Abstract
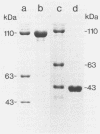
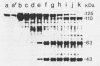
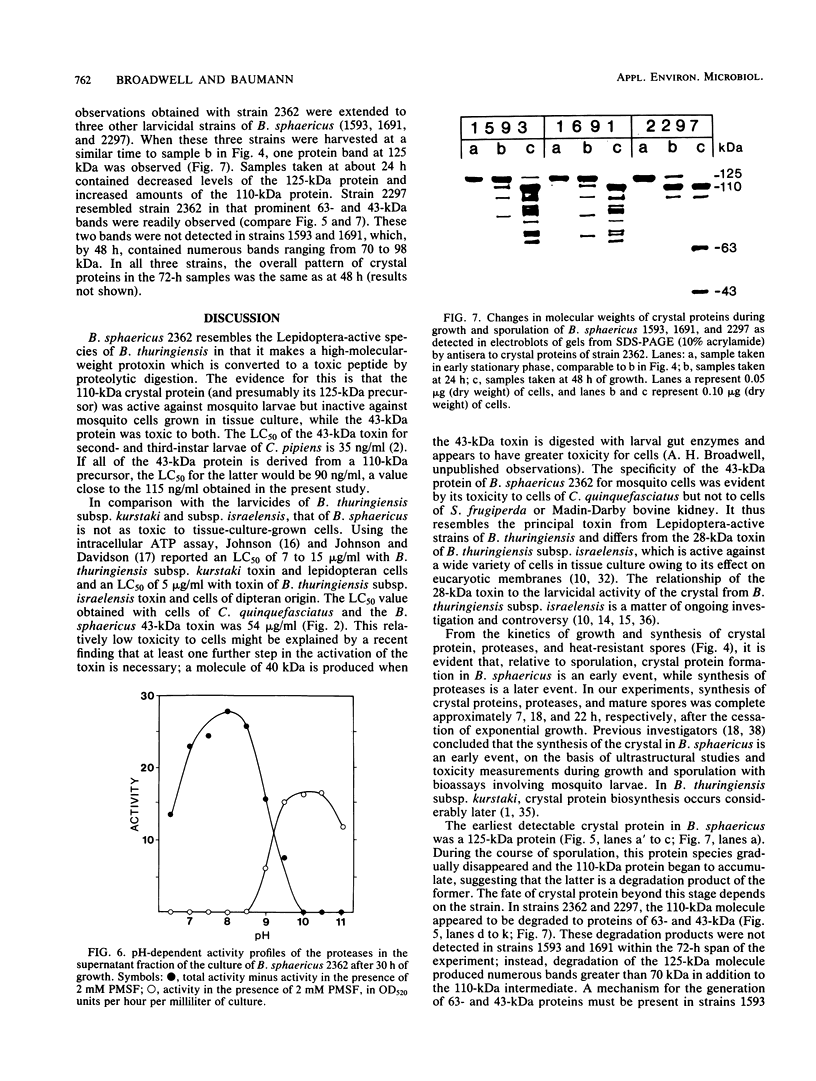
Preparations of the larvicidal crystal from 46-h cultures of Bacillus sphaericus 2362 contain 125-, 110-, 63-, and 43-kilodalton (kDa) proteins (P. Baumann, B. M. Unterman, L. Baumann, A.H. Broadwell, S.J. Abbene, and R.D. Bowditch, J. Bacteriol. 163:738-747, 1985). The 63- and 43-kDa proteins, which have been purified, are not immunologically cross-reactive, and only the 43-kDa protein is toxic to mosquito larvae. Since antigenic determinants of the two smaller proteins have been detected in the higher-molecular-weight proteins (125 and 110 kDa), it has been suggested that the latter are precursors of the 43- and 63-kDa peptides. In the present study, purified 110-kDa protein was found to be toxic to the larvae of Culex pipiens (50% lethal concentration = 115 ng/ml). A luciferase-luciferin assay for intracellular ATP as well as an assay based on the exclusion of Trypan Blue by live cells indicated that the 110-kDa protein had no effect on tissue-culture-grown cells of C. quinquefasciatus, while cells exposed to the 43-kDa protein rapidly lost viability (50% lethal concentration = 54 microgram(s)/ml by the intracellular ATP assay). These findings suggested that the 110-kDa protein and, by extension, the 125-kDa protein are protoxins which are activated during sporulation by cleavage to a 43-kDa toxin. To further investigate the origins and relationships of the crystal proteins of B. sphaericus, we analyzed samples during the growth and sporulation of the culture. Synthesis of crystal proteins was initiated at the end of exponential growth and was completed after about 7 h.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews R. E., Jr, Bibilos M. M., Bulla L. A., Jr Protease activation of the entomocidal protoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):737–742. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.737-742.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Unterman B. M., Baumann L., Broadwell A. H., Abbene S. J., Bowditch R. D. Purification of the larvicidal toxin of Bacillus sphaericus and evidence for high-molecular-weight precursors. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):738–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.738-747.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulla L. A., Jr, Bechtel D. B., Kramer K. J., Shethna Y. I., Aronson A. I., Fitz-James P. C. Ultrastructure, physiology, and biochemistry of Bacillus thuringiensis. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1980;8(2):147–204. doi: 10.3109/10408418009081124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulla L. A., Jr, Kramer K. J., Cox D. J., Jones B. L., Davidson L. I., Lookhart G. L. Purification and characterization of the entomocidal protoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):3000–3004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavira R., Jr, Burnett T. J., Hageman J. H. Assaying proteinases with azocoll. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;136(2):446–450. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. W. Effects of Bacillus sphaericus 1593 and 2362 spore/crystal toxin on cultured mosquito cells. J Invertebr Pathol. 1986 Jan;47(1):21–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(86)90159-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast P. G., Murphy D. W., Sohi S. S. Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin: evidence that toxin acts at the surface of susceptible cells. Experientia. 1978 Jun 15;34(6):762–763. doi: 10.1007/BF01947310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. H., Mao W. H., Cross J. H. Establishment of a line of cells derived from ovarian tissue of Clex quinquefasciatus Say. J Med Entomol. 1970 Dec;7(6):703–707. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/7.6.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. M., Lee S. G., Andrews R. E., Jr, Klowden M. J., Bulla L. A., Jr Separation of the cytolytic and mosquitocidal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 31;126(2):961–965. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90279-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibarra J. E., Federici B. A. Isolation of a relatively nontoxic 65-kilodalton protein inclusion from the parasporal body of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):527–533. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.527-533.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Davidson L. I. Specificity of cultured insect tissue cells for bioassay of entomocidal protein from Bacillus thuringiensis. In Vitro. 1984 Jan;20(1):66–70. doi: 10.1007/BF02633334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalfon A., Charles J. F., Bourgouin C., de Barjac H. Sporulation of Bacillus sphaericus 2297: an electron microscope study of crystal-like inclusion biogenesis and toxicity to mosquito larvae. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Apr;130(4):893–900. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-4-893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecadet M. M., Lescourret M., Klier A. Characterization of an intracellular protease isolated from Bacillus thuringiensis sporulating cells and able to modify homologous RNA polymerase. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 3;79(2):329–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. W., Sohi S. S., Fast P. G. Bacillus thuringiensis enzyme-digested delta endotoxin: effect on cultured insect cells. Science. 1976 Nov 26;194(4268):954–956. doi: 10.1126/science.982053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. M., Davidson E. W. Insecticidal activity of the crystalline parasporal inclusions and other components of the Bacillus sphaericus 1593 spore complex. J Invertebr Pathol. 1984 May;43(3):383–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(84)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priest F. G. Extracellular enzyme synthesis in the genus Bacillus. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):711–753. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.711-753.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER I. DIFFERENTIATION OF LARVAL DROSOPHILA EYE-ANTENNAL DISCS IN VITRO. J Exp Zool. 1964 Jun;156:91–103. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401560107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnepf H. E., Whiteley H. R. Delineation of a toxin-encoding segment of a Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6273–6280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P., Gerard C., Ozols J. The amino acid sequence specificity of a protease from spores of Bacillus megaterium. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3624–3628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P. Protease and peptidase activities in growing and sporulating cells and dormant spores of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):642–649. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.642-649.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P. Purification and properties of a specific proteolytic enzyme present in spores of Bacillus magaterium. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7853–7862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava O. P., Aronson A. I. Isolation and characterization of a unique protease from sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis. Arch Microbiol. 1981 May;129(3):227–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00425256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. E., Ellar D. J. Bacillus thuringiensis var israelensis crystal delta-endotoxin: effects on insect and mammalian cells in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Sci. 1983 Mar;60:181–197. doi: 10.1242/jcs.60.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo A., Aizawa K. Dissolution and Degradation of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-Endotoxin by Gut Juice Protease of the Silkworm Bombyx mori. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):576–580. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.576-580.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong H. C., Schnepf H. E., Whiteley H. R. Transcriptional and translational start sites for the Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1960–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousten A. A. Bacillus sphaericus: microbiological factors related to its potential as a mosquito larvicide. Adv Biotechnol Processes. 1984;3:315–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousten A. A., Davidson E. W. Ultrastructural Analysis of Spores and Parasporal Crystals Formed by Bacillus sphaericus 2297. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1449–1455. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1449-1455.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]