Abstract
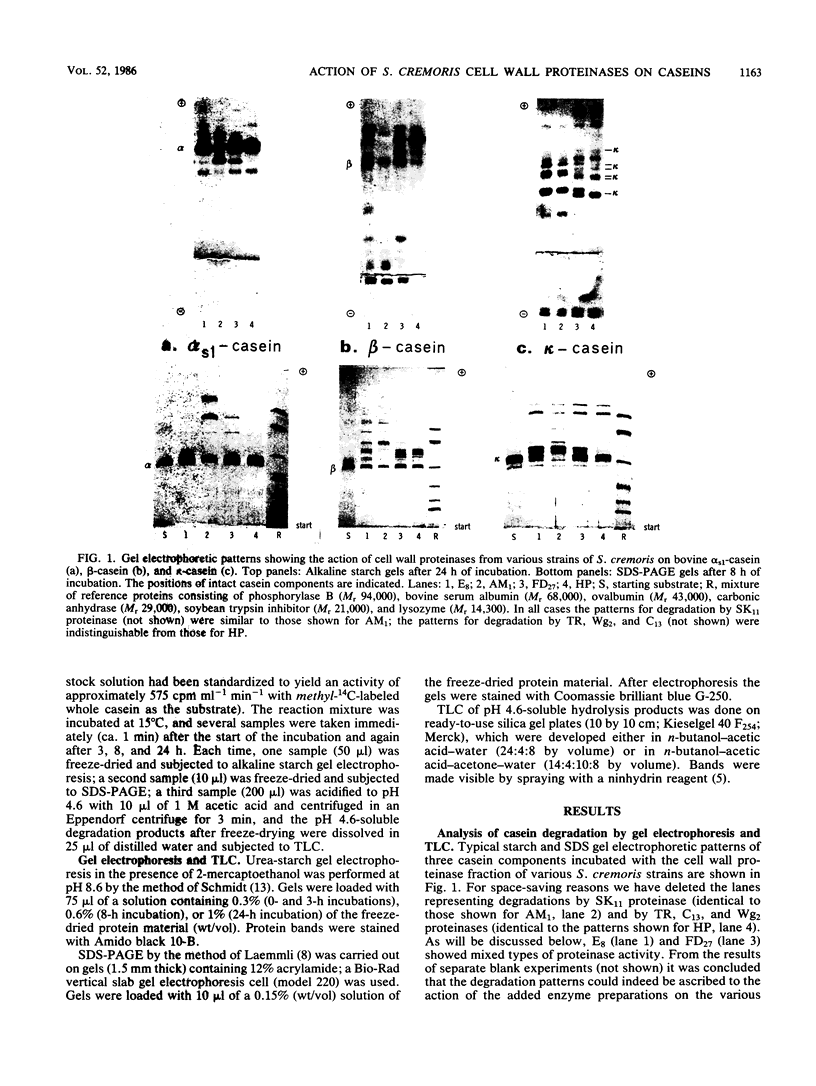
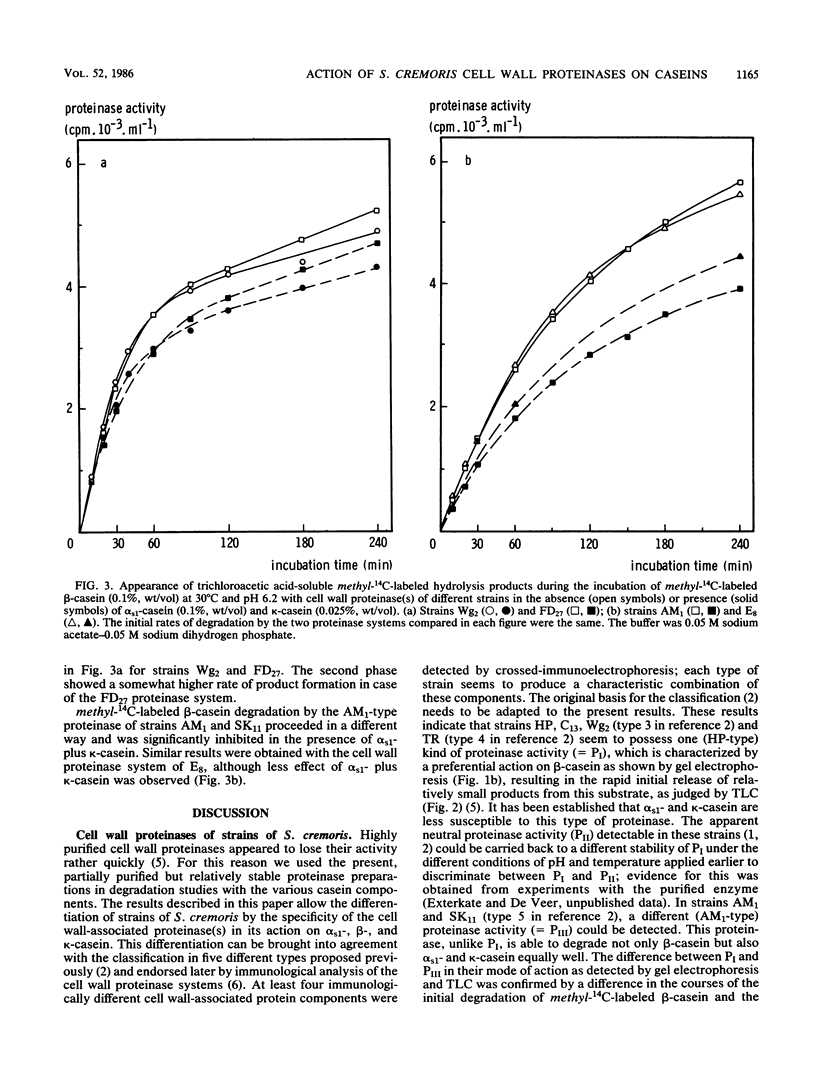
Partially purified cell wall proteinases of eight strains of Streptococcus cremoris were compared in their action on bovine αs1-, β-, and κ-casein, as visualized by starch gel electrophoresis, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and thin-layer chromatography. Characteristic degradation profiles could be distinguished, from which the occurrence of two proteinases, represented by strain HP and strain AM1, was concluded. The action of the HP-type proteinase P1 (also detectable in strains Wg2, C13, and TR) was established by electrophoretic methods to be directed preferentially towards β-casein. The AM1-type proteinase PIII (also detectable in strain SK11) was also able to degrade β-casein, but at the same time split αs1- and κ-casein more extensively than did PI. Strain FD27 exhibited mainly PI activity but also detectable PIII degradation characteristics. The cell wall proteinase preparation of strain E8 showed low PI as well as low PIII activity. All proteinase preparations produced from κ-casein positively charged degradation products with electrophoretic mobilities similar to those of degradation products released by the action of the milk-clotting enzyme chymosin. The differences between PI and PIII in mode of action, as detected by gel electrophoresis and thin-layer chromatography, were reflected by the courses of the initial degradation of methyl-14C-labeled β-casein and by the effect of αs1- plus κ-casein on these degradations. The results are discussed in the light of previous comparative studies of cell wall proteinases in strains of S. cremoris and with respect to the growth of this organism in milk.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Exterkate F. A. Location of Peptidases Outside and Inside the Membrane of Streptococcus cremoris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):177–183. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.177-183.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A., de Veer G. J. Partial Isolation and Degradation of Caseins by Cell Wall Proteinase(s) of Streptococcus cremoris HP. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):328–332. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.328-332.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugenholtz J., Exterkate F., Konings W. N. The Proteolytic Systems of Streptococcus cremoris: an Immunological Analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1105–1110. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1105-1110.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier J. C., Brignon G., Ribadeau-Dumas B. Structure primaire de la caséine kappa B bovine. Séquence complète. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jun;35(2):222–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payens T. A., Heremans K. Effect of pressure on the temperature-dependent association of beta-casein. Biopolymers. 1969;8(3):335–345. doi: 10.1002/bip.1969.360080305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT D. G., PAYENS T. A. THE PURIFICATION AND SOME PROPERTIES OF A CALCIUM-SENSITIVE ALPHA-CASEIN. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 15;78:492–499. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90910-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT D. G. STARCH-GEL ELECTROPHORESIS OF K-CASEIN. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Aug 19;90:411–414. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vreeman H. J., Both P., Brinkhuis J. A., van der Spek C. Purification and some physicochemical properties of bovine kappa-casein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 28;491(1):93–103. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]