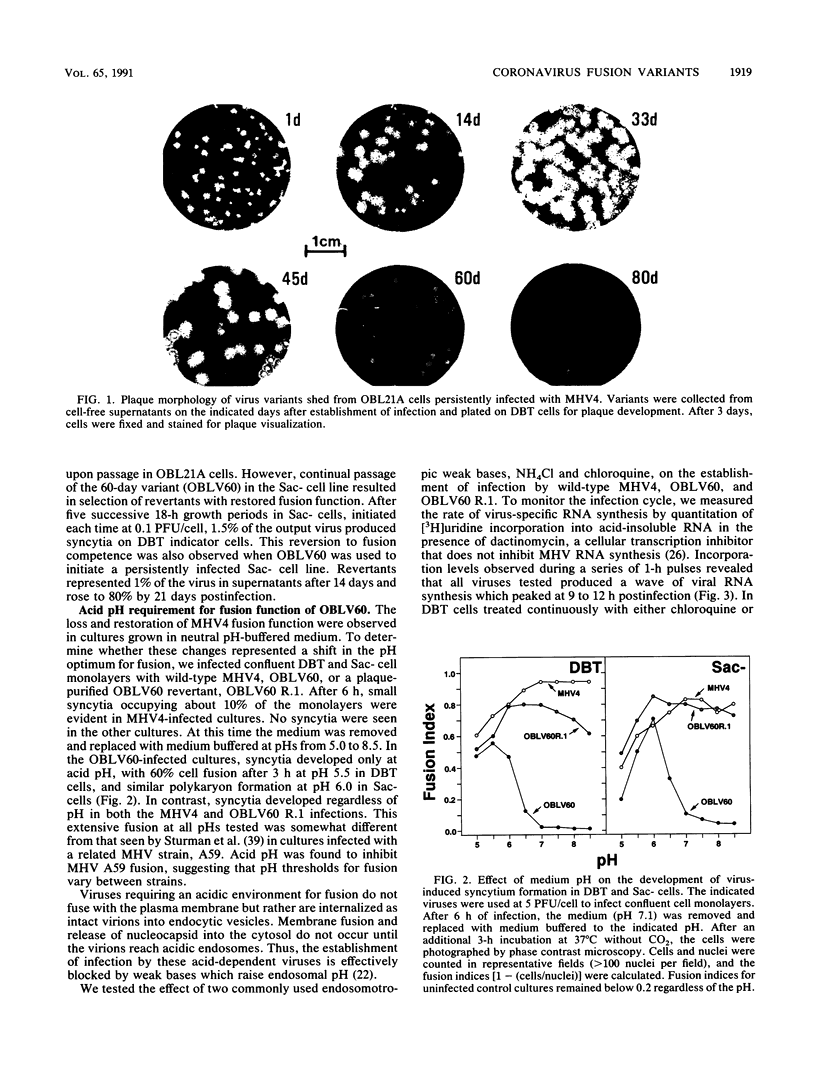
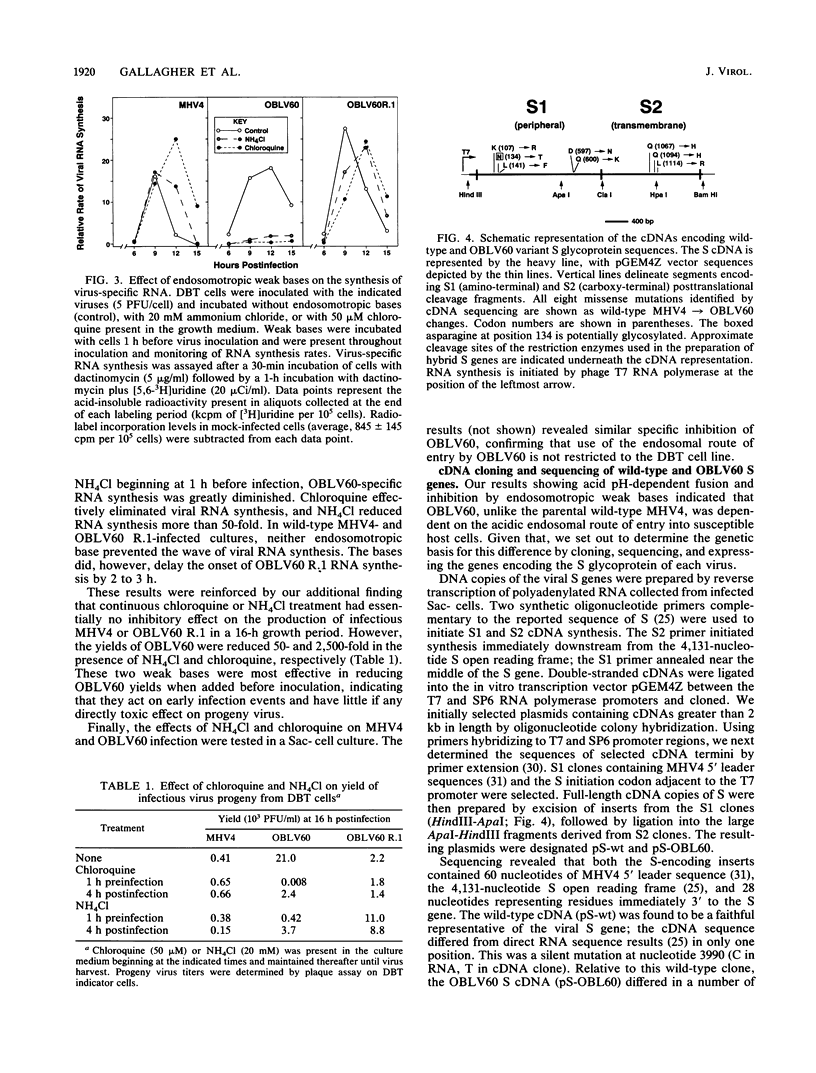
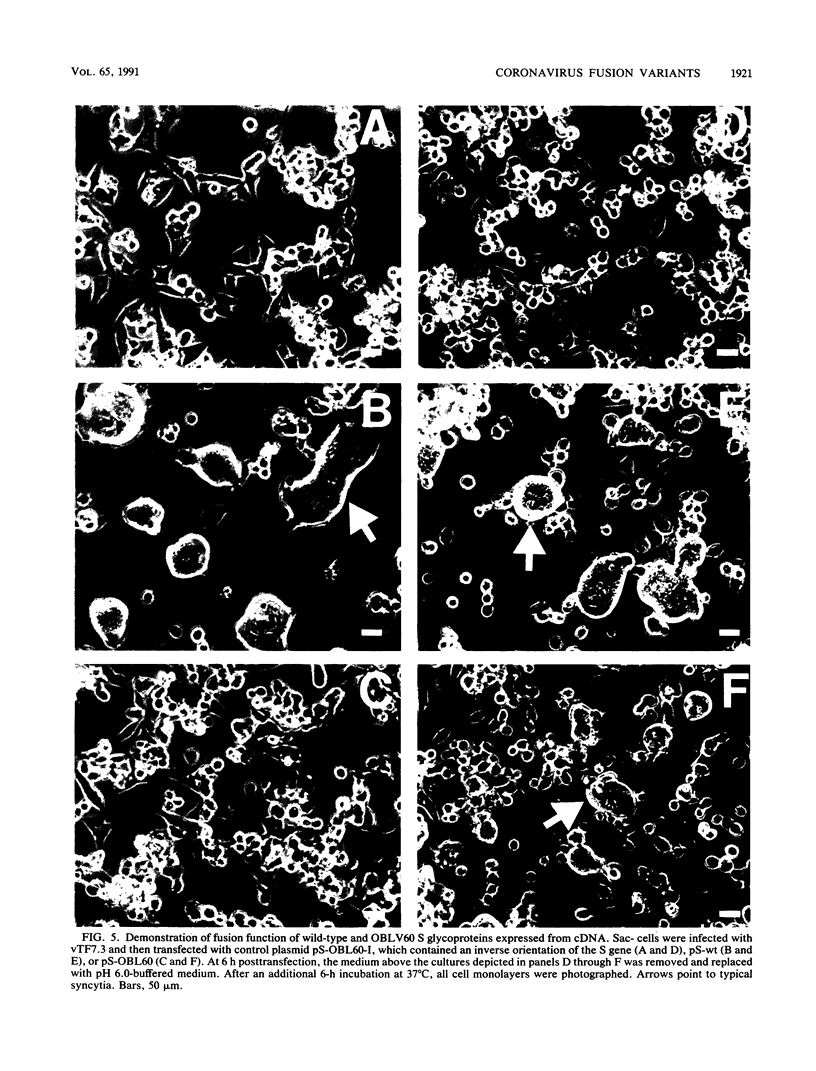
Abstract
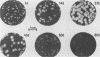
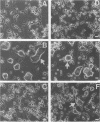
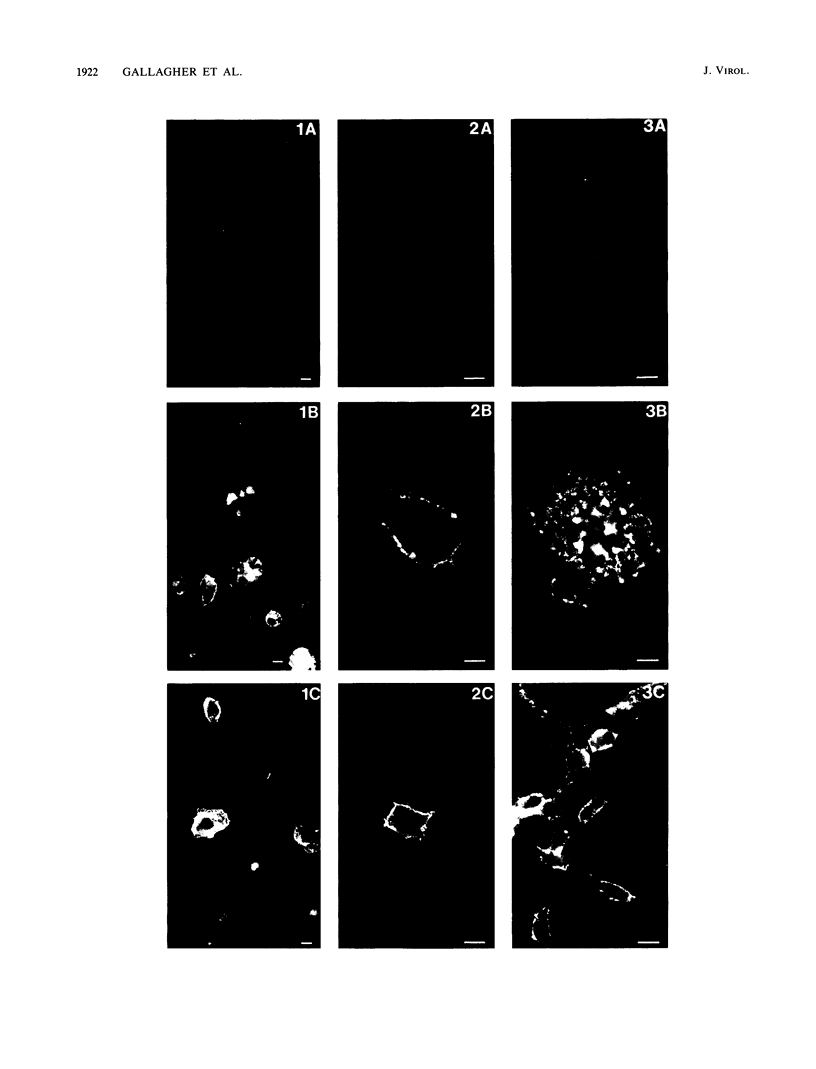
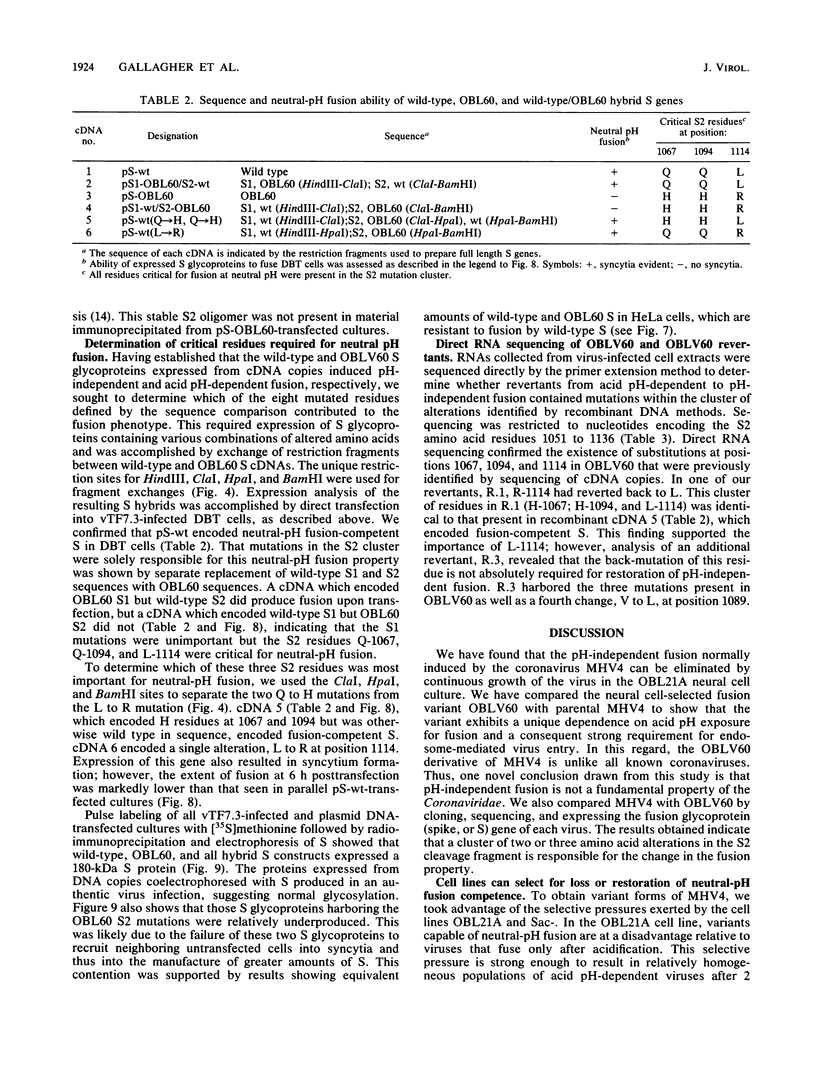
Infection of susceptible murine cells with the coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus type 4 (MHV4) results in extensive cell-cell fusion at pHs from 5.5 to 8.5. The endosomotropic weak bases chloroquine and ammonium chloride do not prevent MHV4 infection. In marked contrast, we have selected variants from a neural cell line persistently infected with MHV4 which are entirely dependent on acid pH to fuse host cells and are strongly inhibited by endosomotropic weak bases. Wild-type and variant viruses were compared at the level of the fusion-active surface (S) glycoprotein gene. Cloning and sequencing of each 4,131-base open reading frame predicted a total of eight amino acid differences which fell into three distinct clusters. Each S glycoprotein, when expressed from cDNA, was synthesized in equivalent amounts, and similar proportions were transported to the cell surface. Wild-type S induced cell-cell fusion at neutral pH, whereas variant S required prolonged exposure to acidic pH to induce fusion. Expression of hybrid S genes prepared by exchange of restriction fragments between wild-type and variant cDNAs revealed that elimination of neutral pH fusion was solely dependent on amino acid alterations at positions 1067 (Q to H), 1094 (Q to H), and 1114 (L to R). These changes lie within a predicted heptad repeat region of the transmembrane cleavage fragment of S (S2). These findings demonstrate that the pH dependence of coronavirus fusion is highly variable and that this variability can be determined by as few as three amino acid residues.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baybutt H. N., Wege H., Carter M. J., ter Meulen V. Adaptation of coronavirus JHM to persistent infection of murine sac(-) cells. J Gen Virol. 1984 May;65(Pt 5):915–924. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-5-915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle J. F., Weismiller D. G., Holmes K. V. Genetic resistance to mouse hepatitis virus correlates with absence of virus-binding activity on target tissues. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):185–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.185-189.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh D. Coronavirus IBV: structural characterization of the spike protein. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2577–2583. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daya M., Cervin M., Anderson R. Cholesterol enhances mouse hepatitis virus-mediated cell fusion. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):276–283. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90267-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmas B., Laude H. Assembly of coronavirus spike protein into trimers and its role in epitope expression. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5367–5375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5367-5375.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Helenius A., White J. Membrane fusion activity of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. The low pH-induced conformational change. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2973–2981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Rothman J. E. Compartmental organization of the Golgi stack. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frana M. F., Behnke J. N., Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V. Proteolytic cleavage of the E2 glycoprotein of murine coronavirus: host-dependent differences in proteolytic cleavage and cell fusion. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):912–920. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.912-920.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher T. M., Parker S. E., Buchmeier M. J. Neutralization-resistant variants of a neurotropic coronavirus are generated by deletions within the amino-terminal half of the spike glycoprotein. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):731–741. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.731-741.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano N., Goto N., Makino S., Fujiwara K. Persistent infection with mouse hepatitis virus, JHM strain in DBT cell culture. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;142:301–308. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0456-3_24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano N., Murakami T., Fujiwara K., Matsumoto M. Utility of mouse cell line DBT for propagation and assay of mouse hepatitis virus. Jpn J Exp Med. 1978 Feb;48(1):71–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Cell membrane antigen isolation with the staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1482–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Virus entry into animal cells. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:107–151. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60583-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizzen L., Hilton A., Cheley S., Anderson R. Attenuation of murine coronavirus infection by ammonium chloride. Virology. 1985 Apr 30;142(2):378–388. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90345-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemann H., Boschek B., Evans D., Rosing M., Tamura T., Klenk H. D. Post-translational glycosylation of coronavirus glycoprotein E1: inhibition by monensin. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1499–1504. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01346.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker S. E., Gallagher T. M., Buchmeier M. J. Sequence analysis reveals extensive polymorphism and evidence of deletions within the E2 glycoprotein gene of several strains of murine hepatitis virus. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):664–673. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90579-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos D. S., Duchala C. S., Stephensen C. B., Holmes K. V., Choppin P. W. Control of virus-induced cell fusion by host cell lipid composition. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):345–357. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90419-R. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder E. F., Snyder E. Y., Cepko C. L. Establishment and characterization of multipotent neural cell lines using retrovirus vector-mediated oncogene transfer. J Neurobiol. 1990 Mar;21(2):356–375. doi: 10.1002/neu.480210209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh C. K., Soe L. H., Makino S., Chang M. F., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. The 5'-end sequence of the murine coronavirus genome: implications for multiple fusion sites in leader-primed transcription. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90412-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Bayley P. M., Brown E. B., Martin S. R., Waterfield M. D., White J. M., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. Changes in the conformation of influenza virus hemagglutinin at the pH optimum of virus-mediated membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W., Cavanagh D., Horzinek M. C. Coronaviruses: structure and genome expression. J Gen Virol. 1988 Dec;69(Pt 12):2939–2952. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-12-2939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Doms R. W., Helenius A. Protein-mediated membrane fusion. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:187–211. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhauer D. A., Holland J. J. Rapid evolution of RNA viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:409–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Brayton P. R., Fleming J. O., Weiner L. P., Lai M. M. Murine coronaviruses: isolation and characterization of two plaque morphology variants of the JHM neurotropic strain. J Gen Virol. 1982 Dec;63(2):265–275. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-63-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V., Behnke J. Isolation of coronavirus envelope glycoproteins and interaction with the viral nucleocapsid. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):449–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.449-462.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Ricard C. S., Holmes K. V. Conformational change of the coronavirus peplomer glycoprotein at pH 8.0 and 37 degrees C correlates with virus aggregation and virus-induced cell fusion. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3042–3050. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3042-3050.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Ricard C. S., Holmes K. V. Proteolytic cleavage of the E2 glycoprotein of murine coronavirus: activation of cell-fusing activity of virions by trypsin and separation of two different 90K cleavage fragments. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):904–911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.904-911.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot P. J., Salmi A. A., Knobler R. L., Buchmeier M. J. Topographical mapping of epitopes on the glycoproteins of murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM): correlation with biological activities. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):250–260. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90032-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze S. A., Tooze J., Warren G. Site of addition of N-acetyl-galactosamine to the E1 glycoprotein of mouse hepatitis virus-A59. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1475–1487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennema H., Heijnen L., Zijderveld A., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. Intracellular transport of recombinant coronavirus spike proteins: implications for virus assembly. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):339–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.339-346.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland E., Mussgay M., Weiland F. Nonproducer malignant tumor cells with rescuable sarcoma virus genome isolated from a recurrent Moloney sarcoma. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):408–423. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M. Viral and cellular membrane fusion proteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:675–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M., Wilson I. A. Anti-peptide antibodies detect steps in a protein conformational change: low-pH activation of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 2):2887–2896. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. J., Luytjes W., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A., Spaan W. J., Lenstra J. A. Evidence for a coiled-coil structure in the spike proteins of coronaviruses. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):963–966. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90422-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]