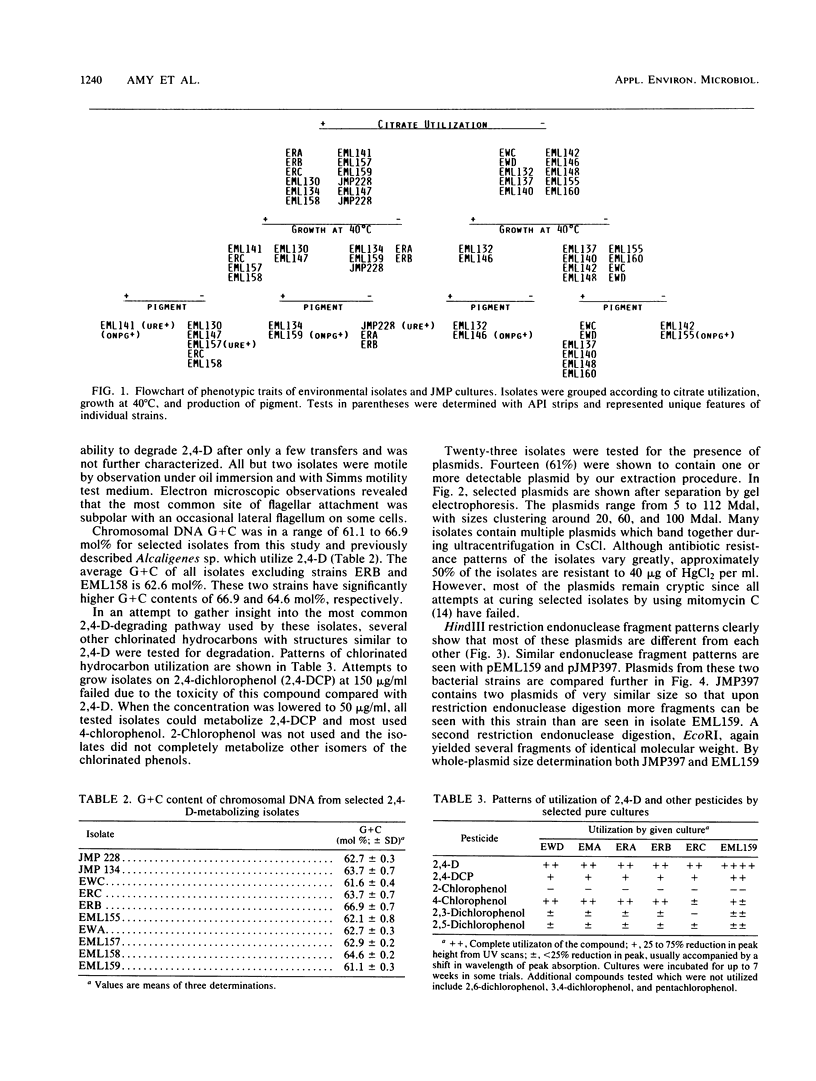
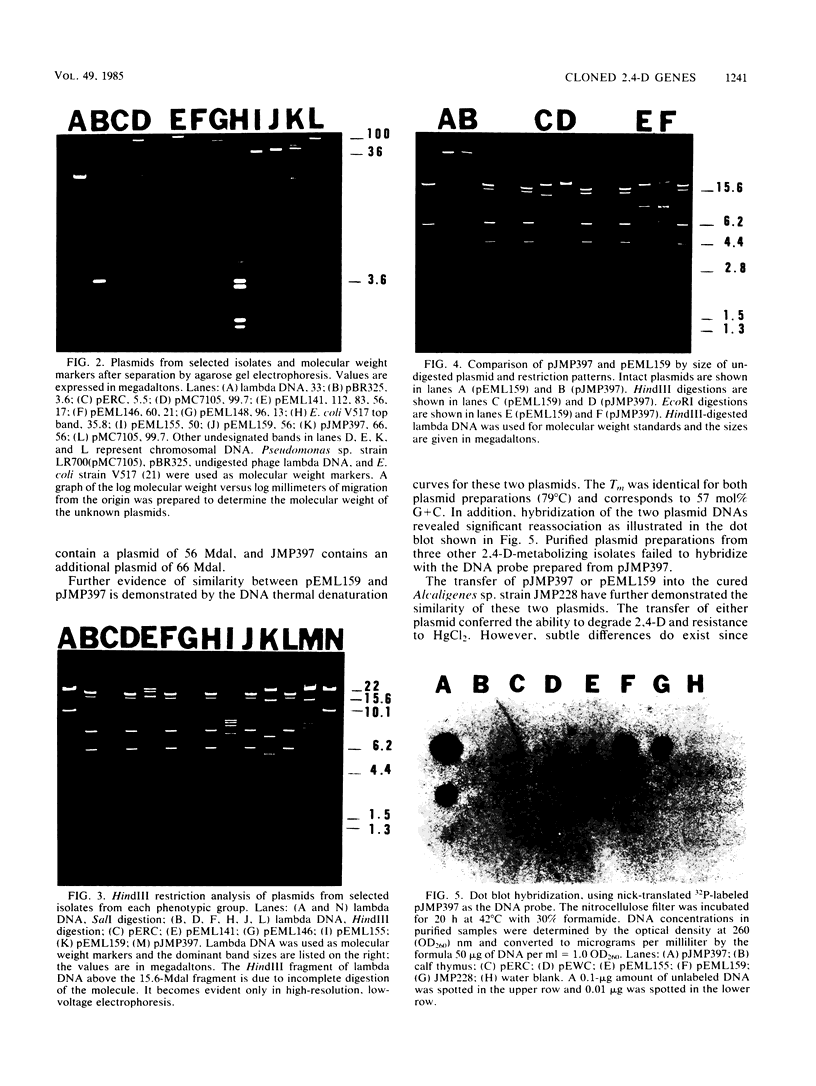
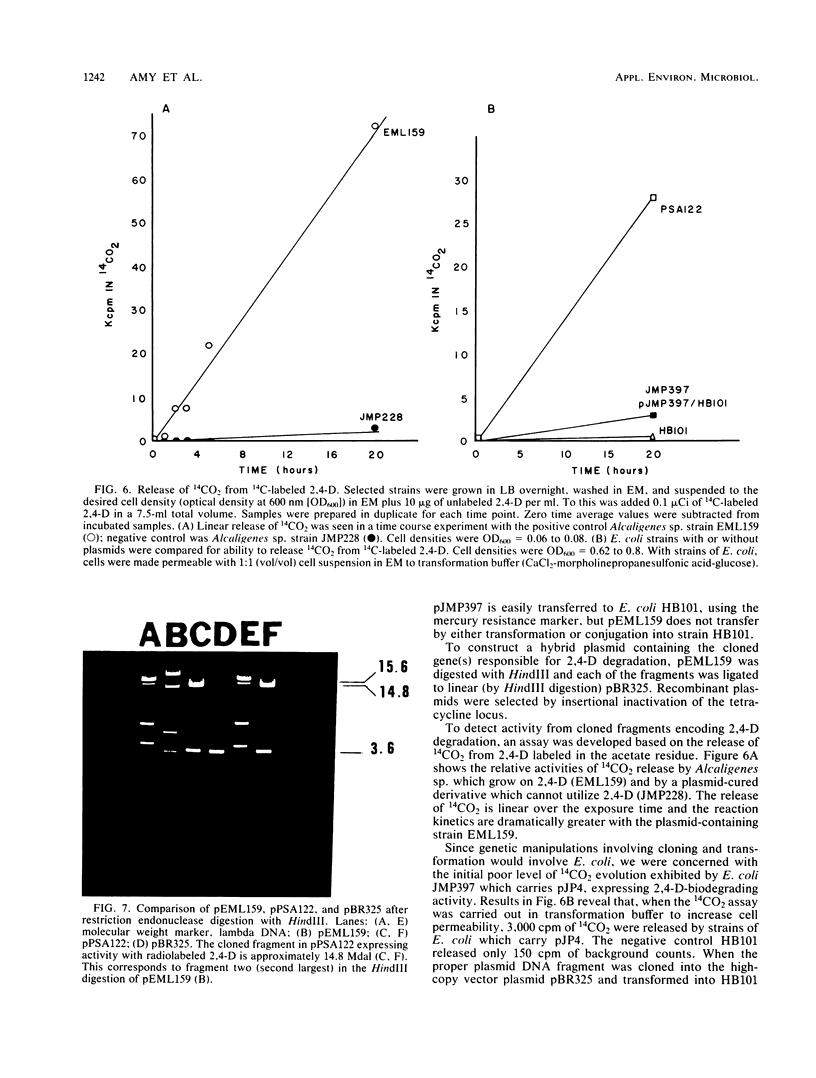
Abstract
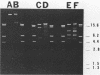
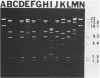
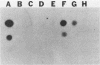
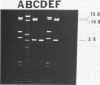
Water samples from rivers, streams, ponds, and activated sewage were tested for the presence of bacteria which utilize 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) as a sole source of carbon. Seventy percent of the attempted enrichments yielded pure cultures of 2,4-D-metabolizing bacteria. All but 1 of the 30 isolates were gram-negative rods, all but 2 were motile, and all were nonfermentative and oxidase and catalase positive. Nine isolates had DNA guanine-plus-cytosine values of 61.1 to 65 mol%. One isolate had a 67 mol% guanine-plus-cytosine value. The results suggest that these 2,4-D-metabolizing bacteria belong to the genus Alcaligenes. Fourteen of 23 isolates contained one or more detectable plasmids of about 20, 60, or 100 megadaltons. HindIII restriction fragment patterns showed these plasmids to be different from each other with one exception. Very similar restriction fragment patterns were revealed with a plasmid isolated from an Alcaligenes eutrophus strain obtained from Australia (pJMP397) and in an Alcaligenes sp. isolated in Oregon (pEML159). These two plasmids were about 56 megadaltons, had the same guanine-plus-cytosine value, were transmissable, and coded for 2,4-D metabolism and resistance to HgCl2. Hybridization of these two plasmids was demonstrated by using nick-translated 32P-labeled pJMP397. The vector pBR325 was used to clone HindIII fragments from pEML159. One cloned fragment of 14.8 megaldaltons expressed in Escherichia coli the ability to release 14CO2 from 2,4-D labeled in the acetate portion.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amy P. S., Morita R. Y. Starvation-survival patterns of sixteen freshly isolated open-ocean bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1109–1115. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.1109-1115.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL G. R. Some morphological and biochemical characteristics of a soil bacterium which decomposes 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Can J Microbiol. 1957 Oct;3(6):821–840. doi: 10.1139/m57-092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M., Mylroie J. R., Friello D. A., Vacca J. G. Transformation of Pseudomonas putida and Escherichia coli with plasmid-linked drug-resistance factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3647–3651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Kosuge T. Involvement of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid in indoleacetic acid synthesis in Pseudomonas savastanoi. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):950–957. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.950-957.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Pemberton J. M. Properties of six pesticide degradation plasmids isolated from Alcaligenes paradoxus and Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):681–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.681-686.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C., Smith B. S., Fernley H. N., Davies J. I. Bacterial metabolism of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):543–551. doi: 10.1042/bj1220543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. R., Appleton J., Pemberton J. M. Isolation and characterization of the pesticide-degrading plasmid pJP1 from Alcaligenes paradoxus. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):798–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.798-804.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw V., Punch J., Allison M. J., Dalton H. P. Frequency of R factor-mediated multiple drug resistance in Klebsiella and Aerobacter. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Feb;17(2):214–218. doi: 10.1128/am.17.2.214-218.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howley P. M., Israel M. A., Law M. F., Martin M. A. A rapid method for detecting and mapping homology between heterologous DNAs. Evaluation of polyomavirus genomes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4876–4883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M. A., Roberts R. N., Alexander M. Phenols as intermediates in the decomposition of phenoxyacetates by an Arthrobacter species. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Jun;13(6):679–690. doi: 10.1139/m67-090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Igambi L., Bergendahl J., Dodson M. L., Jr, Scheltgen E. Correlation of melting temperature and cesium chloride buoyant density of bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):333–338. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.333-338.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton J. M., Fisher P. R. 2,4-D plasmids and persistence. Nature. 1977 Aug 25;268(5622):732–733. doi: 10.1038/268732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEENSON T. I., WALKER N. The pathway of breakdown of 2:4-dichloro- and 4-chloro-2-methyl-phenoxyacetic acid by bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Feb;16(1):146–155. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-1-146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler R. J., Mandel M. Quantitative aspects of deoxyribonucleic acid renaturation: base composition, state of chromosome replication, and polynucleotide homologies. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):608–614. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.608-614.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo L. J., Mills D. Integration and excision of pMC7105 in Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola: involvement of repetitive sequences. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):821–827. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.821-827.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. E., Finn R. K. Growth rates of a pseudomonad on 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2,4-dichlorophenol. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):181–184. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.181-184.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upholt W. B. Estimation of DNA sequence divergence from comparison of restriction endonuclease digests. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1257–1265. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]