Abstract
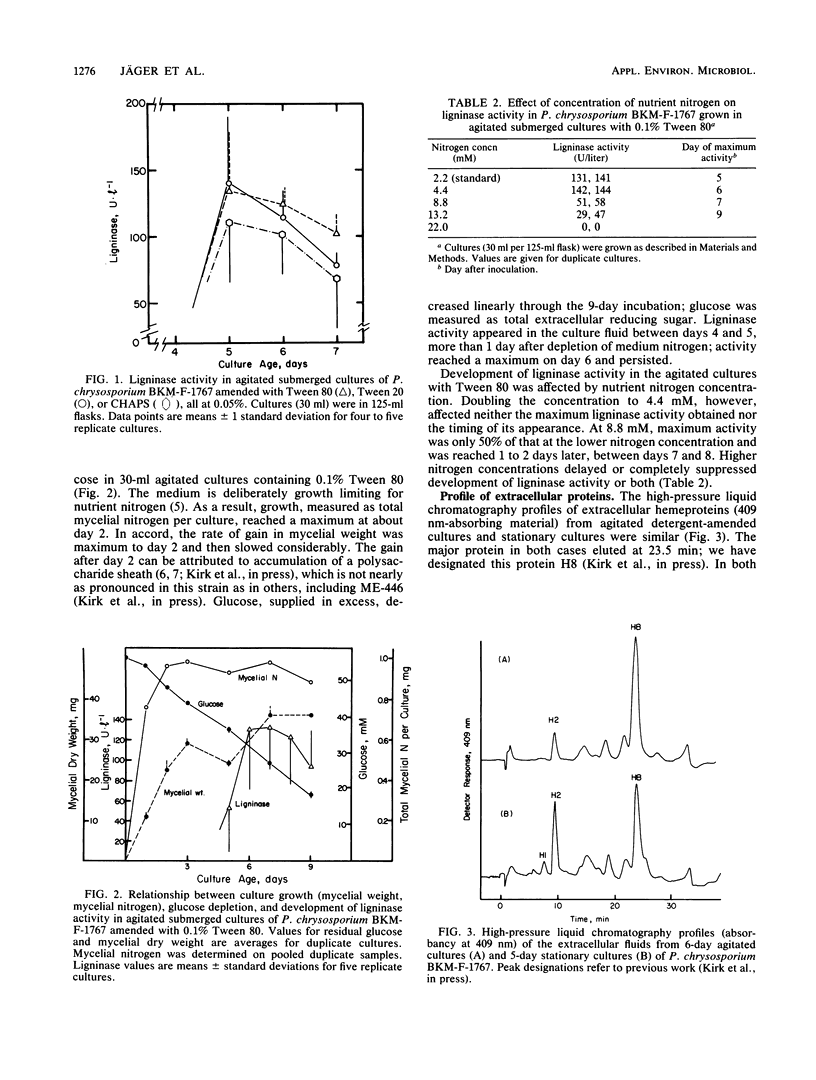
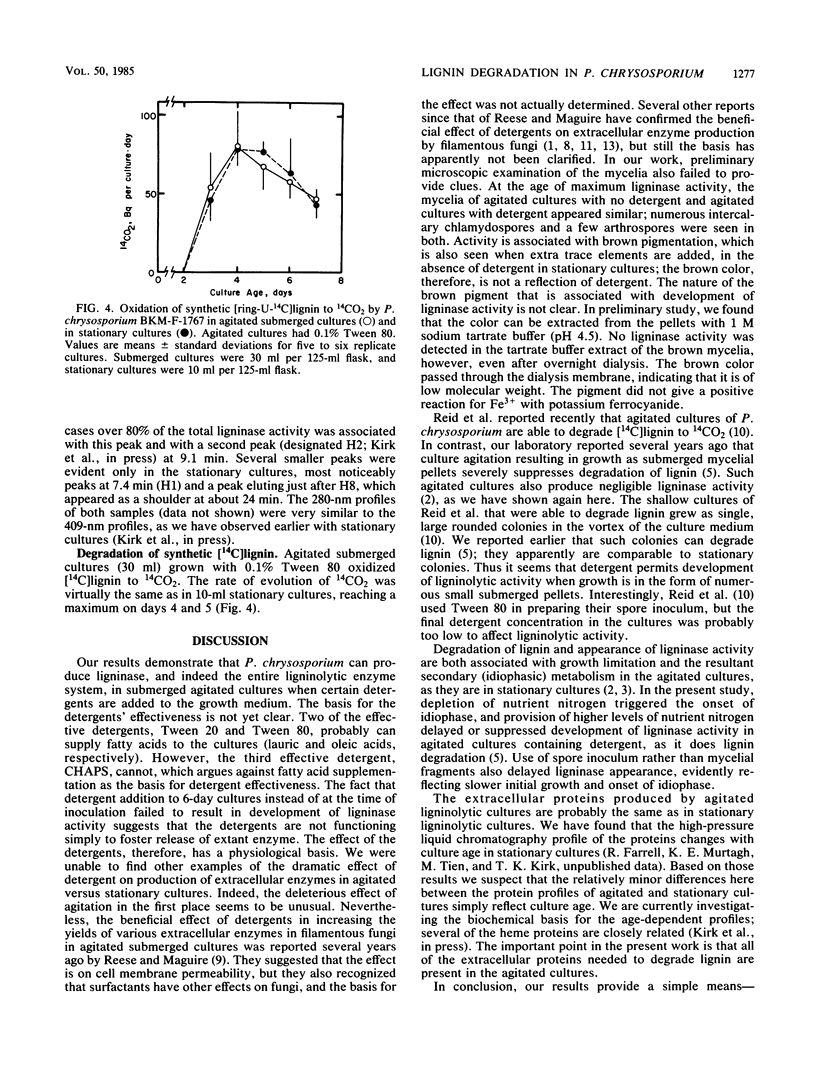
Research on the extracellular hemeprotein ligninases of Phanerochaete chrysosporium has been hampered by the necessity to produce them in stationary culture. This investigation examined the effects of detergents on development of ligninase activity in agitated submerged cultures. Results show that addition of Tween 80, Tween 20, or 3-[(3-colamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]1-propanesulfonate to the cultures permits development of ligninase activity comparable to that routinely obtained in stationary cultures. The detergent-amended cultures express the entire ligninolytic system, assayed as the complete oxidation of [14C]lignin to 14CO2. The detergent effect is evidently not merely in facilitating release of extant enzyme. Development of ligninolytic activity in the agitated cultures, as in stationary cultures, is idiophasic. Ion-exchange fast protein-liquid chromatography indicated that the heme protein profiles in agitated and stationary cultures are very similar. These findings should make it possible to scale up production of ligninolytic enzymes in stirred tank fermentors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Faison B. D., Kirk T. K. Factors Involved in the Regulation of a Ligninase Activity in Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):299–304. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.299-304.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. H., Kuwahara M., Chiu A. A., Glenn J. K. Purification and characterization of an extracellular H2O2-requiring diarylpropane oxygenase from the white rot basidiomycete, Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Nov 1;234(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90280-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk T. K., Connors W. J., Bleam R. D., Hackett W. F., Zeikus J. G. Preparation and microbial decomposition of synthetic [14C]ligins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2515–2519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liwicki R., Paterson A., MacDonald M. J., Broda P. Phenotypic classes of phenoloxidase-negative mutants of the lignin-degrading fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):641–644. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.641-644.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese E. T., Maguire A. Surfactants as stimulants of enzyme production by microorganisms. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Feb;17(2):242–245. doi: 10.1128/am.17.2.242-245.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMOGYI M. Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewale J. G., Sadana J. C. Cellulase and beta-glucosidase production by a basidiomycete species. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Oct;24(10):1204–1216. doi: 10.1139/m78-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien M., Kirk T. K. Lignin-degrading enzyme from Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Purification, characterization, and catalytic properties of a unique H(2)O(2)-requiring oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2280–2284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


