Abstract
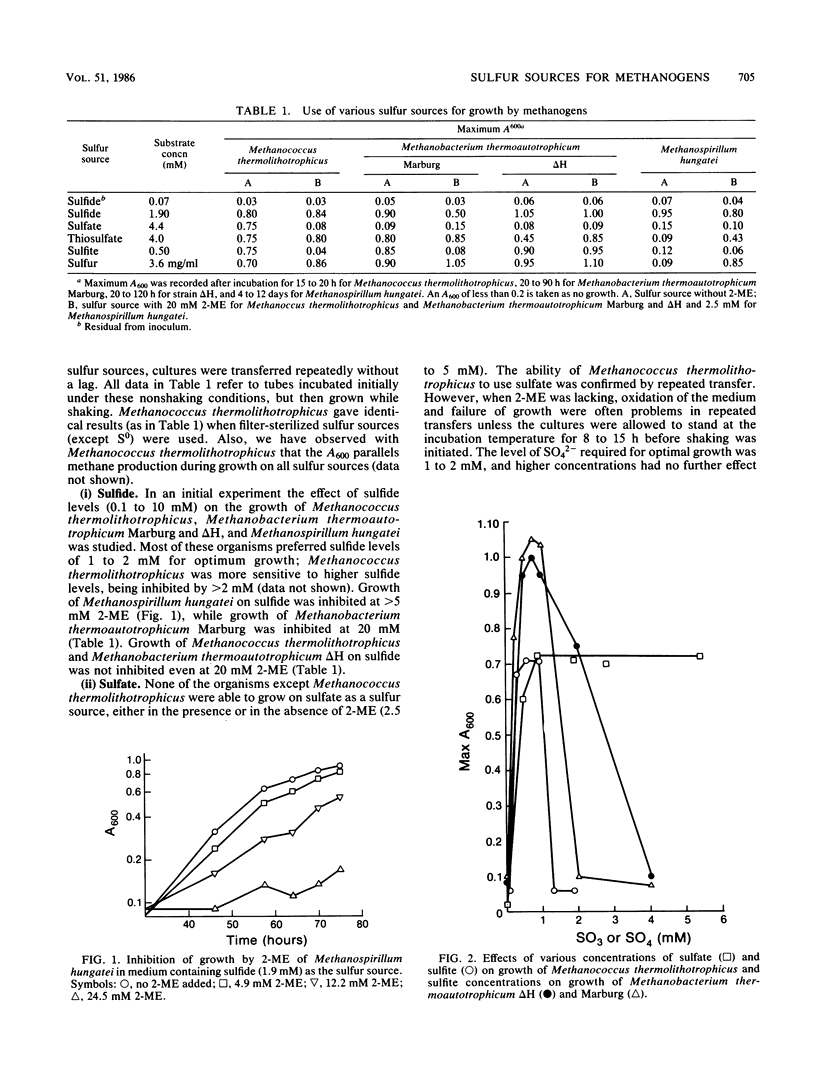
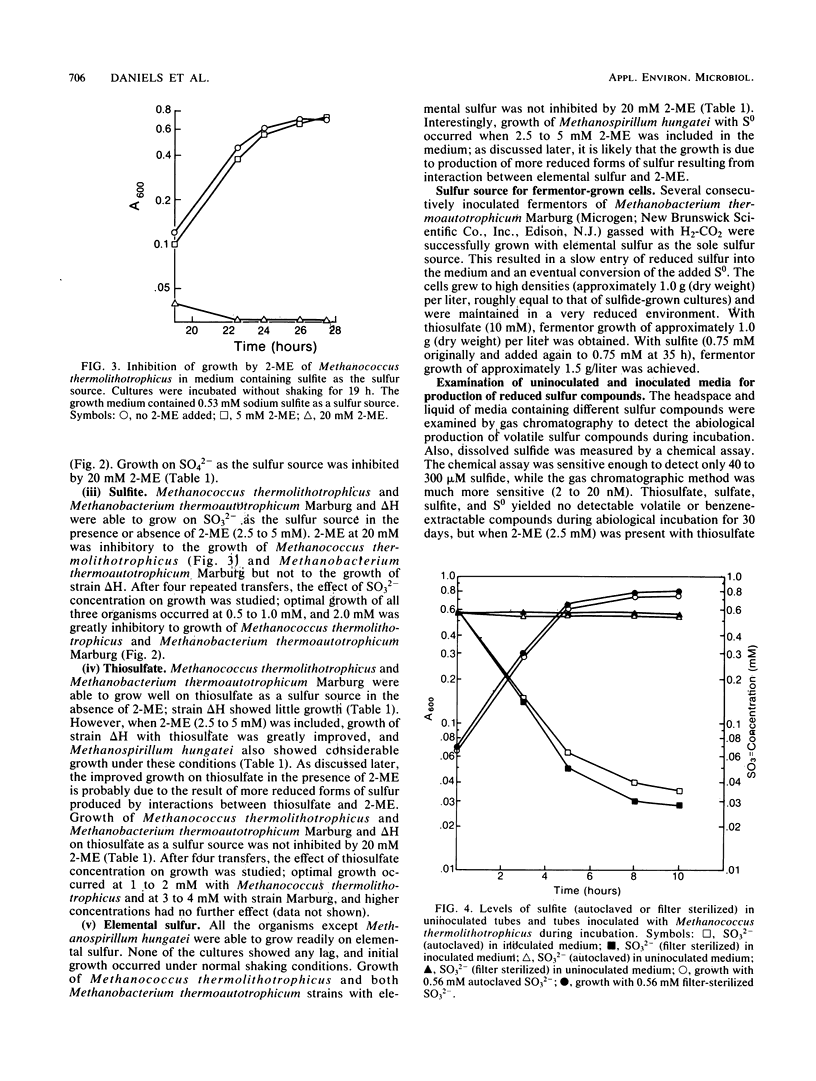
A variety of sulfur-containing compounds were investigated for use as medium reductants and sulfur sources for growth of four methanogenic bacteria. Sulfide (1 to 2 mM) served all methanogens investigated well. Methanococcus thermolithotrophicus and Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum Marburg and delta H grew well with S0, SO3(2-), or thiosulfate as the sole sulfur source. Only Methanococcus thermolithotrophicus was able to grow with SO4(2-) as the sole sulfur source. 2-Mercaptoethanol at 20 mM was greatly inhibitory to growth of Methanococcus thermolithotrophicus on SO4(2-) or SO2(2-) and Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum Marburg on SO3(2-) but not to growth of strain delta H on SO3(2-). Sulfite was metabolized during growth by Methanococcus thermolithotrophicus. Sulfide was produced in cultures of Methanococcus thermolithotrophicus growing on SO4(2-), SO3(2-), thiosulfate, and S0. Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum Marburg was successfully grown in a 10-liter fermentor with S0, SO3(2-), or thiosulfate as the sole sulfur source.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Woese C. R., Wolfe R. S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):260–296. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.260-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S. New approach to the cultivation of methanogenic bacteria: 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid (HS-CoM)-dependent growth of Methanobacterium ruminantium in a pressureized atmosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Dec;32(6):781–791. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.6.781-791.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belkin S., Wirsen C. O., Jannasch H. W. Biological and abiological sulfur reduction at high temperatures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1057–1061. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1057-1061.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar L., Jain M. K., Aubert J. P., Zeikus J. G. Comparison of assimilatory organic nitrogen, sulfur, and carbon sources for growth of methanobacterium species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):785–790. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.785-790.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels L., Sparling R., Sprott G. D. The bioenergetics of methanogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 6;768(2):113–163. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(84)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs G., Stupperich E., Thauer R. K. Acetate assimilation and the synthesis of alanine, aspartate and glutamate in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Apr 27;117(1):61–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00689352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones W. J., Whitman W. B., Fields R. D., Wolfe R. S. Growth and plating efficiency of methanococci on agar media. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):220–226. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.220-226.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountfort D. O., Asher R. A. Effect of inorganic sulfide on the growth and metabolism of Methanosarcina barkeri strain DM. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Apr;37(4):670–675. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.4.670-675.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moura J. J., Moura I., Santos H., Xavier A. V., Scandellari M., LeGall J. Isolation of P590 from Methanosarcina barkeri: evidence for the presence of sulfite reductase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 15;108(3):1002–1009. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel G. B., Roth L. A., van den Berg L., Clark D. S. Characterization of a strain of Methanospirillum hungatti. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Sep;22(9):1404–1410. doi: 10.1139/m76-208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnow P. H., Gunnarsson L. A. Sulfide-dependent methane production and growth of a thermophilic methanogenic bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Oct;42(4):580–584. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.4.580-584.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönheit P., Moll J., Thauer R. K. Nickel, cobalt, and molybdenum requirement for growth of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch Microbiol. 1979 Oct;123(1):105–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00403508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUEPER H. G., SCHLEGEL H. G. SULPHUR METABOLISM IN THIORHODACEAE. I. QUANTITATIVE MEASUREMENTS ON GROWING CELLS OF CHROMATIUM OKENII. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1964;30:225–238. doi: 10.1007/BF02046728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLIN E. A., WOLIN M. J., WOLFE R. S. FORMATION OF METHANE BY BACTERIAL EXTRACTS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2882–2886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellinger A., Wuhrmann K. Influence of sulfide compounds on the metabolism of Methanobacterium strain AZ. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Oct 24;115(1):13–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00427839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman W. B., Ankwanda E., Wolfe R. S. Nutrition and carbon metabolism of Methanococcus voltae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):852–863. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.852-863.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehnder A. J., Wuhrmann K. Titanium (III) citrate as a nontoxic oxidation-reduction buffering system for the culture of obligate anaerobes. Science. 1976 Dec 10;194(4270):1165–1166. doi: 10.1126/science.793008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicus sp. n., an anaerobic, autotrophic, extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):707–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.707-713.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


