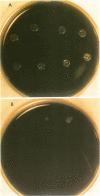
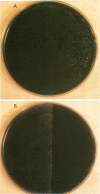
Abstract
Shortwave UV light was assessed as a feasible modality for the control of Legionnaires disease bacterium in water. The results of this study show that Legionella pneumophila and six other Legionella species are very sensitive to low doses of UV. However, all Legionella species tested effectively countered the germicidal effect of UV when subsequently exposed to photoreactiving light.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antopol S. C., Ellner P. D. Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila to ultraviolet radiation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):347–348. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.2.347-348.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baine W. B., Rasheed J. K. Aromatic substrate specificity of browning by cultures of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):619–620. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett C. L. Sporadic cases of Legionnaires' disease in Great Britain. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):592–595. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Steigerwalt A. G., McDade J. E. Classification of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium: Legionella pneumophila, genus novum, species nova, of the family Legionellaceae, familia nova. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):656–658. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson L. A., Petersen N. J. Photoreactivation of Pseudomonas cepacia after ultraviolet exposure: a potential source of contamination in ultraviolet-treated waters. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 May;1(5):462–464. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.5.462-464.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry W. B., Gorman G. W., Orrison L. H., Moss C. W., Steigerwalt A. G., Wilkinson H. W., Johnson S. E., McKinney R. M., Brenner D. J. Legionella jordanis: a new species of Legionella isolated from water and sewage. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):290–297. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.290-297.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordes L. G., Wiesenthal A. M., Gorman G. W., Phair J. P., Sommers H. M., Brown A., Yu V. L., Magnussen M. H., Meyer R. D., Wolf J. S. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from hospital shower heads. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Feb;94(2):195–197. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dondero T. J., Jr, Rendtorff R. C., Mallison G. F., Weeks R. M., Levy J. S., Wong E. W., Schaffner W. An outbreak of Legionnaires' disease associated with a contaminated air-conditioning cooling tower. N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 14;302(7):365–370. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002143020703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Brenner D. J., Moss C. W., Steigerwalt A. G., Francis E. M., George W. L. Legionella wadsworthii species nova: a cause of human pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Dec;97(6):809–813. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-6-809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Smith S. J., Tison D. L., Pope D. H. Ecological distribution of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):9–16. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.9-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Thacker L. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from nonepidemic-related aquatic habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1239–1242. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1239-1242.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W. Legionnaires' disease: four summers' harvest. Am J Med. 1980 Jan;68(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90151-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W., Tsai T. R., Orenstein W., Parkin W. E., Beecham H. J., Sharrar R. G., Harris J., Mallison G. F., Martin S. M., McDade J. E. Legionnaires' disease: description of an epidemic of pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1189–1197. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick T. H., Gregg M. B., Berman B., Mallison G., Rhodes W. W., Jr, Kassanoff I. Pontiac fever. An epidemic of unknown etiology in a health department: I. Clinical and epidemiologic aspects. Am J Epidemiol. 1978 Feb;107(2):149–160. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman G. W., Yu V. L., Brown A., Hall J. A., Martin W. T., Bibb W. F., Morris G. K., Magnussen M. H., Fraser D. W. Isolation of Pittsburgh pneumonia agent from nebulizers used in respiratory therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Oct;93(4):572–573. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-4-572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory D. W., Schaffner W., Alford R. H., Kaiser A. B., McGee Z. A. Sporadic cases of Legionnaires' disease: the expanding clinical spectrum. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):518–521. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gump D. W., Frank R. O., Winn W. C., Jr, Foster R. S., Jr, Broome C. V., Cherry W. B. Legionnaires' disease in patients with associated serious disease. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):538–542. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley C. E., Cohen M. L., Halter J., Meyer R. D. Nosocomial Legionnaires' disease: a continuing common-source epidemic at Wadsworth Medical Center. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):583–586. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harm W. Biological determination of the germicidal activity of sunlight. Radiat Res. 1969 Oct;40(1):63–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAGGER J. Photoreactivation. Bacteriol Rev. 1958 Jun;22(2):99–142. doi: 10.1128/br.22.2.99-142.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby B. D., Snyder K. M., Meyer R. D., Finegold S. M. Legionnaires' disease: report of sixty-five nosocomially acquired cases of review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1980 May;59(3):188–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchta J. M., States S. J., McNamara A. M., Wadowsky R. M., Yee R. B. Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila to chlorine in tap water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1134–1139. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1134-1139.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayock P. P., Bader P. I. Case report. Legionnaires' disease. A review of clinical aspects of 18 sporadic cases. Am J Med Sci. 1979 Mar-Apr;277(2):215–222. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197903000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrison L. H., Cherry W. B., Tyndall R. L., Fliermans C. B., Gough S. B., Lambert M. A., McDougal L. K., Bibb W. F., Brenner D. J. Legionella oakridgensis: unusual new species isolated from cooling tower water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):536–545. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.536-545.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plouffe J. F., Webster L. R., Hackman B. Relationship between colonization of hospital building with Legionella pneumophila and hot water temperatures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):769–770. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.769-770.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristroph J. D., Hedlund K. W., Allen R. G. Liquid medium for growth of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):19–21. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.19-21.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaliy P., Thompson T. A., Gorman G. W., Morris G. K., McEachern H. V., Mackel D. C. Laboratory studies of disinfectants against Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):697–700. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.697-700.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout J., Yu V. L., Vickers R. M., Zuravleff J., Best M., Brown A., Yee R. B., Wadowsky R. Ubiquitousness of Legionella pneumophila in the water supply of a hospital with endemic Legionnaires' disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Feb 25;306(8):466–468. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198202253060807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tison D. L., Pope D. H., Cherry W. B., Fliermans C. B. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in association with blue-green algae (cyanobacteria). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):456–459. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.456-459.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin J. O., Beare J., Dunnill M. S., Fisher-Hoch S., French M., Mitchell R. G., Morris P. J., Muers M. F. Legionnaires' disease in a transplant unit: isolation of the causative agent from shower baths. Lancet. 1980 Jul 19;2(8186):118–121. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadowsky R. M., Yee R. B., Mezmar L., Wing E. J., Dowling J. N. Hot water systems as sources of Legionella pneumophila in hospital and nonhospital plumbing fixtures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1104–1110. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1104-1110.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Inherited Differences in Sensitivity to Radiation in Escherichia Coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1946 Mar;32(3):59–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.32.3.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Freitas J. L., Borst J., Meenhorst P. L. Easy visualisation of Legionella pneumophila by "half-a-gram" stain procedure. Lancet. 1979 Feb 3;1(8110):270–271. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90794-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]