Abstract
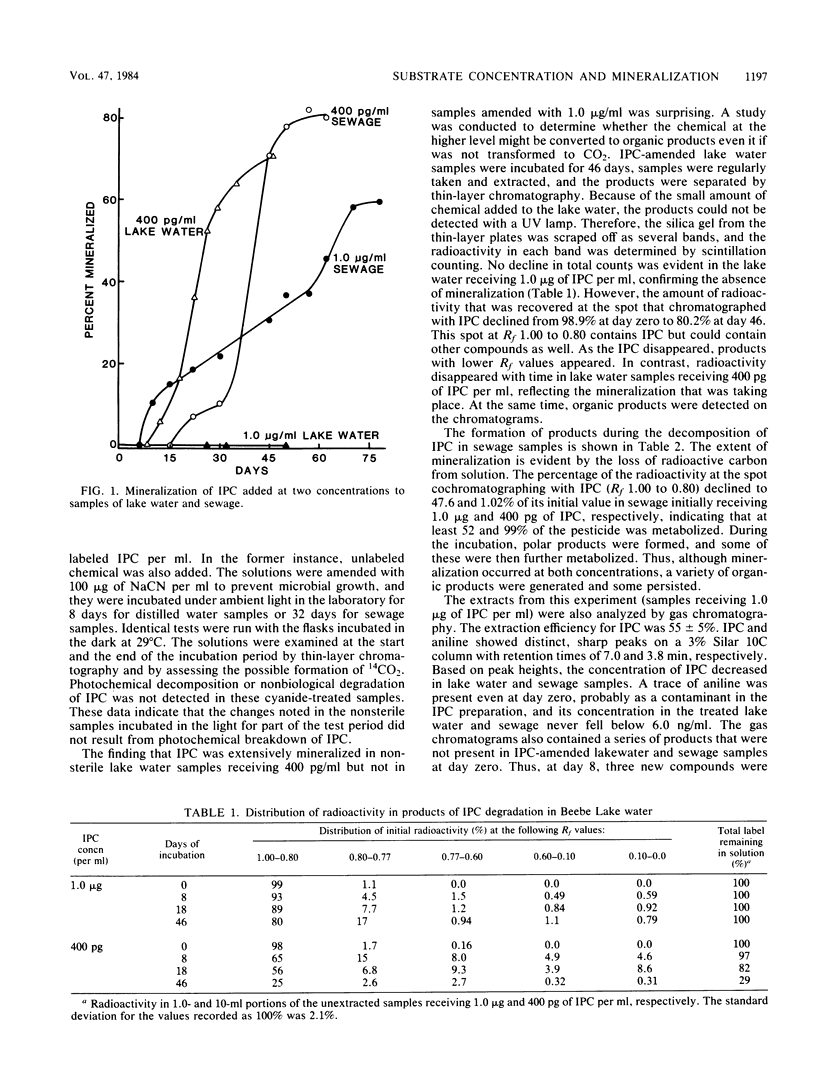
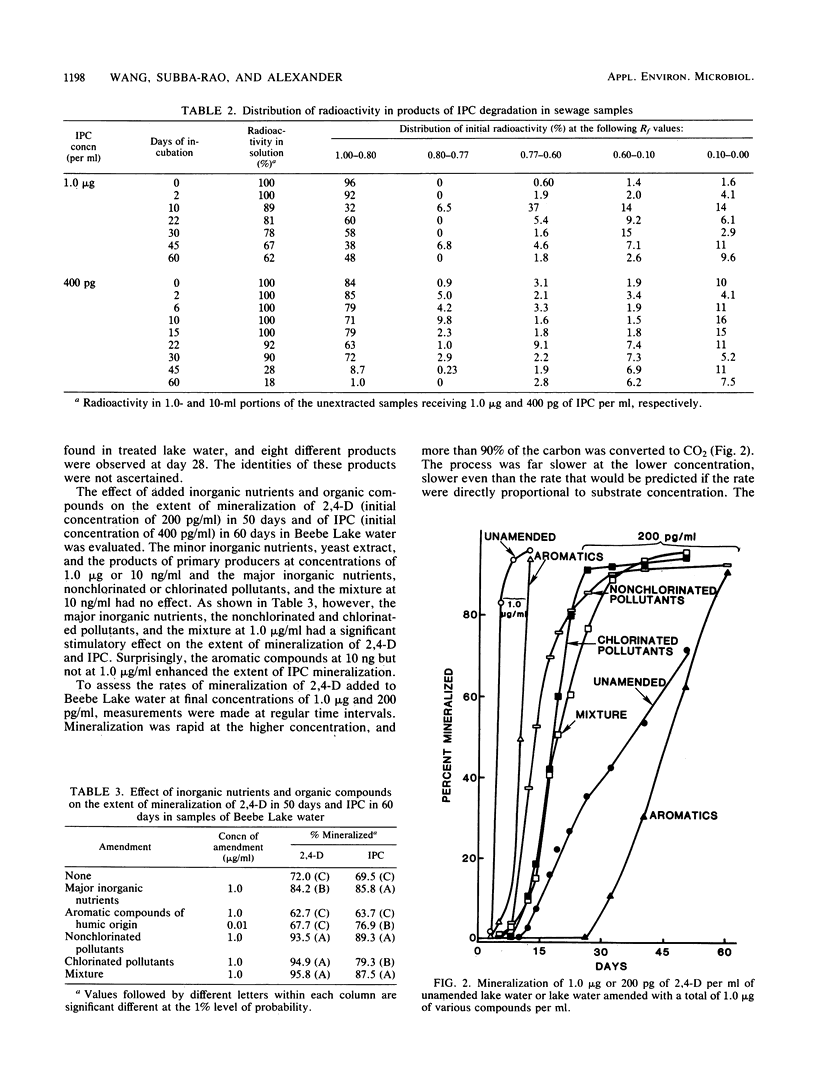
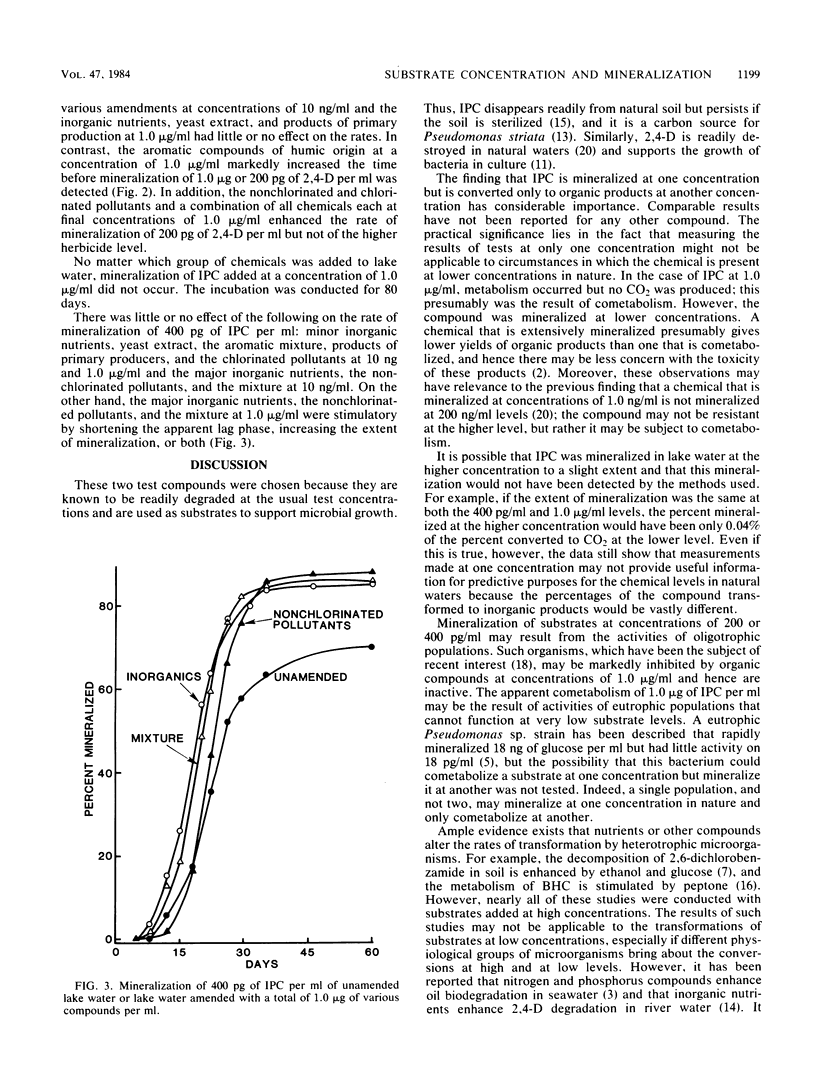
Isopropyl N-phenylcarbamate (IPC) at 400 pg and 1 μg/ml was mineralized in samples of sewage, but only the lower concentration was mineralized in lake water samples in a 50-day period. IPC at 1 μg/ml disappeared from lake water, but it was converted to organic products. Mineralization of IPC at 400 pg/ml in lake water was enhanced by additions of inorganic nutrients or a mixture of nonchlorinated water pollutants but not by yeast extract or mixtures containing aromatic compounds or excretions of primary producers. The mineralization of 200 pg of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate per ml of lake water was not affected by additions of low levels of yeast extract or compounds excreted by primary producers but was enhanced by low concentrations of mixtures of water pollutants. It is suggested that some chemicals that are found to be converted only to organic products, presumably by cometabolism, in tests using the concentrations commonly employed in laboratory evaluations may be mineralized at the lower concentrations prevailing in natural waters.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M. Biodegradation of chemicals of environmental concern. Science. 1981 Jan 9;211(4478):132–138. doi: 10.1126/science.7444456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boethling R. S., Alexander M. Effect of concentration of organic chemicals on their biodegradation by natural microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1211–1216. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1211-1216.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hites R. A., Biemann K. Water pollution: organic compounds in the Charles River, Boston. Science. 1972 Oct 13;178(4057):158–160. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4057.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEADBETTER E. R., FOSTER J. W. Studies on some methane-utilizing bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1958;30(1):91–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00509229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H. E., Subba-Rao R. V., Alexander M. Rates of mineralization of trace concentrations of aromatic compounds in lake water and sewage samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1133–1138. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1133-1138.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subba-Rao R. V., Rubin H. E., Alexander M. Kinetics and extent of mineralization of organic chemicals at trace levels in freshwater and sewage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1139–1150. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1139-1150.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


