Abstract
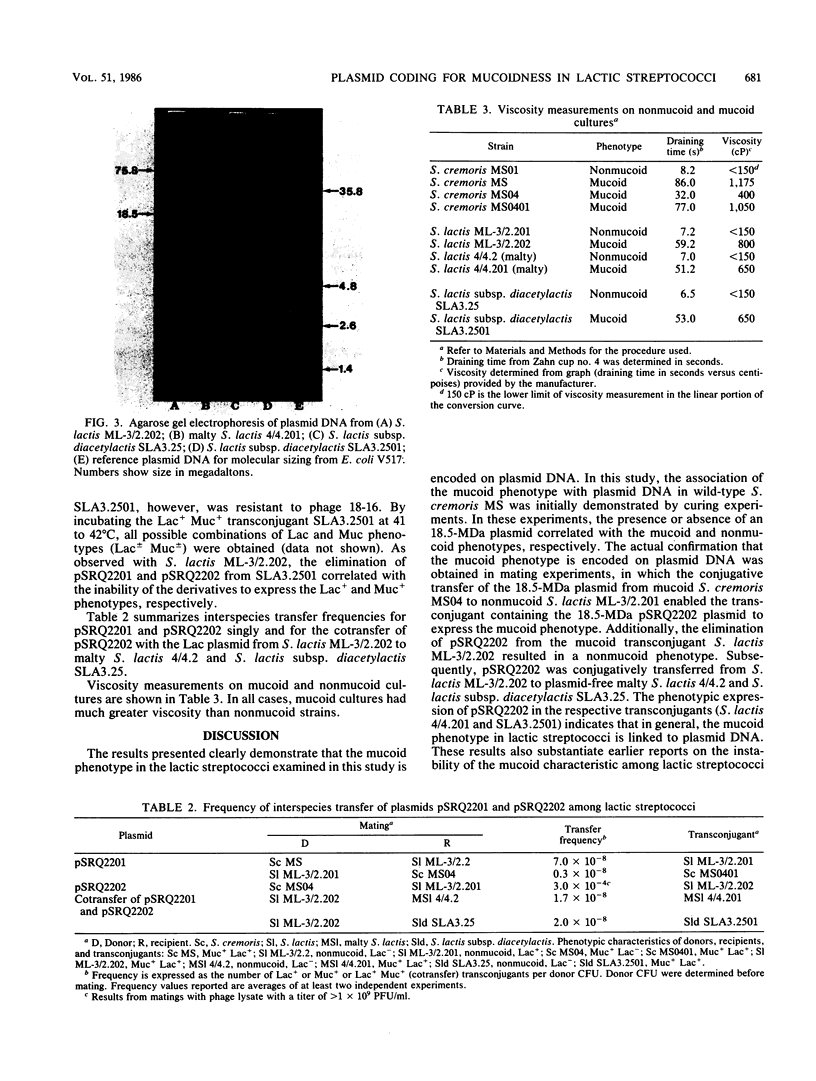
Curing and genetic transfer experiments showed that lactose-fermenting ability (Lac+) and the ability to produce mucoidness in milk cultures (Muc+) in Streptococcus cremoris MS were coded on plasmids. The Lac+ phenotype was associated with a 75.8-megadalton plasmid, pSRQ2201. The Muc+ phenotype was associated with a 18.5-megadalton plasmid, pSRQ2202. The Lac plasmid, pSRQ2201, was first conjugatively transferred from S. cremoris MS to Lac−S. lactis ML-3/2.2. Later, the Muc plasmid, pSRQ2202, was conjugatively transferred from Lac− Muc+S. cremoris MS04 to Lac+ nonmucoid S. lactis transconjugant ML-3/2.201. Subsequently, pSRQ2201 and pSRQ2202 were cotransferred from Lac+ Muc+S. lactis transconjugant ML-3/2.202 to Lac−, nonmucoid, malty S. lactis 4/4.2 and S. lactis subsp. diacetylactis SLA3.25. Transconjugants showing pSRQ2201 were Lac+; those containing pSRQ2202 were Muc+. With the transfer of pSRQ2202, the transconjugants S. lactis ML-3/2.202 and S. lactis subsp. diacetylactis SLA3.2501 not only acquired the Muc+ phenotype but also resistance to bacteriophages, which were lytic to the respective parent strains S. lactis ML-3/2.201 and S. lactis subsp. diacetylactis SLA3.25.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.549-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooker B. E. Cytochemical observations on the extracellular carbohydrate produced by Streptococcus cremoris. J Dairy Res. 1976 Jun;43(2):283–290. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900015843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson M. J. Genetic transfer systems in lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1983 Sep;49(3):275–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00399503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C. F., Kunka B. S. Plasmid transfer in Pediococcus spp.: intergeneric and intrageneric transfer of pIP501. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):81–89. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.81-89.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXTED W. R. Enhancement of streptococcal bacteriophage lysis by hyaluronidase. Nature. 1952 Dec 13;170(4337):1020–1021. doi: 10.1038/1701020b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A. Conjugative 40-megadalton plasmid in Streptococcus lactis subsp. diacetylactis DRC3 is associated with resistance to nisin and bacteriophage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):68–74. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.68-74.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A., Walsh P. M. Conjugal transfer of genetic information in group N streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):84–89. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.84-91.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L. Functional properties of plasmids in lactic streptococci. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1983 Sep;49(3):259–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00399502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niven C. F., Smiley K. L., Sherman J. M. The Hydrolysis of Arginine by Streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1942 Jun;43(6):651–660. doi: 10.1128/jb.43.6.651-660.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxelin M. L., Nurmiaho E. L., Korhola M. P., Sundman V. Partial characterization of a new C3-type capsule-dissolving phage of Streptococcus cremoris. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Oct;25(10):1182–1187. doi: 10.1139/m79-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]