Abstract
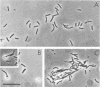
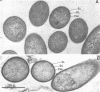
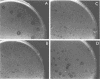
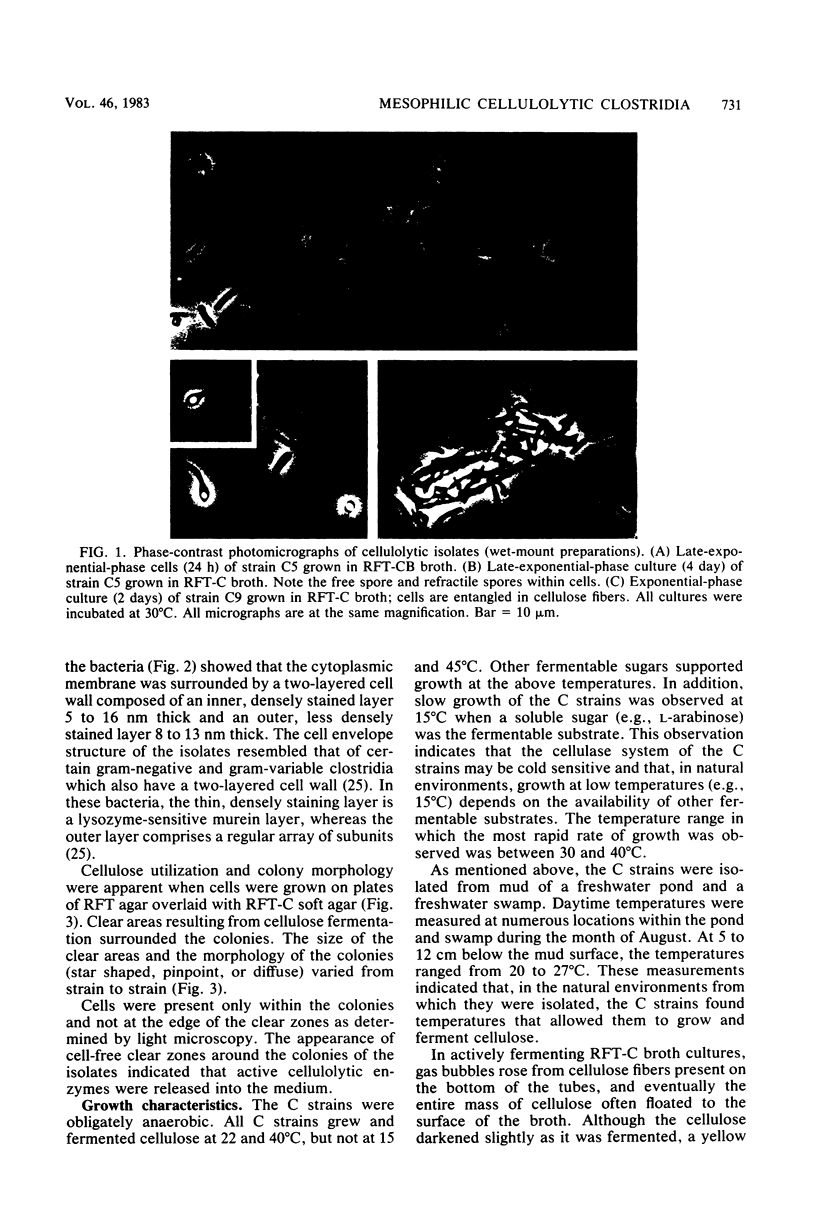
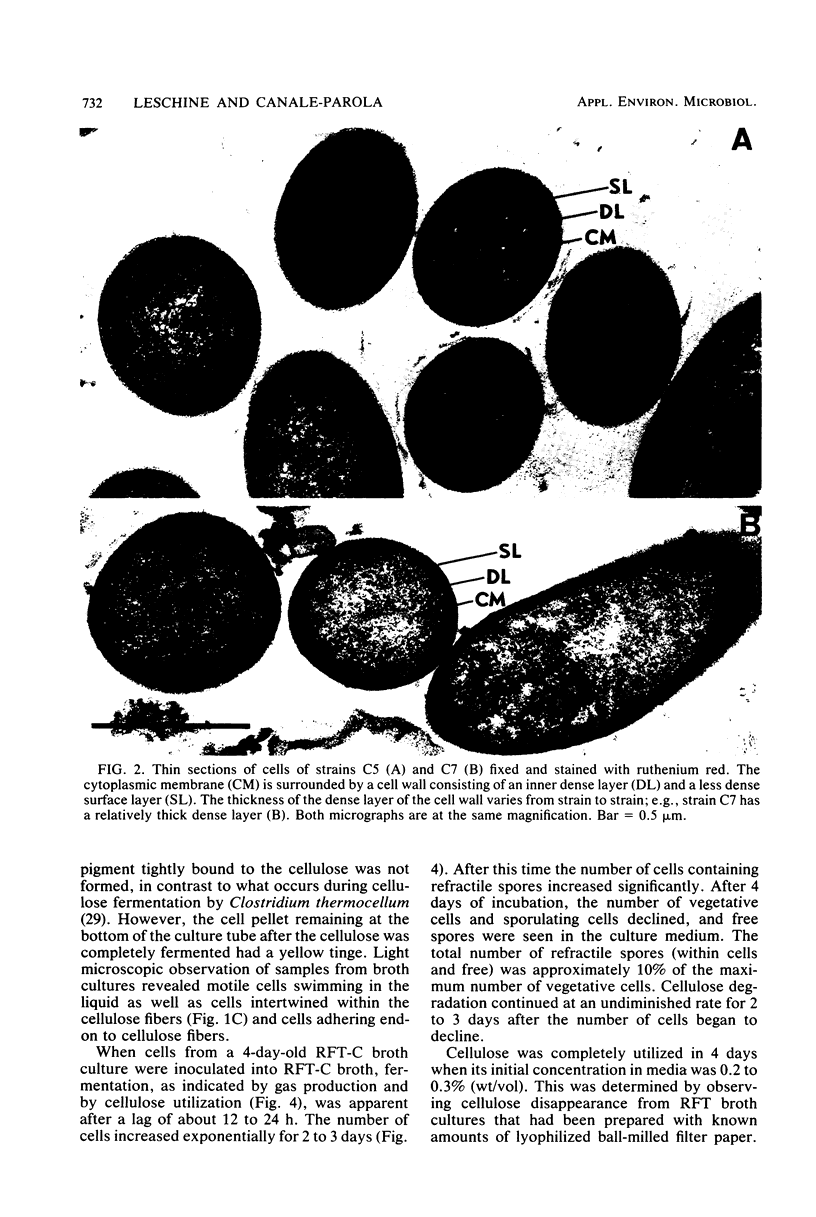
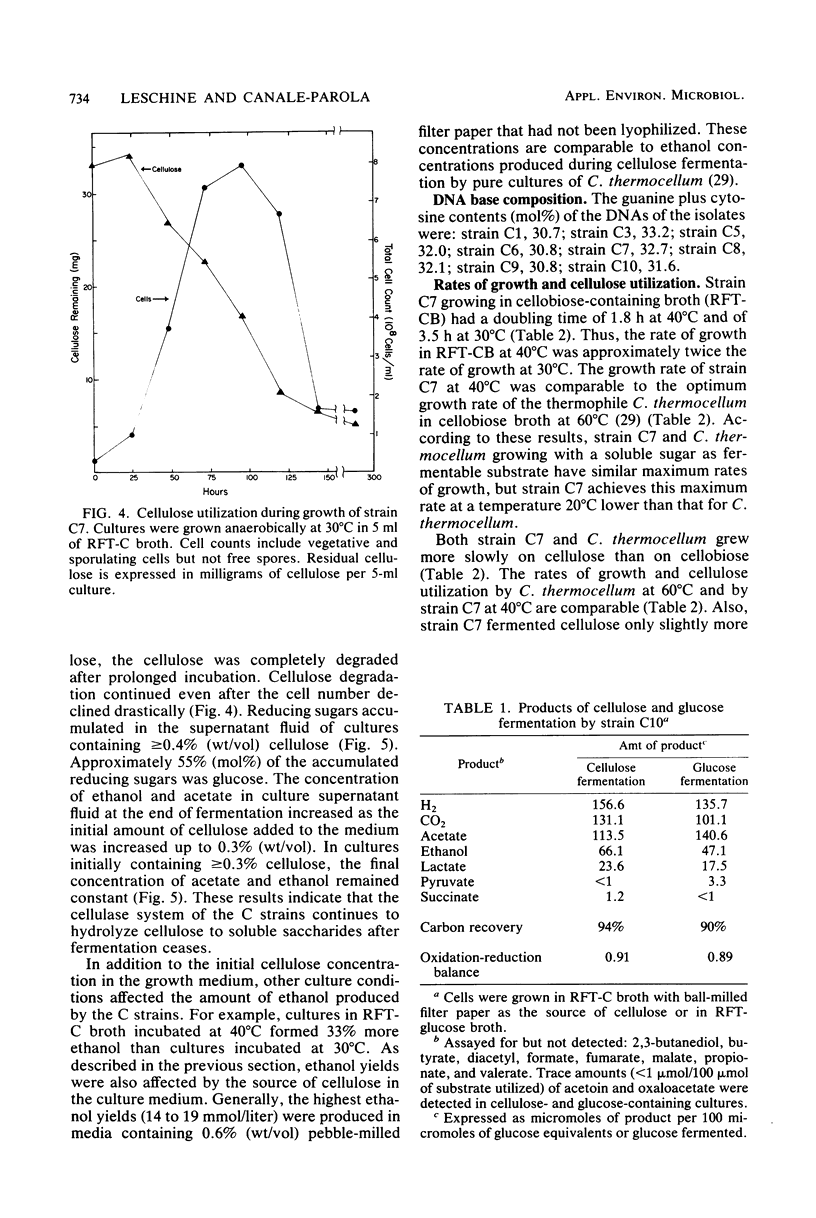
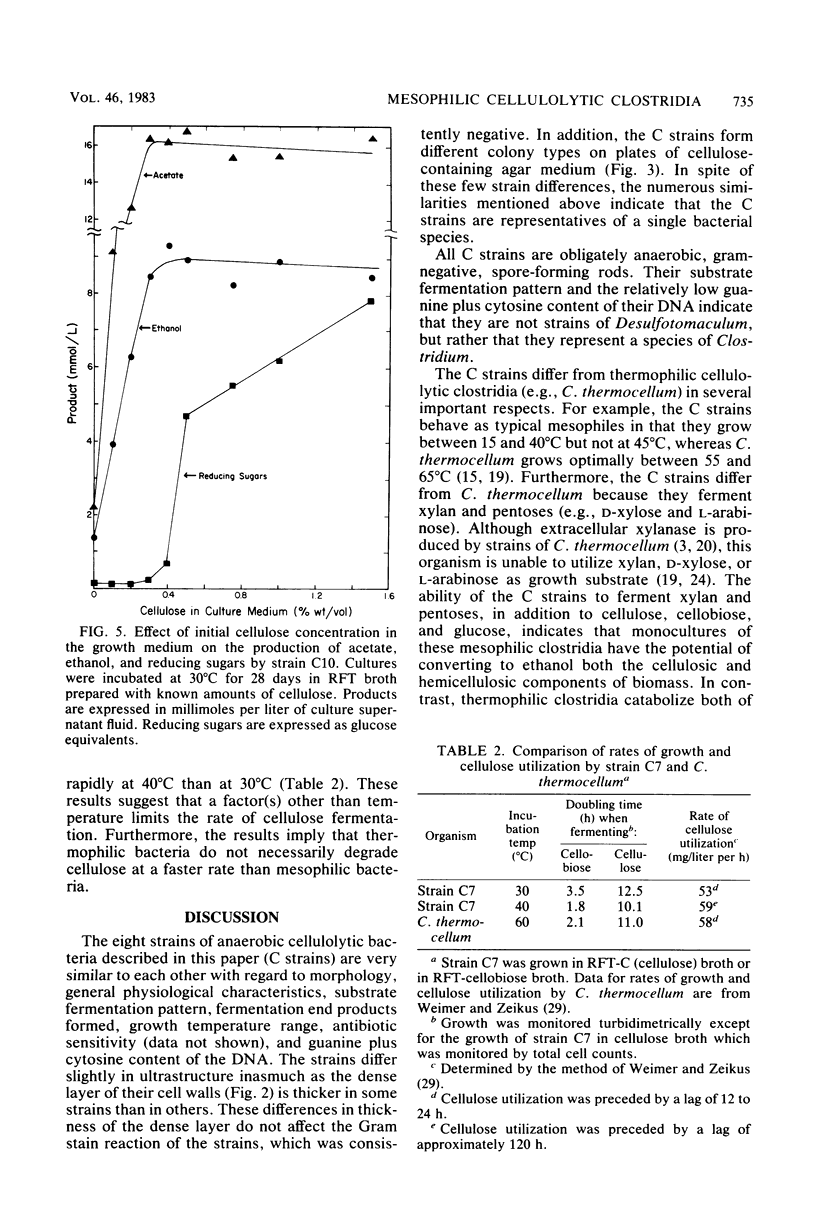
Eight strains of obligately anaerobic, mesophilic, cellulolytic bacteria were isolated from mud of freshwater environments. The isolates (C strains) were rod-shaped, gram negative, and formed terminal spherical to oval spores that swelled the sporangium. The guanine plus cytosine content of the DNA of the C strains ranged from 30.7 to 33.2 mol% (midpoint of thermal denaturation). The C strains fermented cellulose with formation primarily of acetate, ethanol, CO2, and H2. Reducing sugars accumulated in the supernatant fluid of cultures which initially contained ≥0.4% (wt/vol) cellulose. The C strains resembled Clostridium cellobioparum in some phenotypic characteristics and Clostridium papyrosolvens in others, but they were not identical to either of these species. The C strains differed from thermophilic cellulolytic clostridia (e.g., Clostridium thermocellum) not only in growth temperature range but also because they fermented xylan and five-carbon products of plant polysaccharide hydrolysis such as d-xylose and l-arabinose. At 40°C, cellulose was degraded by cellulolytic mesophilic cells (strain C7) at a rate comparable to that at which C. thermocellum degrades cellulose at 60°C. Substrate utilization and growth temperature data indicated that the C strains contribute to the anaerobic breakdown of plant polymers in the environments they inhabit.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooney C. L. Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of solid waste for fuel gas production. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1975 Aug;17(8):1119–1135. doi: 10.1002/bit.260170804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebersold H. R., Cordier J. L., Lüthy P. Bacterial mesosomes: method dependent artifacts. Arch Microbiol. 1981 Sep;130(1):19–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00527066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giallo J., Gaudin C., Belaich J. P., Petitdemange E., Caillet-Mangin F. Metabolism of glucose and cellobiose by cellulolytic mesophilic Clostridium sp. strain H10. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):843–849. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.843-849.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood C. S., Canale-Parola E. Branched-chain amino acid fermentation by a marine spirochete: strategy for starvation survival. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):109–116. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.109-116.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungate R. E. Studies on Cellulose Fermentation: I. The Culture and Physiology of an Anaerobic Cellulose-digesting Bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1944 Nov;48(5):499–513. doi: 10.1128/jb.48.5.499-513.1944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Francis B. S. Taxonomy of the Clostridia: ribosomal ribonucleic acid homologies among the species. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jun;88(2):229–244. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-2-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBEE R. H. The anaerobic thermophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):51–63. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.51-63.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. L., Wolin M. J. A serum bottle modification of the Hungate technique for cultivating obligate anaerobes. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):985–987. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.985-987.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng T. K., Ben-Bassat A., Zeikus J. G. Ethanol Production by Thermophilic Bacteria: Fermentation of Cellulosic Substrates by Cocultures of Clostridium thermocellum and Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jun;41(6):1337–1343. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.6.1337-1343.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng T. K., Weimer T. K., Zeikus J. G. Cellulolytic and physiological properties of Clostridium thermocellum. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Jul 26;114(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00429622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng T. K., Zeikus J. G. Comparison of Extracellular Cellulase Activities of Clostridium thermocellum LQRI and Trichoderma reesei QM9414. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):231–240. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.231-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paster B. J., Canale-Parola E. Physiological diversity of rumen spirochetes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):686–693. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.686-693.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Glauert A. M. Ultrastructure of the cell walls of two closely related clostridia that possess different regular arrays of surface subunits. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):869–882. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.869-882.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton T. B., Canale-Parola E. Enumeration and selective isolation of rumen spirochetes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):965–973. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.965-973.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton T. B., Canale-Parola E. Treponema bryantii sp. nov., a rumen spirochete that interacts with cellulolytic bacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1980 Sep;127(2):145–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00428018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimer P. J., Zeikus J. G. Fermentation of cellulose and cellobiose by Clostridium thermocellum in the absence of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):289–297. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.289-297.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo D. D., Holt S. C., Leadbetter E. R. Ultrastructure of Bacteroides species: Bacteroides asaccharolyticus, Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides melaninogenicus subspecies melaninogenicus, and B. melaninogenicus subspecies intermedius. J Infect Dis. 1979 May;139(5):534–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.5.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]