Abstract
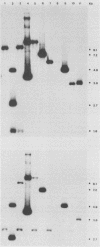
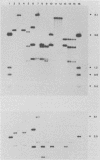
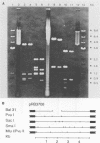
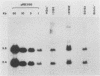
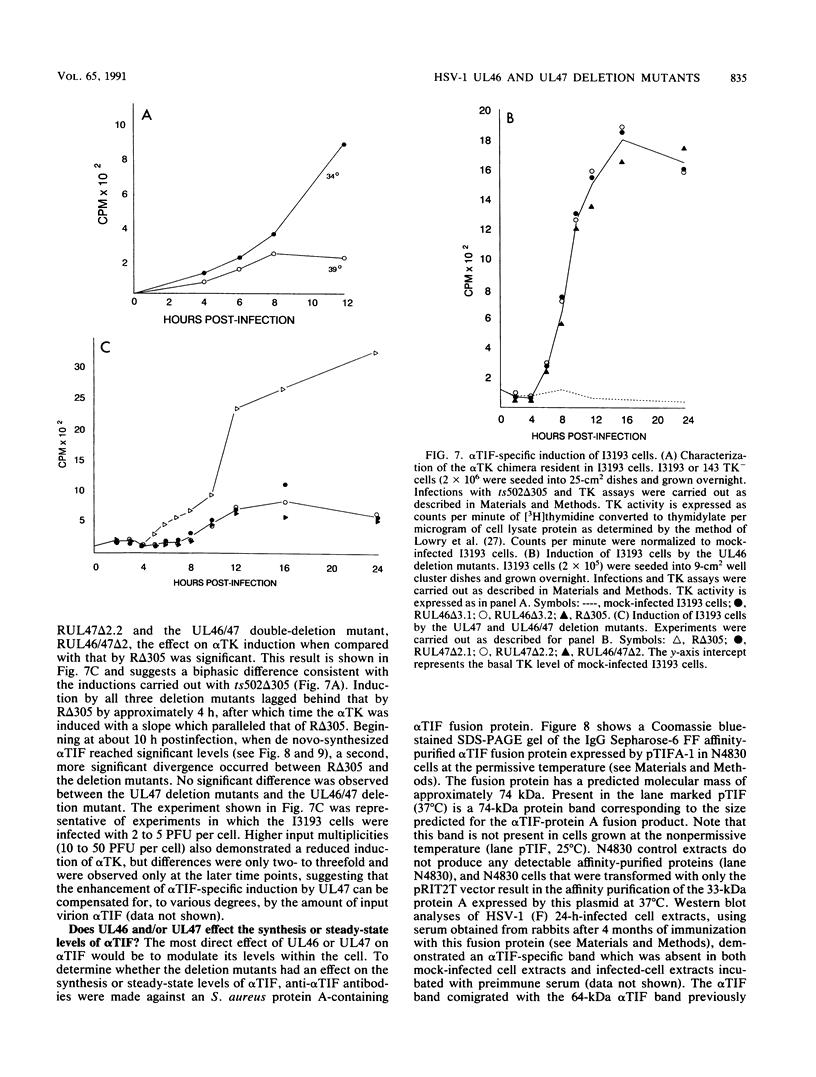
The transcriptional induction of the alpha or immediate-early gene class of herpes simplex virus type 1 effected by the alpha trans-induction factor (alpha TIF, ICP25, VP16, Vmw65) requires an alpha-specific cis-acting site. Increased transcription does not result from the direct, independent binding of alpha TIF, but rather from an alpha TIF-dependent formation of a protein-DNA complex containing, in addition to alpha TIF, at least one host cell factor. One of the host factors is a POU domain protein which recognizes an octamer element in the alpha-specific consensus. There is evidence that alpha TIF may drive the formation of multiple protein-DNA complexes containing a POU protein and additional host factors. Previously, the gene products of UL46 and UL47 have been implicated in modulating the alpha TIF-dependent transcriptional induction of alpha genes. Our current studies have extended these analyses from a transient-expression system to a series of viral deletion mutants. In these studies we demonstrate that neither UL46- nor UL47-encoded gene product, either separately or in combination, is required for viral growth in cell culture. The absence of UL47 reduces by up to 80% the ability of the virus to induce an alpha-regulated thymidine kinase reporter gene resident in 143TK- cells. Autoradiograms of [35S]methionine pulse-labeled infected cell proteins, separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, show that deleting UL46 and/or UL47 has no discernable effect on the synthesis of alpha TIF or alpha TIF-containing proteins. Subsequent Western immunoblot analysis, with rabbit anti-alpha TIF antibodies made to an alpha TIF-Staphylococcus aureus protein A fusion, demonstrated that the accumulation and steady-state levels of alpha TIF or alpha TIF-containing proteins was indistinguishable from that of the thymidine kinase-negative isogenic parental virus, R delta 305.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ace C. I., Dalrymple M. A., Ramsay F. H., Preston V. G., Preston C. M. Mutational analysis of the herpes simplex virus type 1 trans-inducing factor Vmw65. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2595–2605. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ace C. I., McKee T. A., Ryan J. M., Cameron J. M., Preston C. M. Construction and characterization of a herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant unable to transinduce immediate-early gene expression. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2260–2269. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2260-2269.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. E., Roizman B. Identification of three genes nonessential for growth in cell culture near the right terminus of the unique sequences of long component of herpes simplex virus 1. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):684–691. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90534-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batterson W., Roizman B. Characterization of the herpes simplex virion-associated factor responsible for the induction of alpha genes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.371-377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun D. K., Pereira L., Norrild B., Roizman B. Application of denatured, electrophoretically separated, and immobilized lysates of herpes simplex virus-infected cells for detection of monoclonal antibodies and for studies of the properties of viral proteins. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):103–112. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.103-112.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousens D. J., Greaves R., Goding C. R., O'Hare P. The C-terminal 79 amino acids of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein, Vmw65, efficiently activate transcription in yeast and mammalian cells in chimeric DNA-binding proteins. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2337–2342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08361.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Fine-structure mapping and functional analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein VP175. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):189–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.189-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Triezenberg S. J., McKnight S. L. Expression of a truncated viral trans-activator selectively impedes lytic infection by its cognate virus. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):452–454. doi: 10.1038/335452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A herpesvirus trans-activating protein interacts with transcription factor OTF-1 and other cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6347–6351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves R. F., O'Hare P. Structural requirements in the herpes simplex virus type 1 transactivator Vmw65 for interaction with the cellular octamer-binding protein and target TAATGARAT sequences. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2716–2724. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2716-2724.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves R., O'Hare P. Separation of requirements for protein-DNA complex assembly from those for functional activity in the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein Vmw65. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1641–1650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1641-1650.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Draper K. G., Frink R. J., Costa R. H., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus mRNA species mapping in EcoRI fragment I. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):594–607. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.594-607.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Treacy M. N., Simmons D. M., Ingraham H. A., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression of a large family of POU-domain regulatory genes in mammalian brain development. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):35–41. doi: 10.1038/340035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Sturm R. A., Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A., Ingraham H. A., Rosenfeld M. G., Finney M., Ruvkun G. The POU domain: a large conserved region in the mammalian pit-1, oct-1, oct-2, and Caenorhabditis elegans unc-86 gene products. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1513–1516. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubenthal-Voss J., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus 1 reiterated S component sequences (c1) situated between the a sequence and alpha 4 gene are not essential for virus replication. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):509–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.509-514.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., LeBowitz J. H., Sharp P. A. The octamer-binding proteins form multi-protein--DNA complexes with the HSV alpha TIF regulatory protein. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4229–4238. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Differentiation and DNA contact points of host proteins binding at the cis site for virion-mediated induction of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus 1. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1145–1157. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1145-1157.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Host cell proteins bind to the cis-acting site required for virion-mediated induction of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):71–75. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Separation of sequences defining basal expression from those conferring alpha gene recognition within the regulatory domains of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4065–4069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Clustering of genes dispensable for growth in culture in the S component of the HSV-1 genome. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):573–576. doi: 10.1126/science.3033823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Differentiation between alpha promoter and regulator regions of herpes simplex virus 1: the functional domains and sequence of a movable alpha regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Structural features of the herpes simplex virus alpha gene 4, 0, and 27 promoter-regulatory sequences which confer alpha regulation on chimeric thymidine kinase genes. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):939–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.939-949.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Campbell M. E., Haarr L., Frame M. C., Parris D. S., Murphy M., Hope R. G., Muller M. T., Preston C. M. The 65,000-Mr DNA-binding and virion trans-inducing proteins of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2428–2437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2428-2437.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight J. L., Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Binding of the virion protein mediating alpha gene induction in herpes simplex virus 1-infected cells to its cis site requires cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7061–7065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight J. L., Pellett P. E., Jenkins F. J., Roizman B. Characterization and nucleotide sequence of two herpes simplex virus 1 genes whose products modulate alpha-trans-inducing factor-dependent activation of alpha genes. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):992–1001. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.992-1001.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Abrahmsén L., Uhlén M. Immobilization and purification of enzymes with staphylococcal protein A gene fusion vectors. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1075–1080. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03741.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R. Herpes simplex virus regulatory elements and the immunoglobulin octamer domain bind a common factor and are both targets for virion transactivation. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill E. A., Fletcher C., Burrow C. R., Heintz N., Roeder R. G., Kelly T. J. Transcription factor OTF-1 is functionally identical to the DNA replication factor NF-III. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1210–1213. doi: 10.1126/science.3413485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellett P. E., McKnight J. L., Jenkins F. J., Roizman B. Nucleotide sequence and predicted amino acid sequence of a protein encoded in a small herpes simplex virus DNA fragment capable of trans-inducing alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5870–5874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piszkiewicz D., Landon M., Smith E. L. Anomalous cleavage of aspartyl-proline peptide bonds during amino acid sequence determinations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 10;40(5):1173–1178. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90918-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Conley A. J., Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Cloning of reiterated and nonreiterated herpes simplex virus 1 sequences as BamHI fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4201–4205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Roizman B. A generalized technique for deletion of specific genes in large genomes: alpha gene 22 of herpes simplex virus 1 is not essential for growth. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Frame M. C., Campbell M. E. A complex formed between cell components and an HSV structural polypeptide binds to a viral immediate early gene regulatory DNA sequence. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., van Driel W., van der Vliet P. C. Nuclear factor III, a novel sequence-specific DNA-binding protein from HeLa cells stimulating adenovirus DNA replication. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):656–659. doi: 10.1038/322656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Sears A. E. An inquiry into the mechanisms of herpes simplex virus latency. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:543–571. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Spear P. G. Preparation of herpes simplex virus of high titer. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):83–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.83-84.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner I., Spivack J. G., Deshmane S. L., Ace C. I., Preston C. M., Fraser N. W. A herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant containing a nontransinducing Vmw65 protein establishes latent infection in vivo in the absence of viral replication and reactivates efficiently from explanted trigeminal ganglia. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1630-1638.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triezenberg S. J., Kingsbury R. C., McKnight S. L. Functional dissection of VP16, the trans-activator of herpes simplex virus immediate early gene expression. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):718–729. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- apRhys C. M., Ciufo D. M., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Hayward G. S. Overlapping octamer and TAATGARAT motifs in the VF65-response elements in herpes simplex virus immediate-early promoters represent independent binding sites for cellular nuclear factor III. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2798–2812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2798-2812.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]