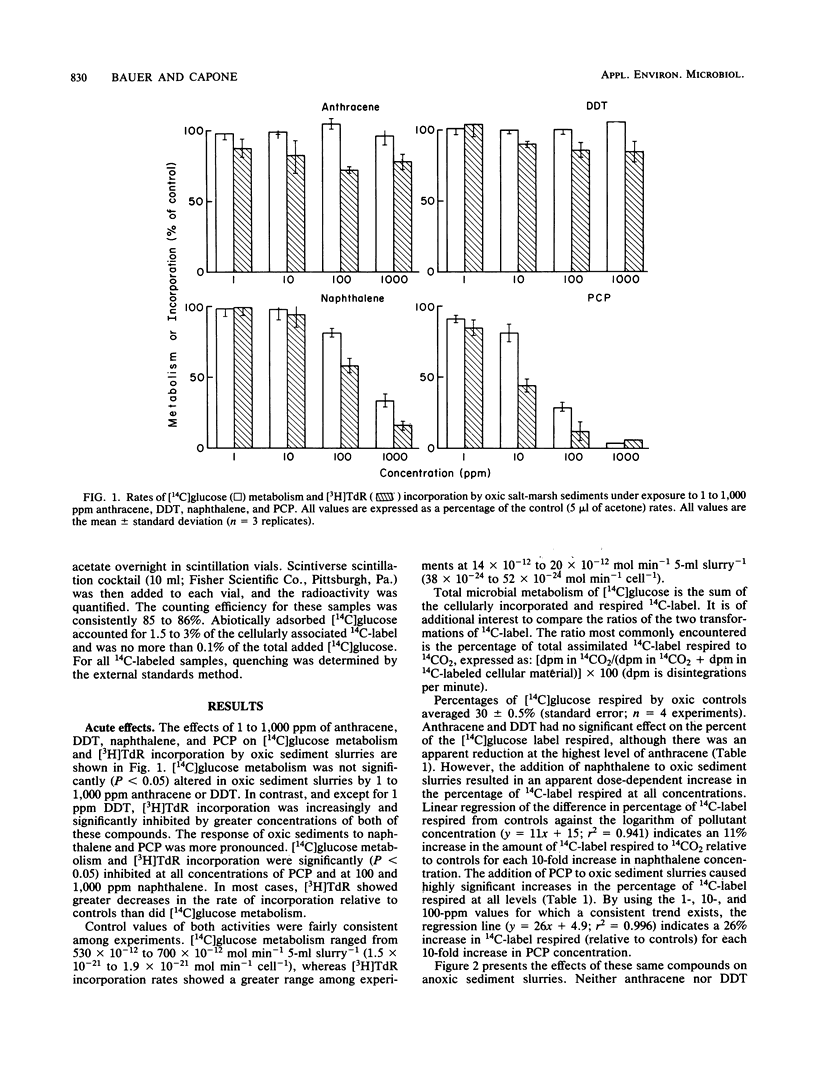
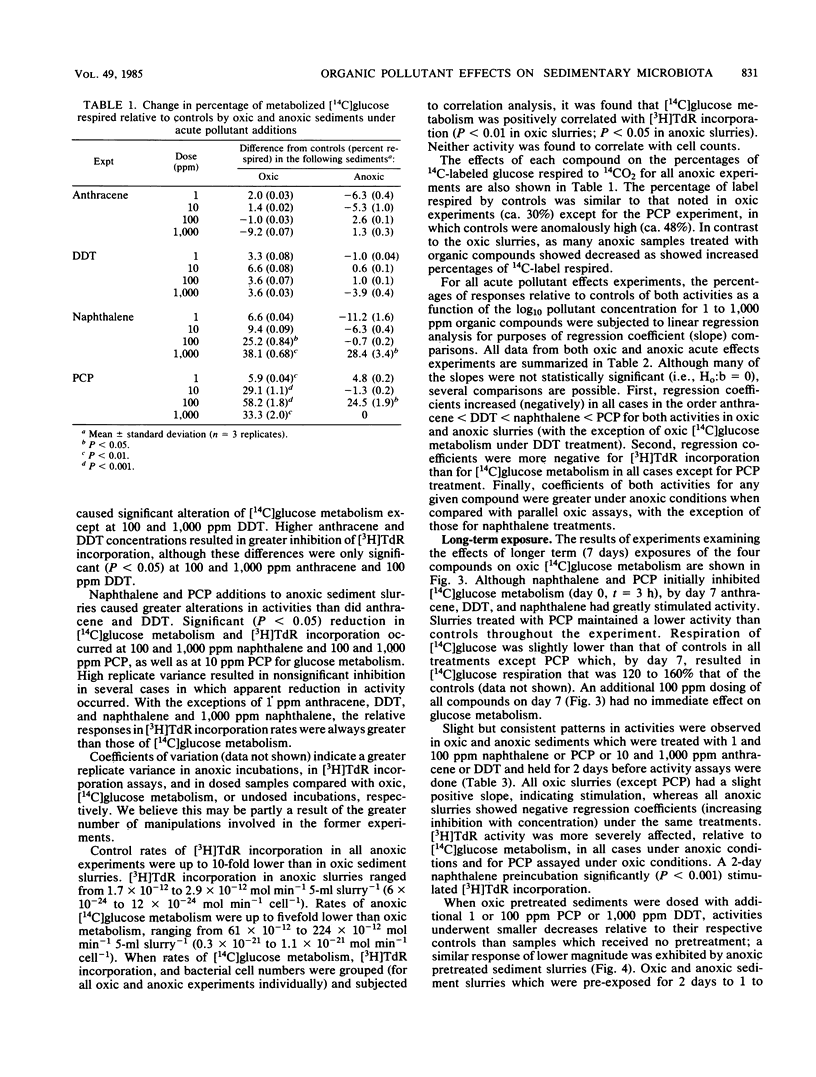
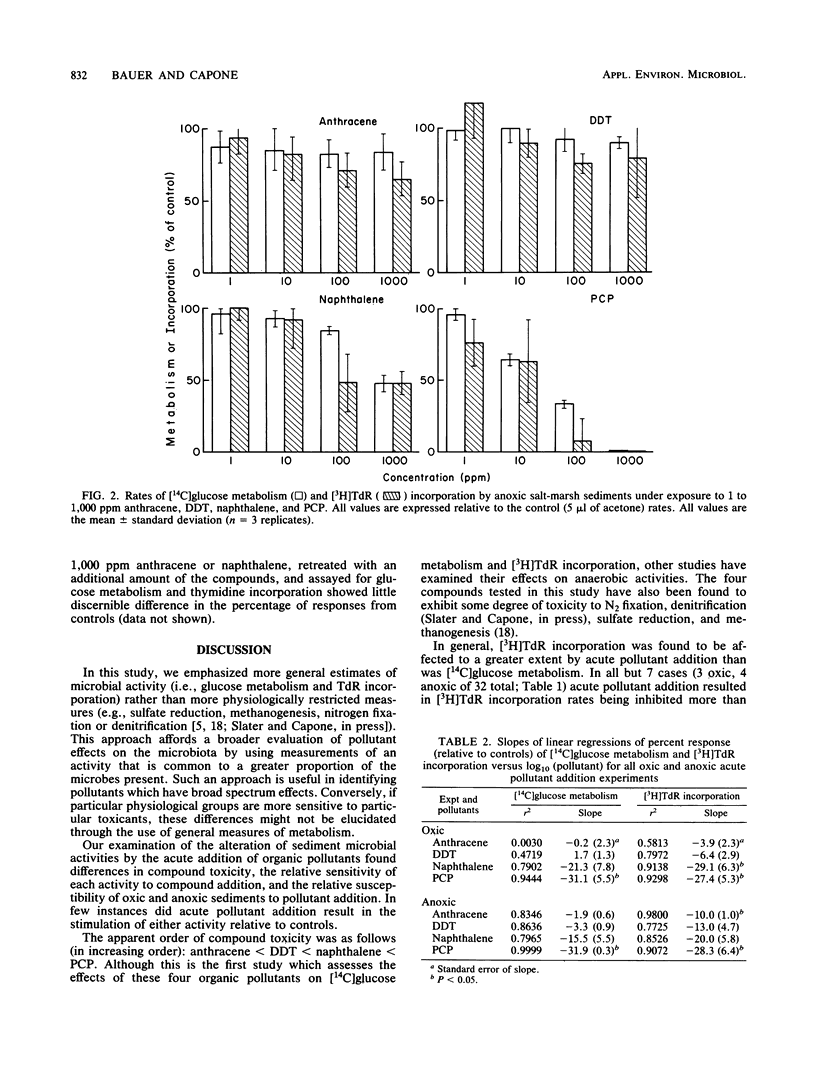
The metabolism of D-[U-14C]glucose and the incorporation of [methyl-3H]thymidine by aerobic and anaerobic marine sediment microbes exposed to 1 to 1,000 ppm anthracene, naphthalene, p,p'-dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, and pentachlorophenol were examined. Cell-specific rates of [14C]glucose metabolism averaged 1.7 X 10(-21) and 0.5 X 10(-21) mol/min per cell for aerobic and anaerobic sediment slurries, respectively; [3H]thymidine incorporation rates averaged 43 X 10(-24) and 9 X 10(-24) mol/min per cell for aerobic and anaerobic slurries, respectively. Aerobic sediments exposed to three of the organic pollutants for 2 to 7 days showed recovery of both activities. Anaerobic sediments showed little recovery after 2 days of pre-exposure to the pollutants. We conclude that (i) anaerobic sediments are more sensitive than aerobic sediments to pollutant additions; (ii) [3H]thymidine incorporation is more sensitive to pollutant additions than is [14C]glucose metabolism; and (iii) the toxicity of the pollutants increased in the following order: anthracene, p,p'-dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, naphthalene, and pentachlorophenol.
Full text
PDF

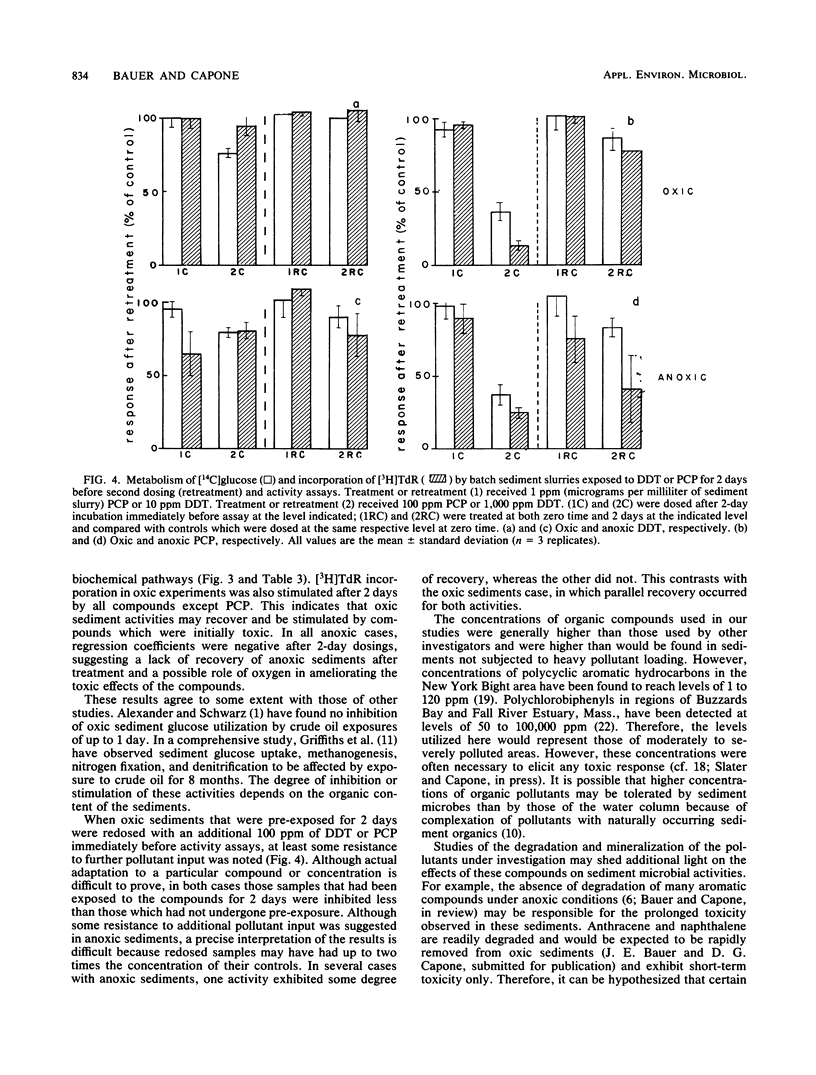

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander S. K., Schwarz J. R. Short-term effects of South louisiana and kuwait crude oils on glucose utilization by marine bacterial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug;40(2):341–345. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.2.341-345.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore R. P. Effects of polychlorinated biphenyls on macromolecular synthesis by a heterotrophic marine bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):329–336. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.329-336.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumer M., Youngblood W. W. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils and recent sediments. Science. 1975 Apr 4;188(4183):53–55. doi: 10.1126/science.188.4183.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capone D. G., Reese D. D., Kiene R. P. Effects of metals on methanogenesis, sulfate reduction, carbon dioxide evolution, and microbial biomass in anoxic salt marsh sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1586–1591. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1586-1591.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman J. A., Azam F. Bacterioplankton secondary production estimates for coastal waters of british columbia, antarctica, and california. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jun;39(6):1085–1095. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.6.1085-1095.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths R. P., Caldwell B. A., Broich W. A., Morita R. Y. Long-term effects of crude oil on uptake and respiration of glucose and glutamate in arctic and subarctic marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):792–801. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.792-801.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths R. P., Hanus F. J., Morita R. Y. The effects of various water-sample treatments on the apparent uptake of glutamic acid by natural marine microbial populations. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Sep;20(9):1261–1266. doi: 10.1139/m74-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths R. P., Hayasaka S. S., McNamara T. M., Morita R. Y. Comparison between two methods of assaying relative microbial activity in marine environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Dec;34(6):801–805. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.6.801-805.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths R. P., McNamara T. M., Caldwell B. A., Morita R. Y. Field observations on the acute effect of crude oil on glucose and glutamate uptake in samples collected from arctic and subarctic waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jun;41(6):1400–1406. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.6.1400-1406.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas R. B., Gilmour C. C., Stoner D. L., Weir M. M., Tuttle J. H. Comparison of methods to measure acute metal and organometal toxicity to natural aquatic microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):1005–1011. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.1005-1011.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


