Abstract
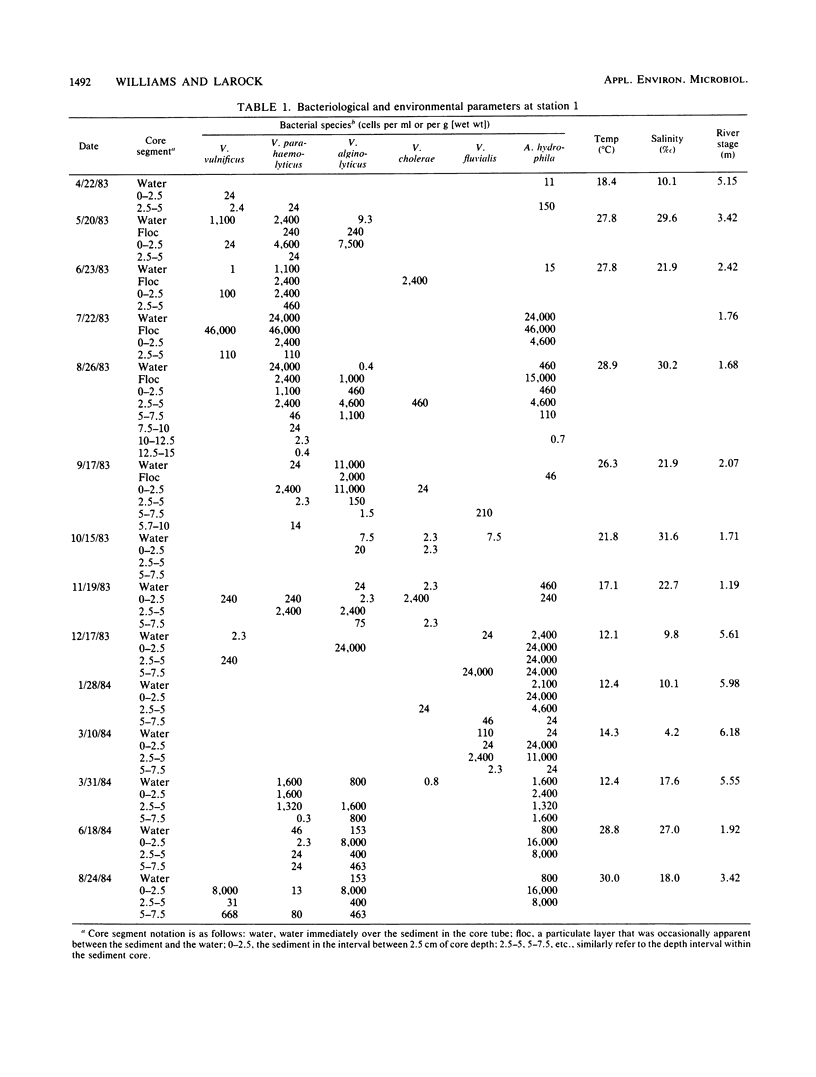
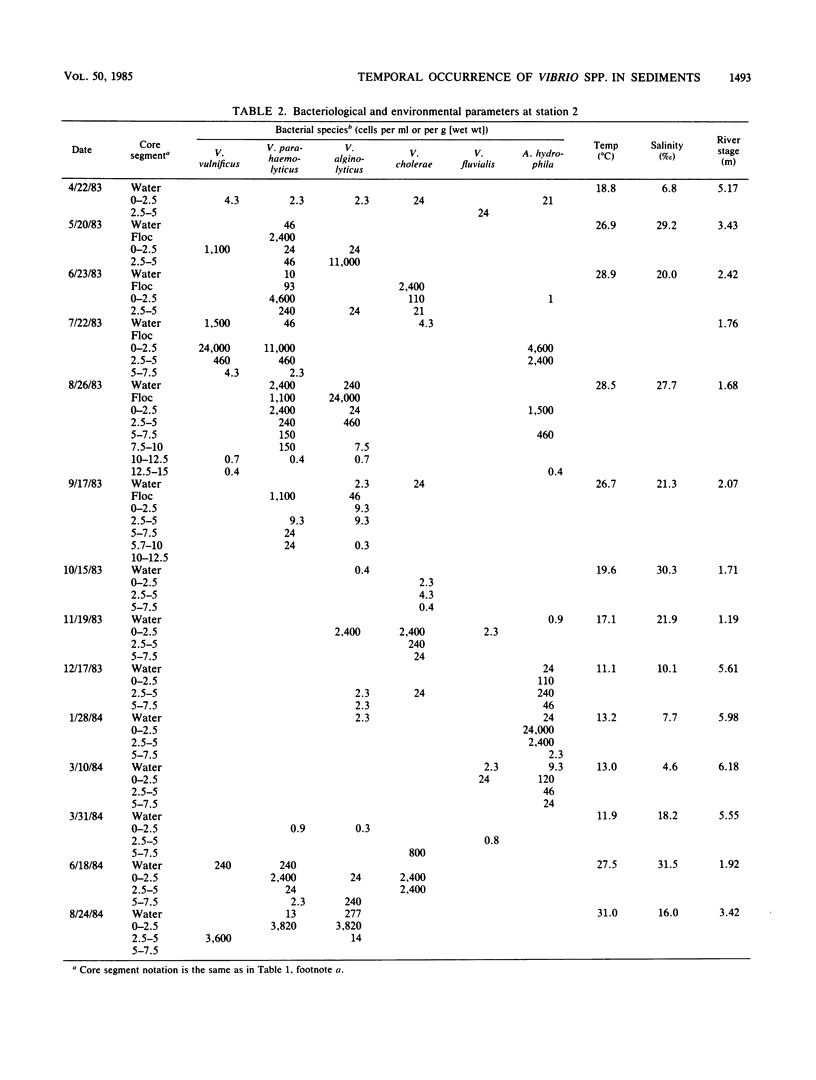
Marine sediments were assayed for their concentration of Vibrio spp. and Aeromonas hydrophila over 1 year. A temporal variation was observed in which A. hydrophila, and to a lesser degree V. fluvialis, were found in the winter months, V. parahaemolyticus and V. vulnificus predominated in the spring and summer, with non-O-1 V. cholerae and V. alginolyticus detected in the late summer and fall. These organisms were found in greatest numbers in the top 5 cm of sediment, but were detectable down to 15 cm. Epidemiological data revealed a predominance of non-O-1 V. cholerae infections at the time the organisms were observed to flourish in the sediments.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Colwell R. R., Seidler R. J., Kaper J., Joseph S. W., Garges S., Lockman H., Maneval D., Bradford H., Roberts N., Remmers E. Occurrence of Vibrio cholerae serotype O1 in Maryland and Louisiana estuaries. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):555–558. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.555-558.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. W., Sizemore R. K. Incidence of Vibrio species associated with blue crabs (Callinectes sapidus) collected from Galveston Bay, Texas. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1092–1097. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1092-1097.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen T. C., Fliermans C. B., Hirsch R. P., Esch G. W. Prevalence and distribution of Aeromonas hydrophila in the United States. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Nov;36(5):731–738. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.5.731-738.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood M. A., Ness G. E., Rodrick G. E. Isolation of Vibrio cholerae serotype O1 from the eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):559–560. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.559-560.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood M. A., Ness G. E. Survival of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli in estuarine waters and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):578–584. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.578-584.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huq A., Small E. B., West P. A., Huq M. I., Rahman R., Colwell R. R. Ecological relationships between Vibrio cholerae and planktonic crustacean copepods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):275–283. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.275-283.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J., Lockman H., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W. Ecology, serology, and enterotoxin production of Vibrio cholerae in Chesapeake Bay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):91–103. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.91-103.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouf M. A., Rigney M. M. Growth temperatures and temperature characteristics of Aeromonas. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Oct;22(4):503–506. doi: 10.1128/am.22.4.503-506.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton F. L., Attwell R. W., Jangi M. S., Colwell R. R. Influence of salinity and organic nutrient concentration on survival and growth of Vibrio cholerae in aquatic microcosms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1080–1085. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1080-1085.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton F. L., Attwell R., Jangi S., Colwell R. R. Effects of temperature and salinity on Vibrio cholerae growth. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Nov;44(5):1047–1058. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.5.1047-1058.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sochard M. R., Wilson D. F., Austin B., Colwell R. R. Bacteria associated with the surface and gut of marine copepods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Apr;37(4):750–759. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.4.750-759.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


