Abstract
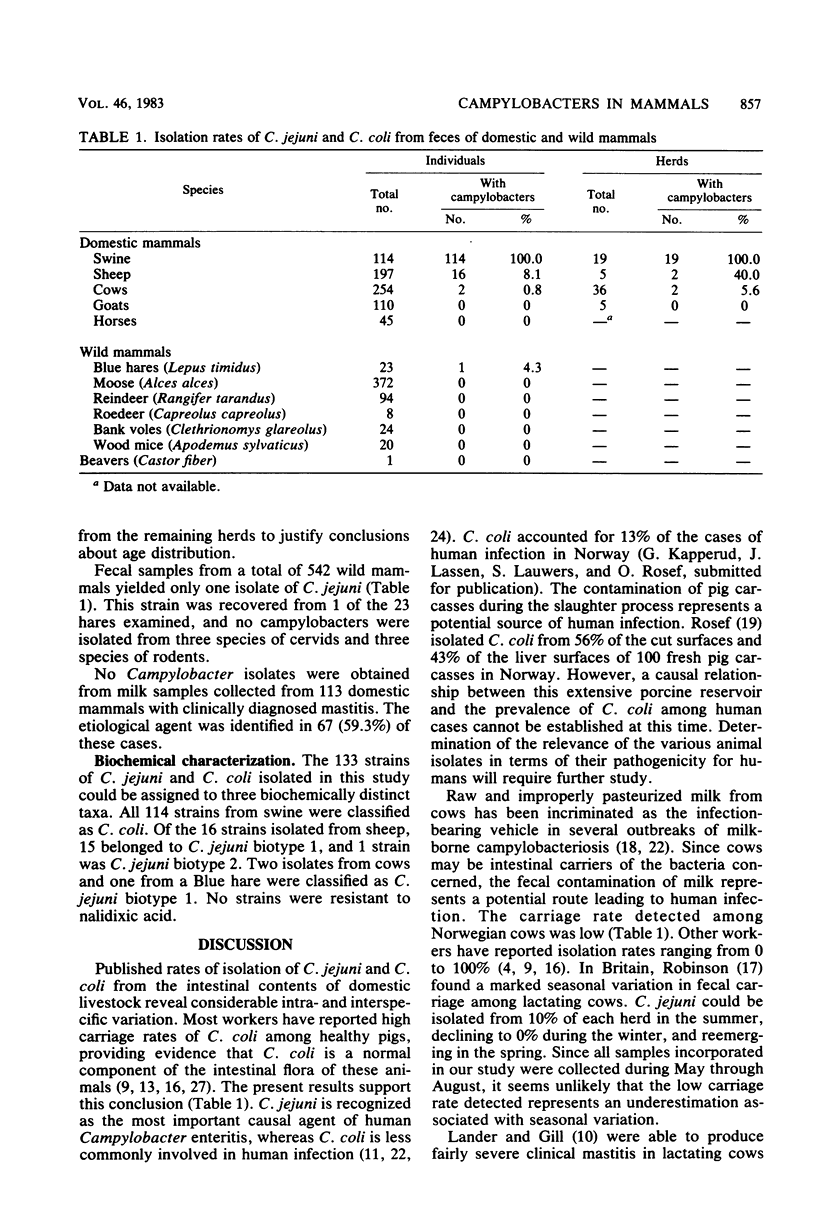
A total of 1,262 domestic and wild mammals from Norway were surveyed for fecal carriage of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Of the five species of domestic mammals examined, the highest isolation rate was recorded among swine (100.0%), followed by sheep (8.1%) and cows (0.8%). No strains were recovered from horses or goats. Among wild mammals, C. jejuni was isolated from 1 of 23 hares, and no isolated were obtained from three species of cervids and three species of rodents. Of the 133 Campylobacter strains isolated, 114 were classified as C. coli, 18 were C. jejuni biotype 1, and 1 belonged to C. jejuni biotype 2. All 114 strains from swine were C. coli. Milk samples from 113 domestic animals with clinically diagnosed mastitis (106 cows, 5 sheep, 1 horse, and 1 pig) were negative for campylobacters.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J., Wells J. G., Feldman R. A., Pollard R. A., Allen J. R. Campylobacter enteritis in the United States. A multicenter study. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Mar;98(3):360–365. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-3-360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton F. J., Dawkins H. C., Robertson L. Campylobacter jejuni/coli in abattoirs and butchers shops. J Infect. 1982 May;4(3):243–245. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(82)92542-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. P., Roman D. J. Prevalence and survival of Campylobacter jejuni in unpasteurized milk. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Nov;44(5):1154–1158. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.5.1154-1158.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. G. Campylobacteriosis--a "new" disease in laboratory animals. Lab Anim Sci. 1982 Dec;32(6):625–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill C. O., Harris L. M. Contamination of red-meat carcasses by Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):977–980. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.977-980.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang M. N., Ederer G. M. Rapid hippurate hydrolysis method for presumptive identification of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):114–115. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.114-115.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G., Rosef O. Avian wildlife reservoir of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni, Yersinia spp., and Salmonella spp. in Norway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):375–380. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.375-380.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kist M. Infektionen durch Campylobacter jejuni/coli. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1983 Jan 14;108(2):67–72. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1069504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander K. P., Gill K. P. Experimental infection of the bovine udder with Campylobacter coli/jejuni. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Jun;84(3):421–428. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luechtefeld N. A., Blaser M. J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni from migratory waterfowl. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):406–408. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.406-408.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Munroe D. L. Campylobacter jejuni enteritis in man and domestic animals. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1982 Dec 15;181(12):1524–1530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. A., Jones D. M. Milk-borne campylobacter infection. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Apr 25;282(6273):1374–1376. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6273.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandven P., Solberg O., Odegaard K., Myhre G. Improved medium for the transportation of gonococcal specimens. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Feb;90(1):73–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B., Benjamin J. Differentiation of enteropathogenic Campylobacter. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Nov;33(11):1122–1122. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.11.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis - the first five years. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Oct;89(2):175–184. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sticht-Groh V. Campylobacter in healthy slaughter pigs: a possible source of infection for man. Vet Rec. 1982 Jan 30;110(5):104–106. doi: 10.1136/vr.110.5.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedhem A., Kaijser B. Campylobacter fetus subspecies jejuni: a common cause of diarrhea in Sweden. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):353–359. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedhem A., Kaijser B., Sjögren E. The occurrence of Campylobacter jejuni in fresh food and survival under different conditions. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Dec;87(3):421–425. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400069667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


