Abstract
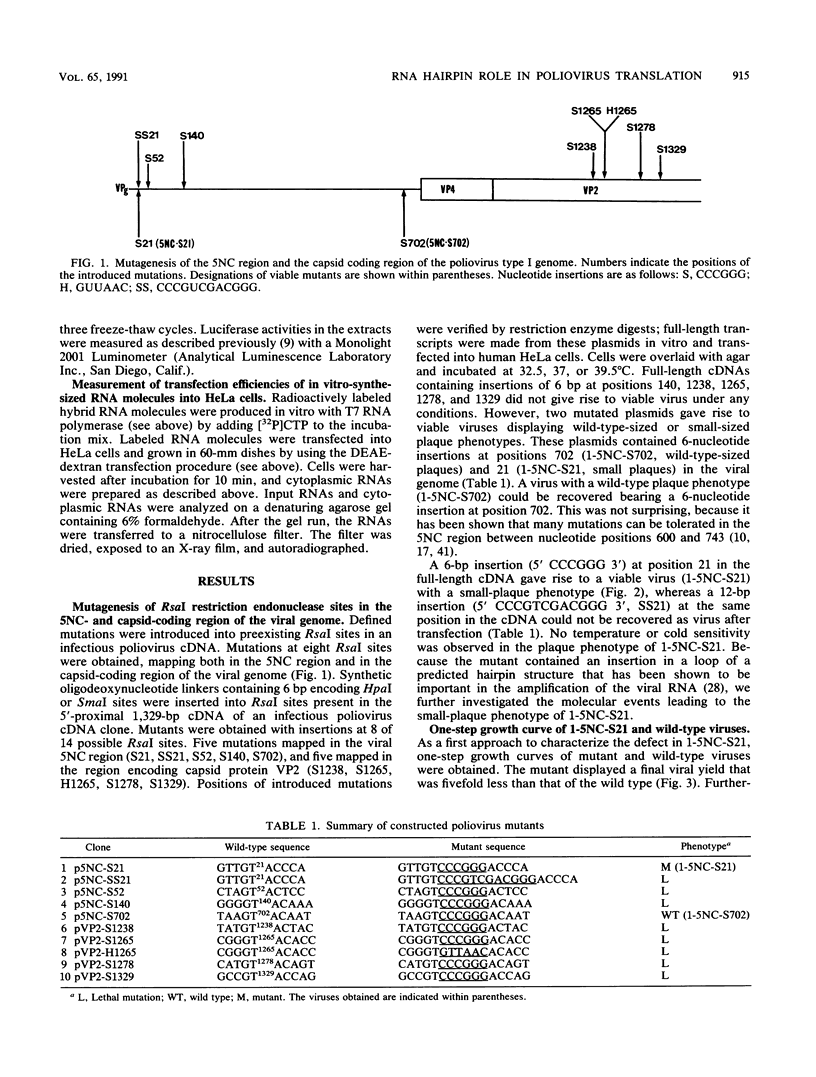
Several mutations were introduced into an infectious poliovirus cDNA clone by inserting different oligodeoxynucleotide linkers into preexisting DNA restriction endonuclease sites in the viral cDNA. Ten mutated DNAs were constructed whose lesions mapped in the 5' noncoding region or in the capsid coding region of the viral genome. Eight of these mutated cDNAs did not give rise to infectious virus upon transfection into human cells, one yielded virus with a wild-type phenotype, and one gave rise to a viral mutant with a small-plaque phenotype. This last mutant, designated 1-5NC-S21, bears a 6-nucleotide insertion in the loop of a stable RNA hairpin at the very 5' end of the viral genome. Detailed analysis of the biological properties of 1-5NC-S21 showed that the primary defect in mutant-infected cells is a fivefold decrease in translation relative to wild-type-infected cells. Transfection into HeLa cells of in vitro-synthesized RNA molecules bearing either the 5' noncoding region of 1-5NC-S21 or wild-type poliovirus upstream of a luciferase reporter gene showed that the mutated RNA hairpin was responsible for the observed decrease in viral translation in mutant-infected cells and conferred this defect to heterologous RNAs. These findings indicate that an RNA hairpin located at the extreme 5' end of the viral RNA and highly conserved among enteroviruses and rhinoviruses profoundly affects the translation efficiency of poliovirus RNA in infected cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein H. D., Sarnow P., Baltimore D. Genetic complementation among poliovirus mutants derived from an infectious cDNA clone. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1040-1049.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that does not selectively inhibit host cell protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2913–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienkowska-Szewczyk K., Ehrenfeld E. An internal 5'-noncoding region required for translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):3068–3072. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.3068-3072.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Digard P., Inglis S. C. Characterization of an efficient coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal: requirement for an RNA pseudoknot. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90124-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey J., Cameron V., de Haseth P. L., Uhlenbeck O. C. Sequence-specific interaction of R17 coat protein with its ribonucleic acid binding site. Biochemistry. 1983 May 24;22(11):2601–2610. doi: 10.1021/bi00280a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dildine S. L., Semler B. L. The deletion of 41 proximal nucleotides reverts a poliovirus mutant containing a temperature-sensitive lesion in the 5' noncoding region of genomic RNA. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):847–862. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.847-862.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Milburn S. C., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Hershey J. W. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis following poliovirus infection correlates with the proteolysis of a 220,000-dalton polypeptide associated with eucaryotic initiation factor 3 and a cap binding protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14806–14810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELLERT M., SMITH C. E., NEVILLE D., FELSENFELD G. ACTINOMYCIN BINDING TO DNA: MECHANISM AND SPECIFICITY. J Mol Biol. 1965 Mar;11:445–457. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M. W., Rouault T. A., Caughman S. W., Dancis A., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. A cis-acting element is necessary and sufficient for translational regulation of human ferritin expression in response to iron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6730–6734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influences of mRNA secondary structure on initiation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Toyoda H., Etchison D., Wimmer E. Poliovirus proteinase 2A induces cleavage of eucaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide p220. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2711–2718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2711-2718.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuge S., Nomoto A. Construction of viable deletion and insertion mutants of the Sabin strain of type 1 poliovirus: function of the 5' noncoding sequence in viral replication. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1478–1487. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1478-1487.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen G. R., Semler B. L., Wimmer E. Stable hairpin structure within the 5'-terminal 85 nucleotides of poliovirus RNA. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):328–335. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.328-335.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najita L., Sarnow P. Oxidation-reduction sensitive interaction of a cellular 50-kDa protein with an RNA hairpin in the 5' noncoding region of the poliovirus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5846–5850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Insertion mutagenesis to increase secondary structure within the 5' noncoding region of a eukaryotic mRNA reduces translational efficiency. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):515–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):320–325. doi: 10.1038/334320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilipenko E. V., Blinov V. M., Romanova L. I., Sinyakov A. N., Maslova S. V., Agol V. I. Conserved structural domains in the 5'-untranslated region of picornaviral genomes: an analysis of the segment controlling translation and neurovirulence. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Cloned poliovirus complementary DNA is infectious in mammalian cells. Science. 1981 Nov 20;214(4523):916–919. doi: 10.1126/science.6272391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Molecular cloning of poliovirus cDNA and determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Meriam C. Poliovirus temperature-sensitive mutant containing a single nucleotide deletion in the 5'-noncoding region of the viral RNA. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):498–507. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera V. M., Welsh J. D., Maizel J. V., Jr Comparative sequence analysis of the 5' noncoding region of the enteroviruses and rhinoviruses. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):42–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90656-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouault T. A., Hentze M. W., Caughman S. W., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Binding of a cytosolic protein to the iron-responsive element of human ferritin messenger RNA. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1207–1210. doi: 10.1126/science.3413484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Bernstein H. D., Baltimore D. A poliovirus temperature-sensitive RNA synthesis mutant located in a noncoding region of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):571–575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Jacobson S. J., Najita L. Poliovirus genetics. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;161:155–188. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75602-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P. Role of 3'-end sequences in infectivity of poliovirus transcripts made in vitro. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):467–470. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.467-470.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P. Translation of glucose-regulated protein 78/immunoglobulin heavy-chain binding protein mRNA is increased in poliovirus-infected cells at a time when cap-dependent translation of cellular mRNAs is inhibited. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5795–5799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. A., Racaniello V. R., Dunn G., Cooper J., Minor P. D., Almond J. W. New model for the secondary structure of the 5' non-coding RNA of poliovirus is supported by biochemical and genetic data that also show that RNA secondary structure is important in neurovirulence. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):379–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90261-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobell H. M. The stereochemistry of actinomycin binding to DNA and its implications in molecular biology. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1973;13:153–190. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60103-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Regulation of translation by poliovirus. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:175–204. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. K., Draper D. E. Unusual mRNA pseudoknot structure is recognized by a protein translational repressor. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):531–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Kohara M., Kataoka Y., Suganuma T., Omata T., Imura N., Nomoto A. Complete nucleotide sequences of all three poliovirus serotype genomes. Implication for genetic relationship, gene function and antigenic determinants. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):561–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D., Andino R., Baltimore D. An RNA sequence of hundreds of nucleotides at the 5' end of poliovirus RNA is involved in allowing viral protein synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2291–2299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2291-2299.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D., Pelletier J., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Translation in mammalian cells of a gene linked to the poliovirus 5' noncoding region. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):445–448. doi: 10.1126/science.2839901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walden W. E., Patino M. M., Gaffield L. Purification of a specific repressor of ferritin mRNA translation from rabbit liver. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13765–13769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Bradley J., Wimmer E., Studier F. W., Dunn J. J. Synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA by purified T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






