Abstract
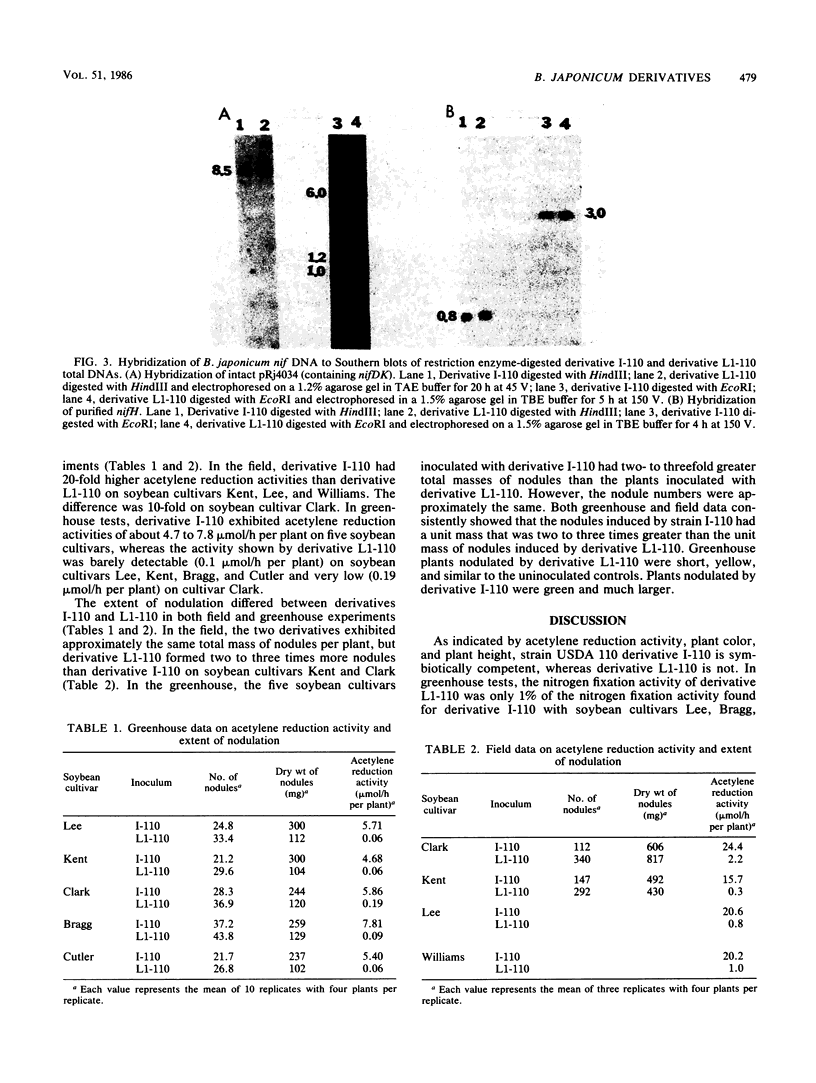
DNAs from Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA 110 derivatives that differ in nitrogen-fixing ability produced similar electrophoretic patterns with five different restriction enzymes. Our data support the hypothesis of common ancestry for these derivatives. Derivatives I-110 and L1-110 differed as much as 100-fold in acetylene reduction activity when they were tested with several soybean cultivars in both greenhouse and field experiments. While possessing nodulating ability, derivative L1-110 is deficient in symbiotic nitrogen-fixing ability, whereas derivative I-110 is symbiotically competent. Hybridization of nifDK and nifH probes from B. japonicum to Southern blots of restricted DNAs from strain USDA 110 derivatives produced similar patterns. This finding indicates similar structural gene organization for both derivative I-110 and derivative L1-110 and implies that the difference in symbiotic nitrogen fixation is probably not due to structural gene rearrangements. However, our hybridization data do not rule out the possibility of differences in expression of structural nif genes or alterations in the structure or expression of other genes required for symbiotic nitrogen fixation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour W. M., Mathis J. N., Elkan G. H. Evidence for plasmid- and chromosome-borne multiple nif genes in Rhizobium fredii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jul;50(1):41–44. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.1.41-44.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. A., Elkan G. H. Transmissible resistance to penicillin G, neomycin, and chloramphenicol in Rhizobium japonicum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):248–253. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt T. A rapid method for the identification of plasmid desoxyribonucleic acid in bacteria. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):584–588. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann M., Hennecke H. Rhizobium japonicum nitrogenase Fe protein gene (nifH). J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1005–1011. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1005-1011.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza K., Fuhrmann M., Hahn M., Regensburger B., Hennecke H. In Rhizobium japonicum the nitrogenase genes nifH and nifDK are separated. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):915–918. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.915-918.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuykendall L. D., Elkan G. H. Rhizobium japonicum derivatives differing in nitrogen-fixing efficiency and carbohydrate utilization. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):511–519. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.511-519.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuykendall L. D., Elkan G. H. Some features of mannitol metabolism in Rhizobium japonicum. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jan;98(1):291–295. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-1-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterson R. V., Russell P. R., Atherly A. G. Nitrogen fixation (nif) genes and large plasmids of Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):928–931. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.928-931.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielenz J. R., Jackson L. E., O'Gara F., Shanmugam K. T. Fingerprinting bacterial chromosomal DNA with restriction endonuclease EcoRI: comparison of Rhizobium spp. and identification of mutants. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jul;25(7):803–807. doi: 10.1139/m79-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V. Rapid and simple removal of contaminating RNA from plasmid DNA without the use of RNase. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 1;113(1):34–42. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upchurch R. G., Elkan G. H. Comparison of colony morphology, salt tolerance, and effectiveness in Rhizobium japonicum. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1118–1122. doi: 10.1139/m77-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang R., Lis J., Wu R. Elution of DNA from agarose gels after electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:176–182. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]