Abstract
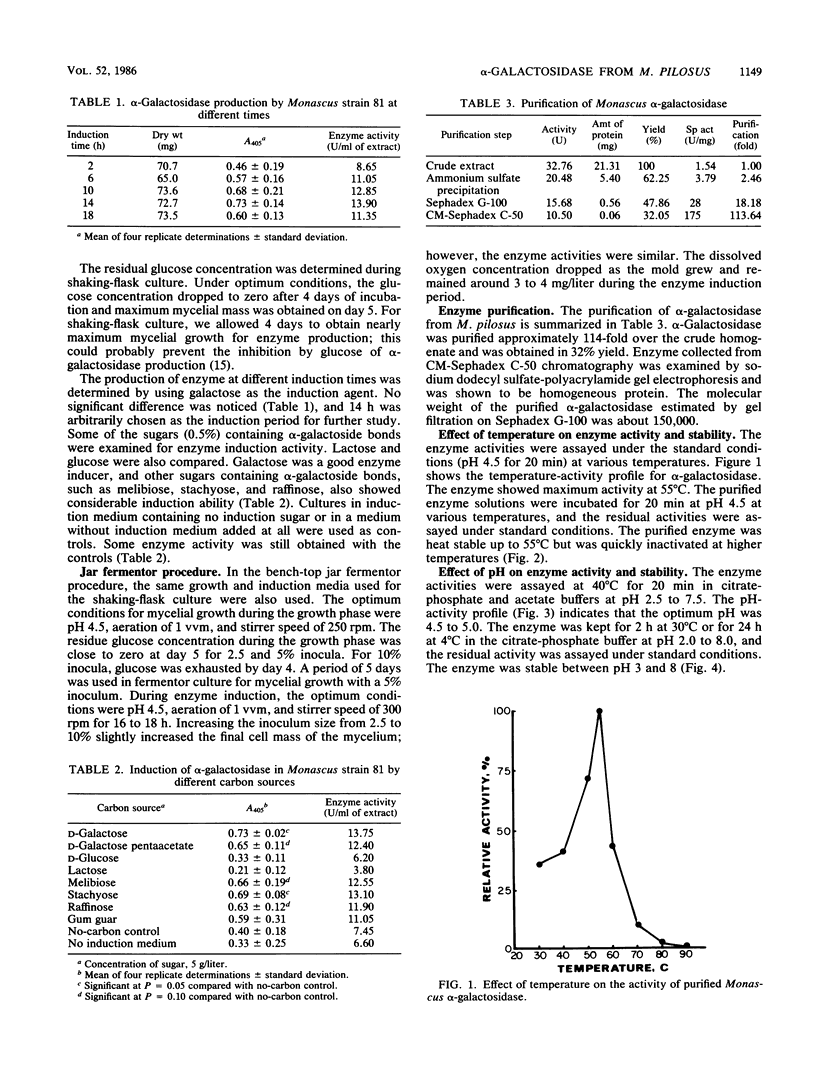
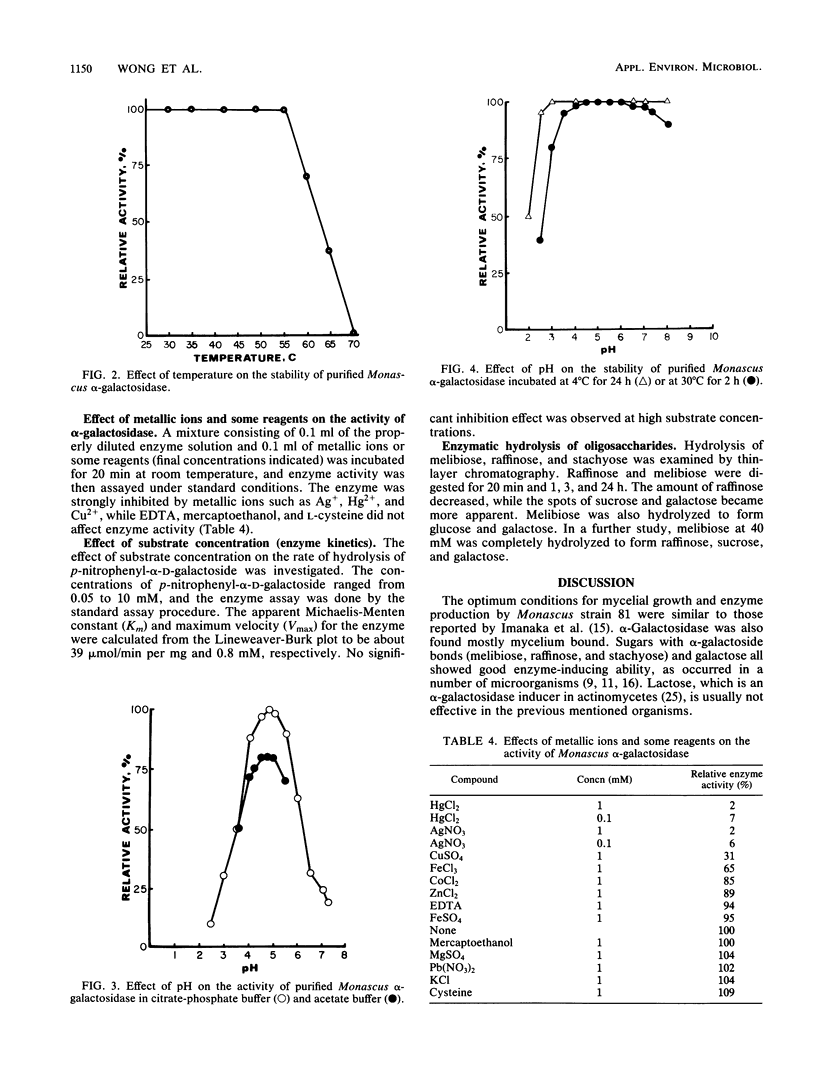
A Monascus pilosus strain was selected for production of intracellular α-galactosidase. Optimum conditions for mycelial growth and enzyme induction were determined. Galactose was one of the best enzyme inducers. The enzyme was purified by ammonium sulfate precipitation, gel filtration, and ion exchange chromatography and was demonstrated to be homogeneous by slab gel electrophoresis. The molecular weight of this enzyme, estimated by gel filtration, was about 150,000. The optimum conditions for the enzyme reaction was pH 4.5 to 5.0 at 55°C. The purified enzyme was stable at 55°C or below and in buffer at pH 3 to 8. The activity was inhibited by mercury, silver, and copper ions. The kinetics of this enzyme, with p-nitrophenyl-α-d-galactoside as substrate, was determined: Km was about 0.8 mM, and Vmax was 39 μmol/min per mg of protein. Enzymatic hydrolysis of melibiose, raffinose, and stachyose was analyzed by thin-layer chromatography.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adya S., Elbein A. D. Glycoprotein enzymes secreted by Aspergillus niger: purification and properties of alpha-glaactosidase. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):850–856. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.850-856.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. F., Desnick R. J. Affinity purification of alpha-galactosidase A from human spleen, placenta, and plasma with elimination of pyrogen contamination. Properties of the purified splenic enzyme compared to other forms. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1307–1316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinen I., Nakamura T., Fukuda N. Purification and properties of alpha-galactosidase from immature stalks of Saccharum officinarum (sugar cane). J Biochem. 1981 Nov;90(5):1453–1461. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dey P. M., Pridham J. B. Purification and properties of alpha-galactosidases from Vicia faba seeds. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):49–55. doi: 10.1042/bj1130049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flórez I. G., Lazo P. S., Ochoa A. G., Gascón S. The specificity of induction of alpha-galactosidase from Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 17;674(1):71–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghebregzabher M., Rufini S., Sapia G. M., Lato M. Improved thin-layer chromatographic method for sugar separations. J Chromatogr. 1979 Nov 28;180(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)80169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gherardini F., Babcock M., Salyers A. A. Purification and characterization of two alpha-galactosidases associated with catabolism of guar gum and other alpha-galactosides by Bacteroides ovatus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):500–506. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.500-506.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J., Hseu T. H. Specificity of the acid protease from Monascus kaoliang towards the B-chain of oxidized insulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 7;614(2):607–612. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90250-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusiak J. W., Quirk J. M., Brady R. O. Purification and properties of the two major isozymes of alpha-galactosidase from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):184–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid K., Schmitt R. Raffinose metabolism in Escherichia coli K12. Purification and properties of a new alpha-galactosidase specified by a transmissible plasmid. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):95–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


