Abstract
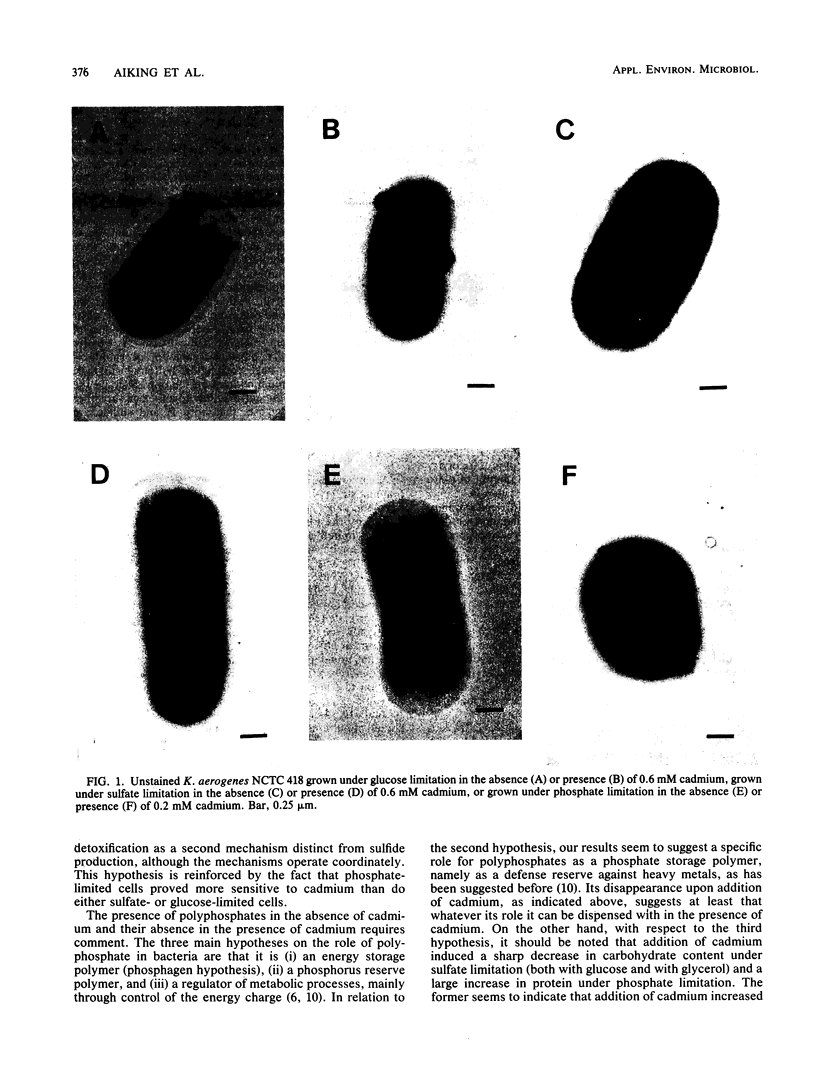
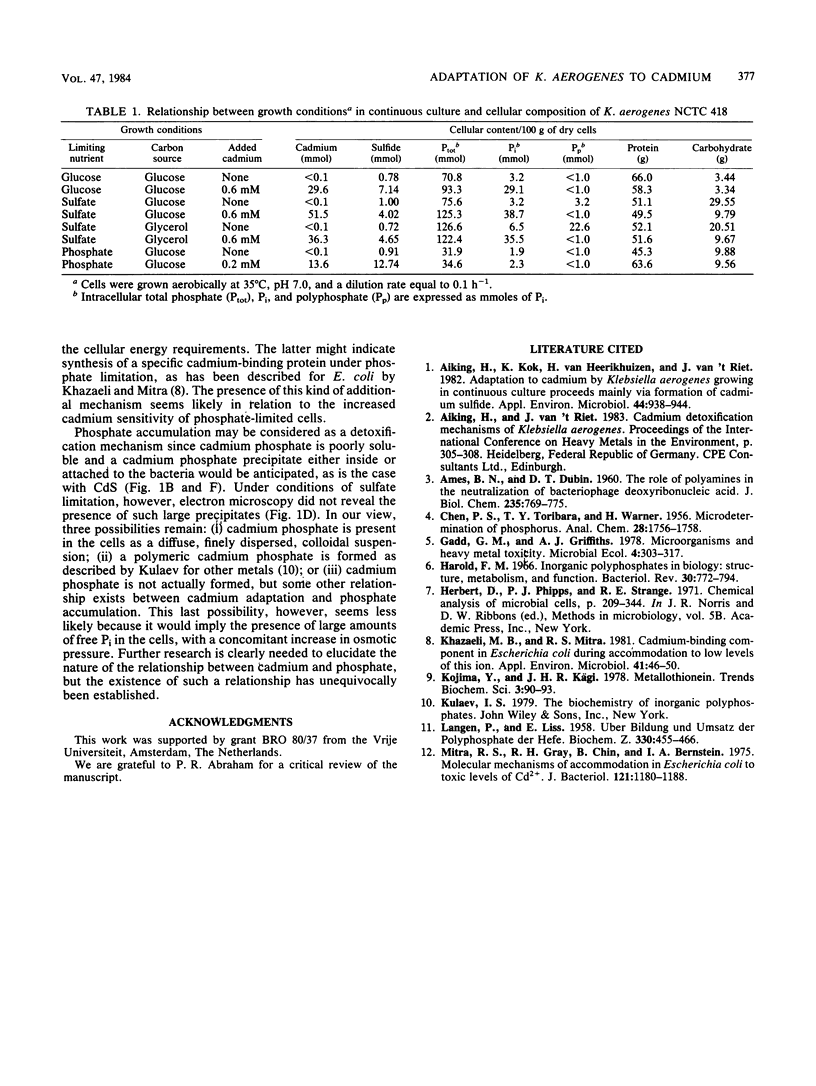
Klebsiella aerogenes NCTC 418, growing in the presence of cadmium under glucose-, sulfate-, or phosphate-limited conditions in continuous culture, exhibits two different cadmium detoxifying mechanisms. In addition to sulfide formation, increased accumulation of Pi is demonstrated as a novel mechanism. Intracellular cadmium is always quantitatively counterbalanced by a concerted increase in both inorganic sulfide and Pi contents of the cells. This led to the conclusion that production of sulfide and accumulation of Pi are detoxification mechanisms present in K. aerogenes but that their relative importance is crucially dependent on the strain and the growth conditions employed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiking H., Kok K., van Heerikhuizen H., van 't Riet J. Adaptation to Cadmium by Klebsiella aerogenes Growing in Continuous Culture Proceeds Mainly via Formation of Cadmium Sulfide. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):938–944. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.938-944.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Inorganic polyphosphates in biology: structure, metabolism, and function. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Dec;30(4):772–794. doi: 10.1128/br.30.4.772-794.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khazaeli M. B., Mitra R. S. Cadmium-binding component in Escherichia coli during accommodation to low levels of this ion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):46–50. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.46-50.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGEN P., LISS E. Uber Bildung und Umsatz der Polyphosphate der Hefe. Biochem Z. 1958;330(6):455–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra R. S., Gray R. H., Chin B., Bernstein I. A. Molecular mechanisms of accommodation in Escherichia coli to toxic levels of Cd2+. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1180–1188. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1180-1188.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



