Abstract
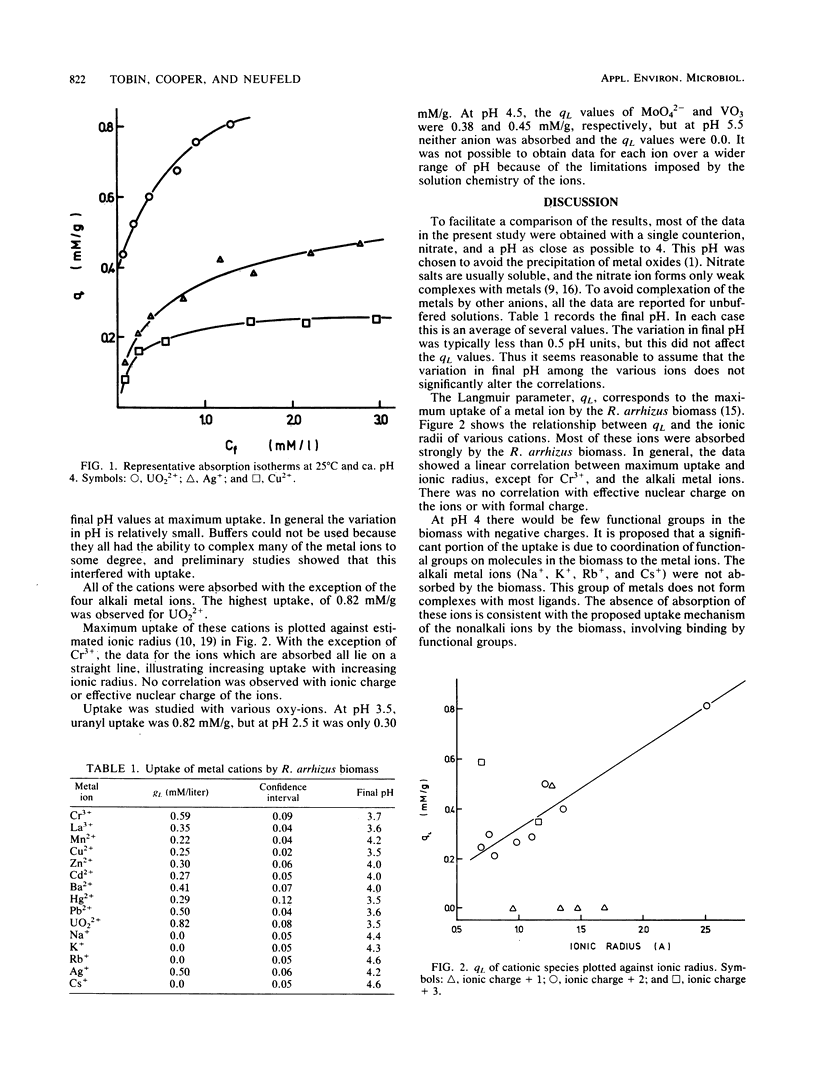
Rhizopus arrhizus biomass was found to absorb a variety of different metal cations and anions but did not absorb alkali metal ions. The amount of uptake of the cations was directly related to ionic radii of La3+, Mn2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Ba2+, Hg2+, Pb2+, UO22+, and Ag+. The uptake of all the cations is consistent with absorption of the metals by sites in the biomass containing phosphate, carboxylate, and other functional groups. The uptake of the molybdate and vanadate anions was strongly pH dependent, and it is proposed that the uptake mechanism involves electrostatic attraction to positively charged functional groups.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTNICKI-GARCIA S., NICKERSON W. J. Isolation, composition, and structure of cell walls of filamentous and yeast-like forms of Mucor rouxii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Mar 26;58:102–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90822-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Koval S. F. Binding of metals to cell envelopes of Escherichia coli K-12. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):325–335. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.325-335.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Sites of metal deposition in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):876–887. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.876-887.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Uptake and retention of metals by cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1502–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1502-1518.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J. The response of cell walls of Bacillus subtilis to metals and to electron-microscopic stains. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Feb;24(2):89–104. doi: 10.1139/m78-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galun M., Keller P., Malki D., Feldstein H., Galun E., Siegel S. M., Siegel B. Z. Removal of Uranium(VI) from Solution by Fungal Biomass and Fungal Wall-Related Biopolymers. Science. 1983 Jan 21;219(4582):285–286. doi: 10.1126/science.219.4582.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandberg G. W., Shumate S. E., Parrott J. R. Microbial Cells as Biosorbents for Heavy Metals: Accumulation of Uranium by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):237–245. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.237-245.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerberg A., Diver A., Peeri Z., Gutnick D. L., Rosenberg E. Emulsifier of Arthrobacter RAG-1: chemical and physical properties. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):414–420. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.414-420.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


