Abstract
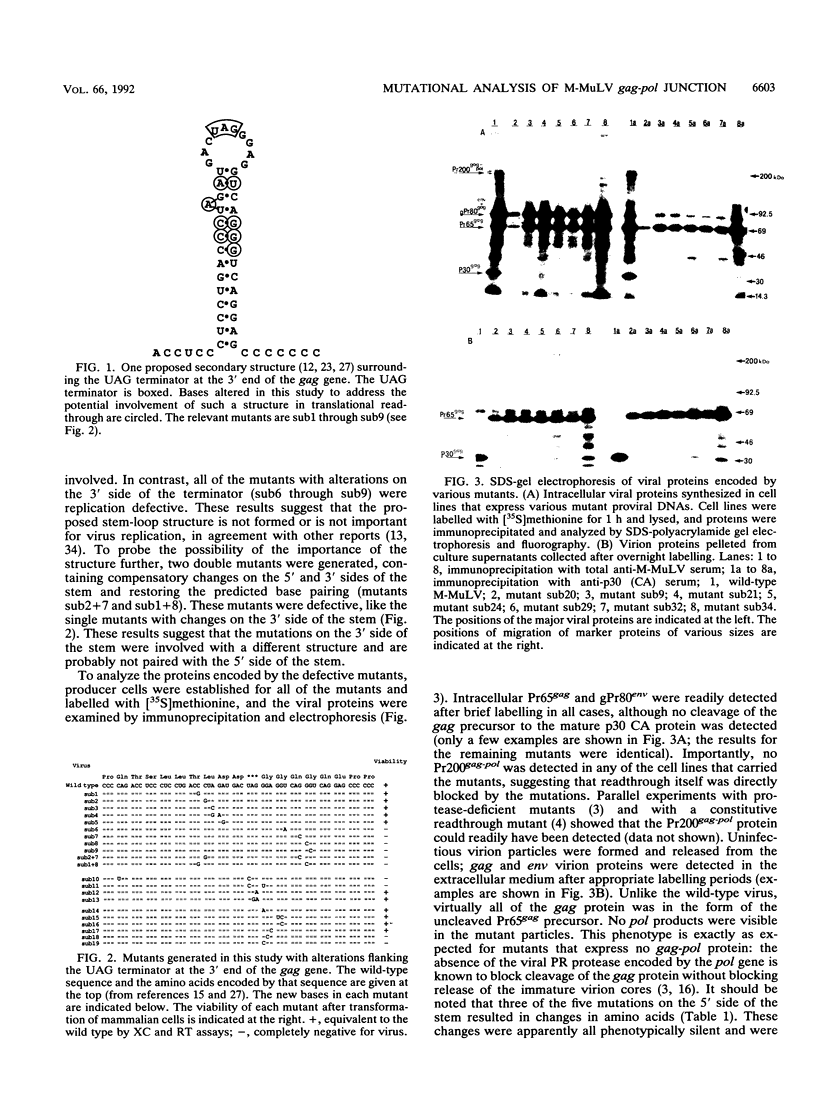
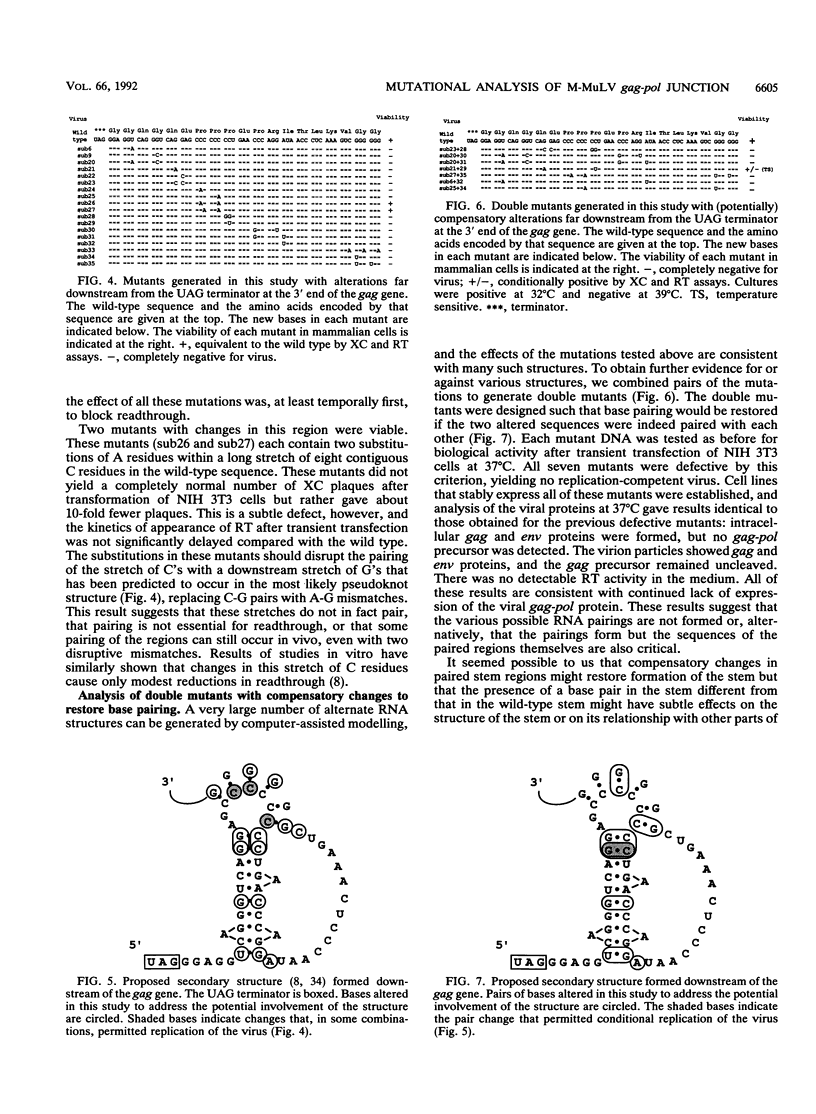
The gag-pol polyprotein of the murine and feline leukemia viruses is expressed by translational readthrough of a UAG terminator codon at the 3' end of the gag gene. To explore the cis-acting sequence requirements for the readthrough event in vivo, we generated a library of mutants of the Moloney murine leukemia virus with point mutations near the terminator codon and tested the mutant viral DNAs for the ability to direct synthesis of the gag-pol fusion protein and formation of infectious virus. The analysis showed that sequences 3' to the terminator are necessary and sufficient for the process. The results do not support a role for one proposed stem-loop structure that includes the terminator but are consistent with the involvement of another stem-loop 3' to the terminator. One mutant, containing two compensatory changes in this stem structure, was temperature sensitive for replication and for formation of the gag-pol protein. The results suggest that RNA sequence and structure are critical determinants of translational readthrough in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bossi L. Context effects: translation of UAG codon by suppressor tRNA is affected by the sequence following UAG in the message. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 15;164(1):73–87. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Sequence and spacing requirements of a retrovirus integration site. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90378-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford S., Goff S. P. A deletion mutation in the 5' part of the pol gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus blocks proteolytic processing of the gag and pol polyproteins. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):899–907. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.899-907.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein K. M., Goff S. P. Expression of the gag-pol fusion protein of Moloney murine leukemia virus without gag protein does not induce virion formation or proteolytic processing. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2179–2182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2179-2182.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Y. X., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S., Rein A., Levin J. G. Identification of amino acids inserted during suppression of UAA and UGA termination codons at the gag-pol junction of Moloney murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8860–8863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Y. X., Hatfield D. L., Rein A., Levin J. G. Translational readthrough of the murine leukemia virus gag gene amber codon does not require virus-induced alteration of tRNA. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2405–2410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2405-2410.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Y. X., Levin J. G., Hatfield D. L., Schaefer T. S., Gorelick R. J., Rein A. Suppression of UAA and UGA termination codons in mutant murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2870–2873. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2870-2873.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Y. X., Yuan H., Rein A., Levin J. G. Bipartite signal for read-through suppression in murine leukemia virus mRNA: an eight-nucleotide purine-rich sequence immediately downstream of the gag termination codon followed by an RNA pseudoknot. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5127–5132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5127-5132.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S., Traktman P., Baltimore D. Isolation and properties of Moloney murine leukemia virus mutants: use of a rapid assay for release of virion reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):239–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.239-248.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield D. L., Levin J. G., Rein A., Oroszlan S. Translational suppression in retroviral gene expression. Adv Virus Res. 1992;41:193–239. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60037-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W. Nucleotide sequence of AKV murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):471–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.471-478.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honigman A., Wolf D., Yaish S., Falk H., Panet A. cis Acting RNA sequences control the gag-pol translation readthrough in murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90144-Z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. Translational suppression in gene expression in retroviruses and retrotransposons. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;157:93–124. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75218-6_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. S., Nemoto F., Kuchino Y., Masuda M., Yoshikura H., Nishimura S. The effect of specific mutations at and around the gag-pol gene junction of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):5933–5945. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.5933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh I., Yoshinaka Y., Rein A., Shibuya M., Odaka T., Oroszlan S. Murine leukemia virus maturation: protease region required for conversion from "immature" to "mature" core form and for virus infectivity. Virology. 1985 Sep;145(2):280–292. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90161-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchino Y., Beier H., Akita N., Nishimura S. Natural UAG suppressor glutamine tRNA is elevated in mouse cells infected with Moloney murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2668–2672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E. C., Jr, Kopchick J. J., Watson K. F., Arlinghaus R. B. Cell-free synthesis of a precursor polyprotein containing both gag and pol gene products by Rauscher murine leukemia virus 35S RNA. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):359–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90204-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E. C., Jr, Wills N., Arlinghaus R. B. Suppression of murine retrovirus polypeptide termination: effect of amber suppressor tRNA on the cell-free translation of Rauscher murine leukemia virus, Moloney murine leukemia virus, and Moloney murine sarcoma virus 124 RNA. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):464–473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.464-473.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T. Retroviral gag gene amber codon suppression is caused by an intrinsic cis-acting component of the viral mRNA. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3574–3580. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3574-3580.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L., Andersson P., Olshevsky U., Weinberg R., Baltimore D., Gesteland R. Translation of MuLV and MSV RNAs in nuclease-treated reticulocyte extracts: enhancement of the gag-pol polypeptide with yeast suppressor tRNA. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):189–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Roth M. J., Goff S. P. Analysis of retroviral pol gene products with antisera raised against fusion proteins produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):328–340. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.328-340.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Weber K. Natural read-through at the UGA termination signal of Q-beta coat protein cistron. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 15;234(50):206–209. doi: 10.1038/newbio234206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills N. M., Gesteland R. F., Atkins J. F. Evidence that a downstream pseudoknot is required for translational read-through of the Moloney murine leukemia virus gag stop codon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6991–6995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. N., Uhlenbeck O. C. Role of a bulged A residue in a specific RNA-protein interaction. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8221–8227. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaka Y., Katoh I., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S. Murine leukemia virus protease is encoded by the gag-pol gene and is synthesized through suppression of an amber termination codon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1618–1622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Dam E. B., Pleij C. W., Bosch L. RNA pseudoknots: translational frameshifting and readthrough on viral RNAs. Virus Genes. 1990 Jul;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00678404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]