Abstract
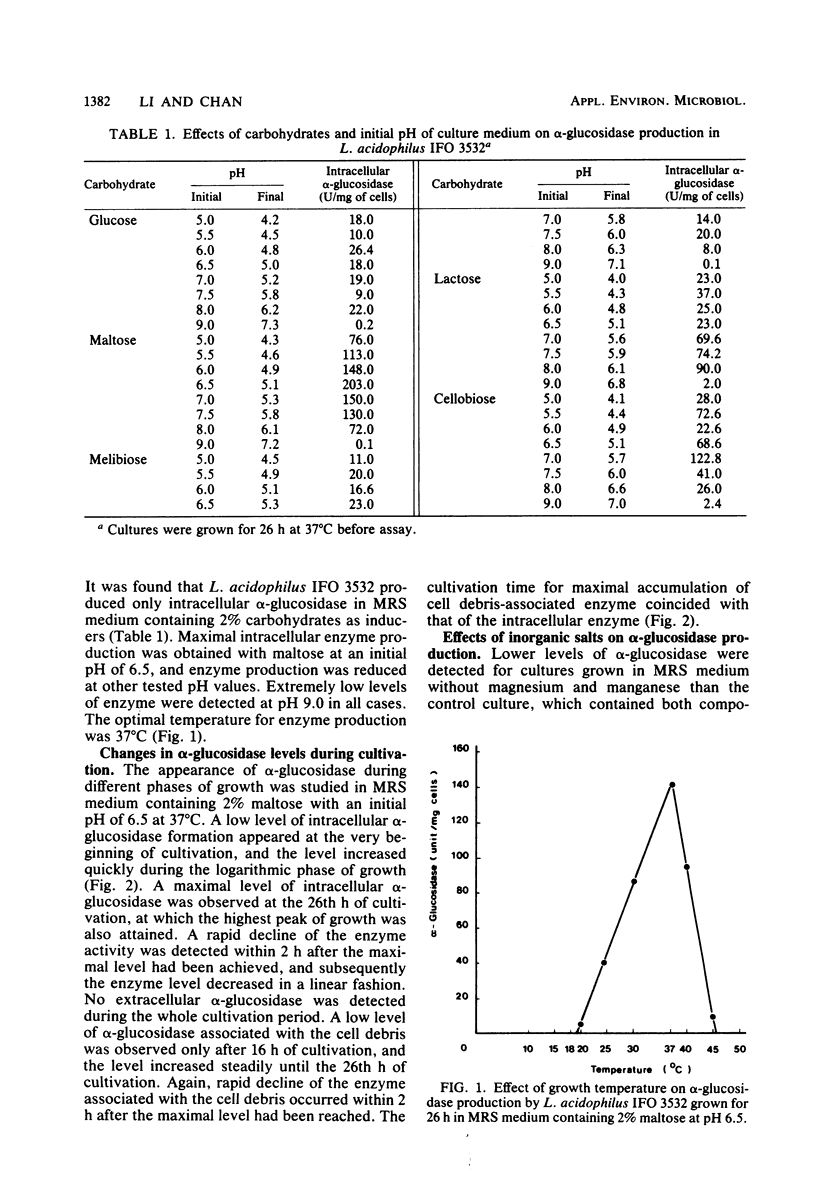
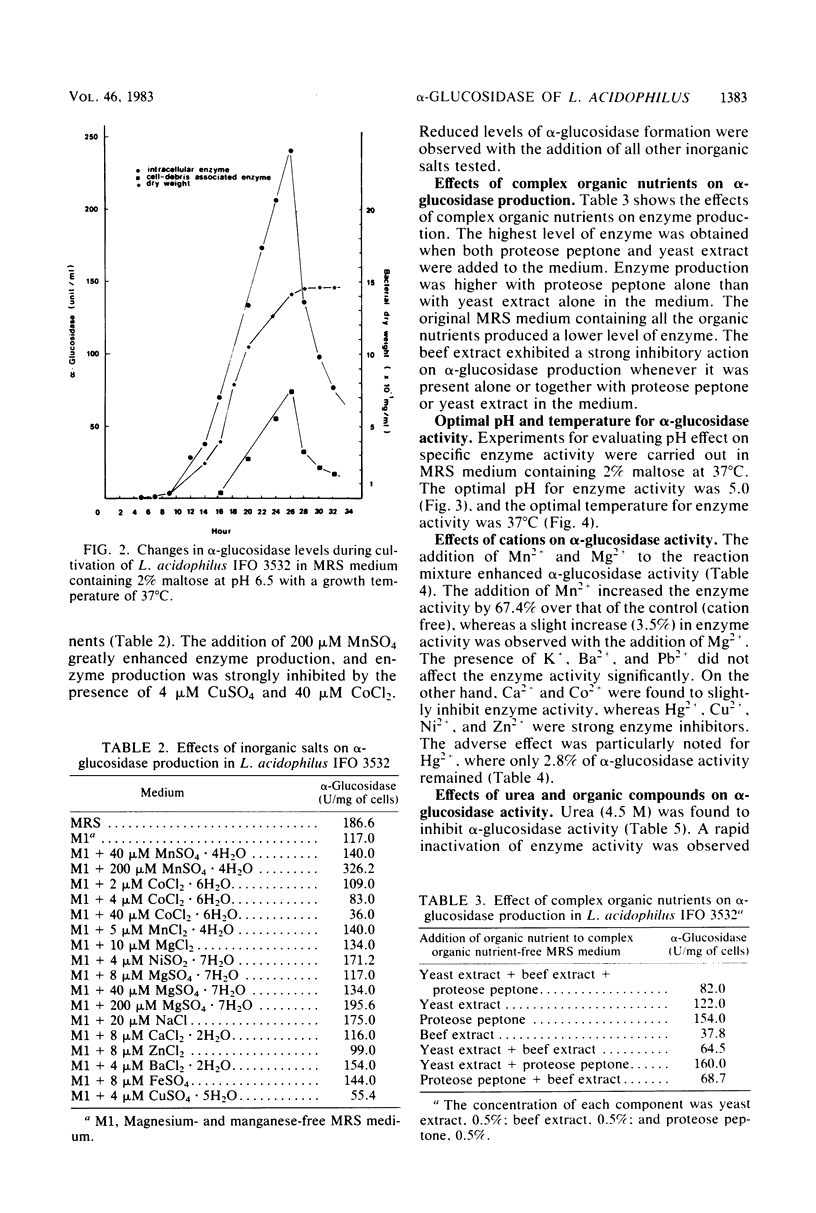
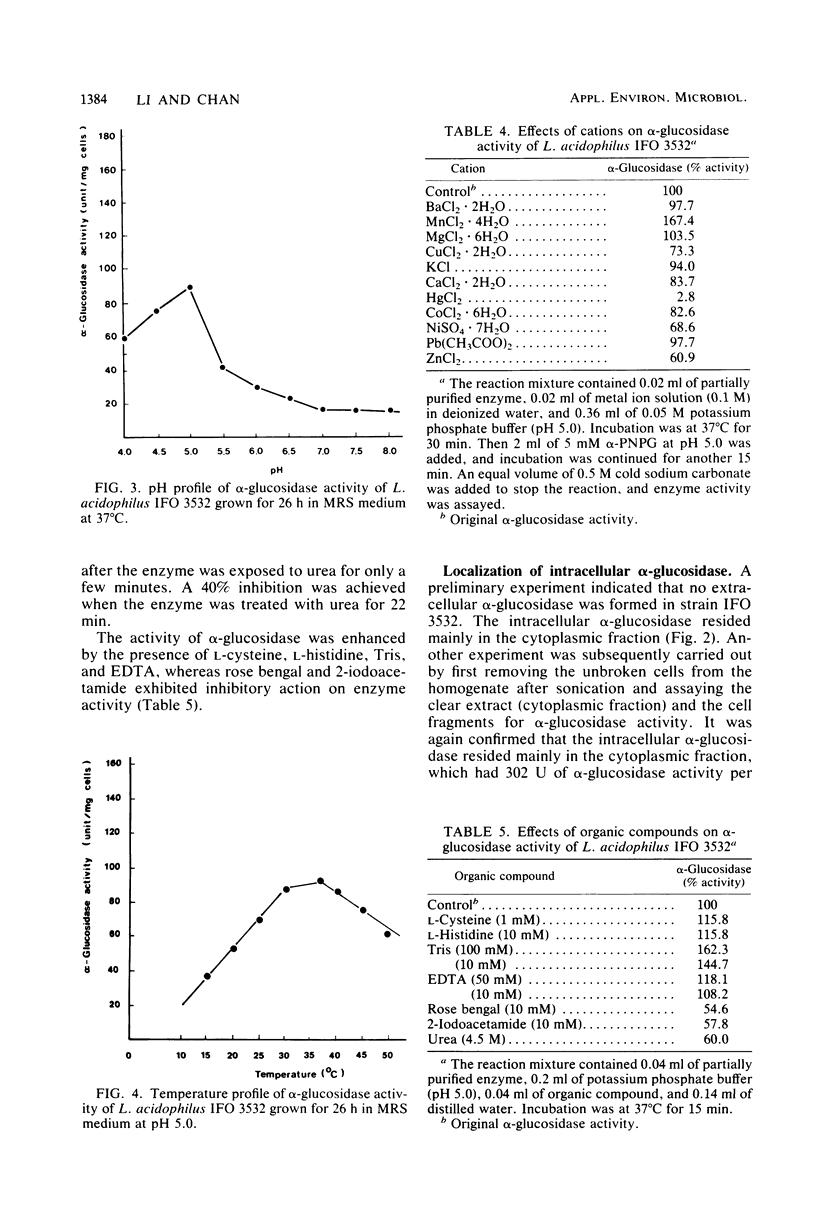
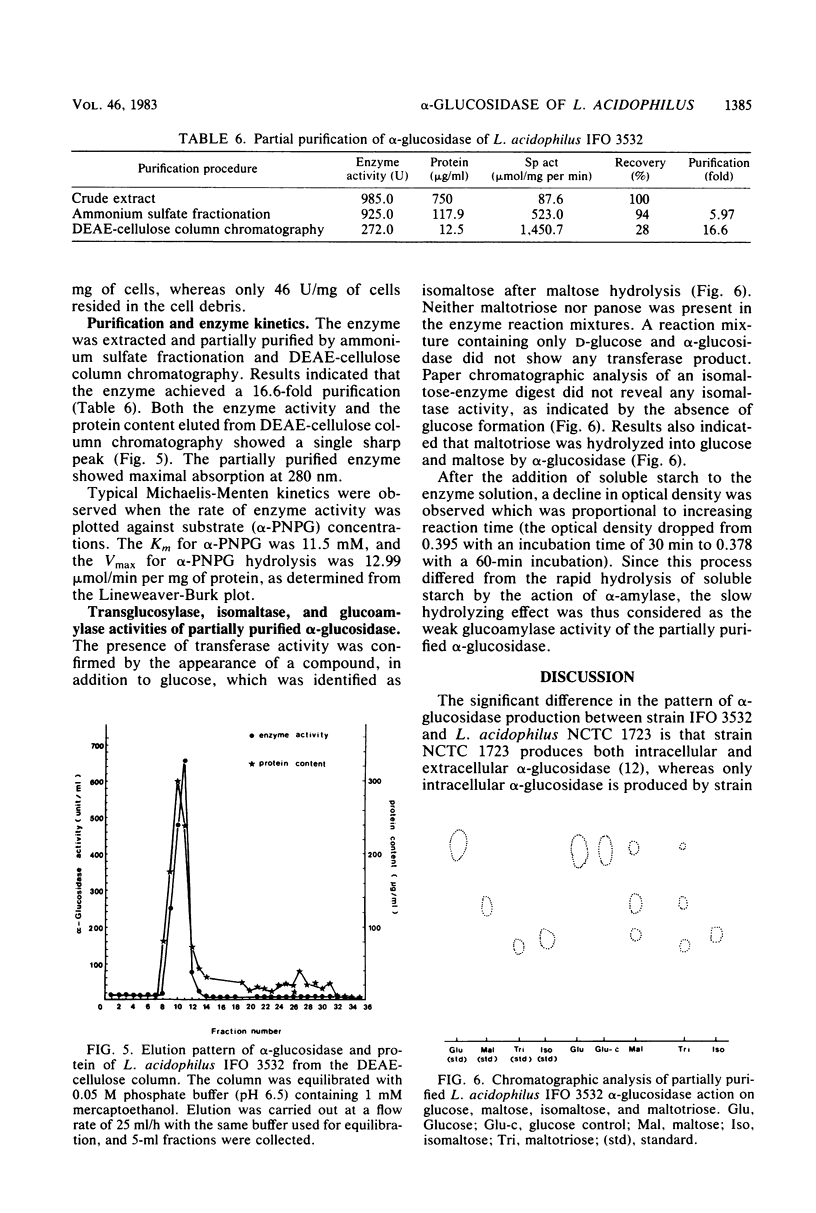
Lactobacillus acidophilus IFO 3532 was found to produce only intracellular alpha-glucosidase (alpha-D-glucoside glucohydrolase; EC 3.2.1.20). Maximum enzyme production was obtained in a medium containing 2% maltose as inducer at 37 degrees C and at an initial pH of 6.5. The enzyme was formed in the cytoplasm and accumulated as a large pool during the logarithmic growth phase. Enzyme production was strongly inhibited by 4 microM CuSO4, 40 microM CoCl2, and beef extract; MnSO4 and the presence of proteose peptone and yeast extract in the medium greatly enhanced enzyme production. A 16.6-fold purification of alpha-glucosidase was achieved by (NH4)2SO4 fractionation and DEAE-cellulose column chromatography. The enzyme showed high specificity for maltose. The Km for alpha-p-nitrophenyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside was 11.5 mM, and the Vmax for alpha-p-nitrophenyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside hydrolysis was 12.99 mumol/min per mg of protein. The optimal pH and temperature for enzyme activity were 5.0 and 37 degrees C, respectively. The enzyme activity was inhibited by Hg2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, Zn2+, Ca2+, Co2+, urea, rose bengal, and 2-iodoacetamide, whereas Mn2+, Mg2+, L-cysteine, L-histidine, Tris, and EDTA stimulated enzyme activity. Transglucosylase activity was present in the partially purified enzyme, and isomaltose was the only glucosyltransferase product. Amylase activity in the purified preparation was relatively weak, and no isomaltase activity was detected.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg J. O., Lindqvist L., Nord C. E. Purification of glycoside hydrolases from Bacteroides fragilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):40–47. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.40-47.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. O., Nord C. E., Wadström T. Formation of glycosidases in batch and continuous culture of Bacteroides fragilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):269–273. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.269-273.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolin L. E., Panos C. The alpha-glucosidases of Streptococcus pyogenes and derived L form. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jul 30;184(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming L. W., Duerksen J. D. Purification and characterization of yeast beta-glucosidases. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):135–141. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.135-141.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland S. E., Speck M. L., Morgan C. G. Detection of Lactobacillus acidophilus in feces of humans, pigs, and chickens. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Oct;30(4):541–545. doi: 10.1128/am.30.4.541-545.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Corpe W. A. Partial purification and characterization of alpha-glucosidase from Pseudomonas fluorescens W. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Apr 1;107(3):269–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00425338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guntermann U., Tan I., Hüttermann A. Induction of alpha-glucosidase and synthesis during the cell cycle of Myxobacter AL-1. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):86–91. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.86-91.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEJEUNE N., THINES-SEMPOUX D., HERS H. G. Tissue fractionation studies. 16. Intracellular distribution and properties of alpha-glucosidases in rat liver. Biochem J. 1963 Jan;86:16–21. doi: 10.1042/bj0860016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. J., Taylor P. M. Acid alpha-D-glucosidases from plant sources. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jan 22;42(2):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWethy S. J., Hartman P. A. Extracellular Maltase of Bacillus brevis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1096–1102. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1096-1102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord C. E., Linder L., Wadström T., Lindberg A. A. Formation of glycoside-hydrolases by oral streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Mar;18(3):391–402. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAZUR J. H., ANDO T. The isolation and the mode of action of a fungal transglycosylase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Apr;93:43–49. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90313-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAZUR J. H., FRENCH D. The action of transglucosidase of Aspergillus oryzae on maltose. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;196(1):265–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premi L., Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Lactose-hydrolyzing enzymes of Lactobacillus species. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jul;24(1):51–57. doi: 10.1128/am.24.1.51-57.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto T., Amemura A., Harada T. Formations of extracellular isoamylase and intracellular alpha-glucosidase and amylase(s) by Pseudomonas SB15 and a mutant strain. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Sep;28(3):336–339. doi: 10.1128/am.28.3.336-339.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Kishigami T., Abe S. Production of extracellular alpha-glucosidase by a thermophilic Bacillus species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):807–812. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.807-812.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELKER N. E., CAMPBELL L. L. EFFECT OF CARBON SOURCES ON FORMATION OF ALPHA-AMYLASE BY BACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:681–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.681-686.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Hartman P. A. Purification and some properties of an extracellular maltase from Bacillus subtilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jan;31(1):108–118. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.1.108-118.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


