Abstract
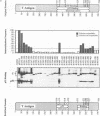
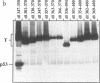
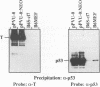
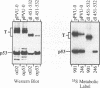
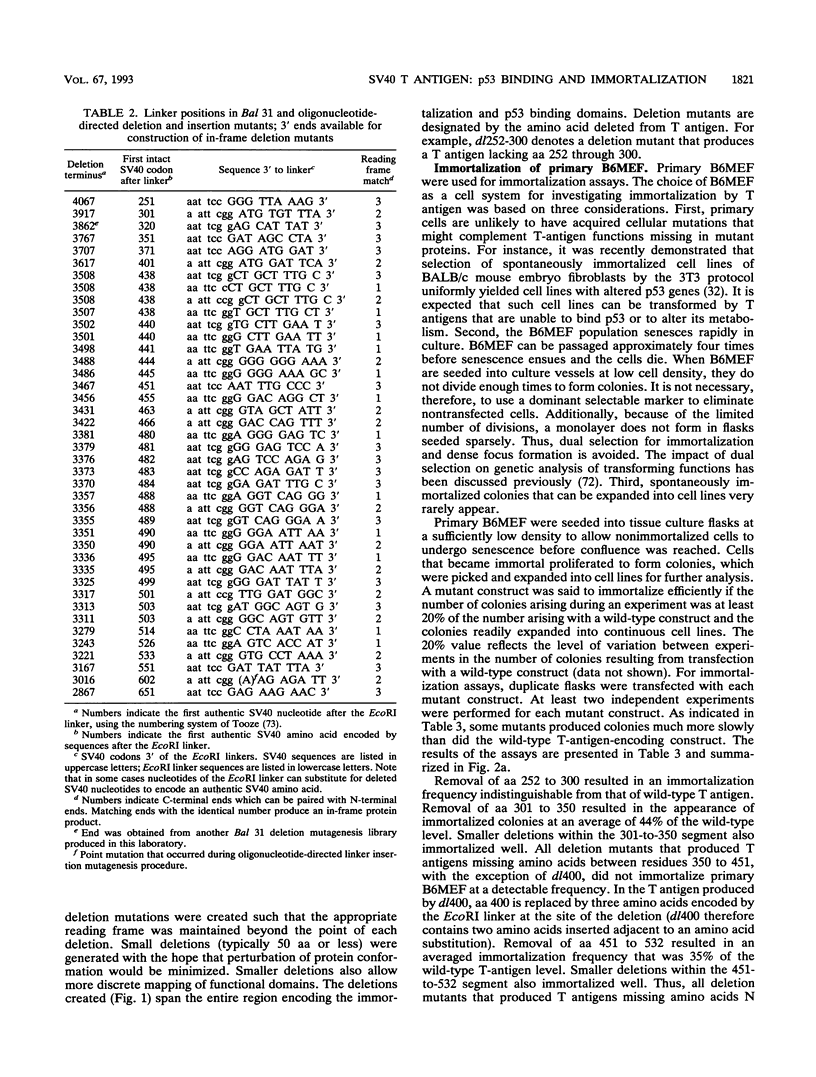
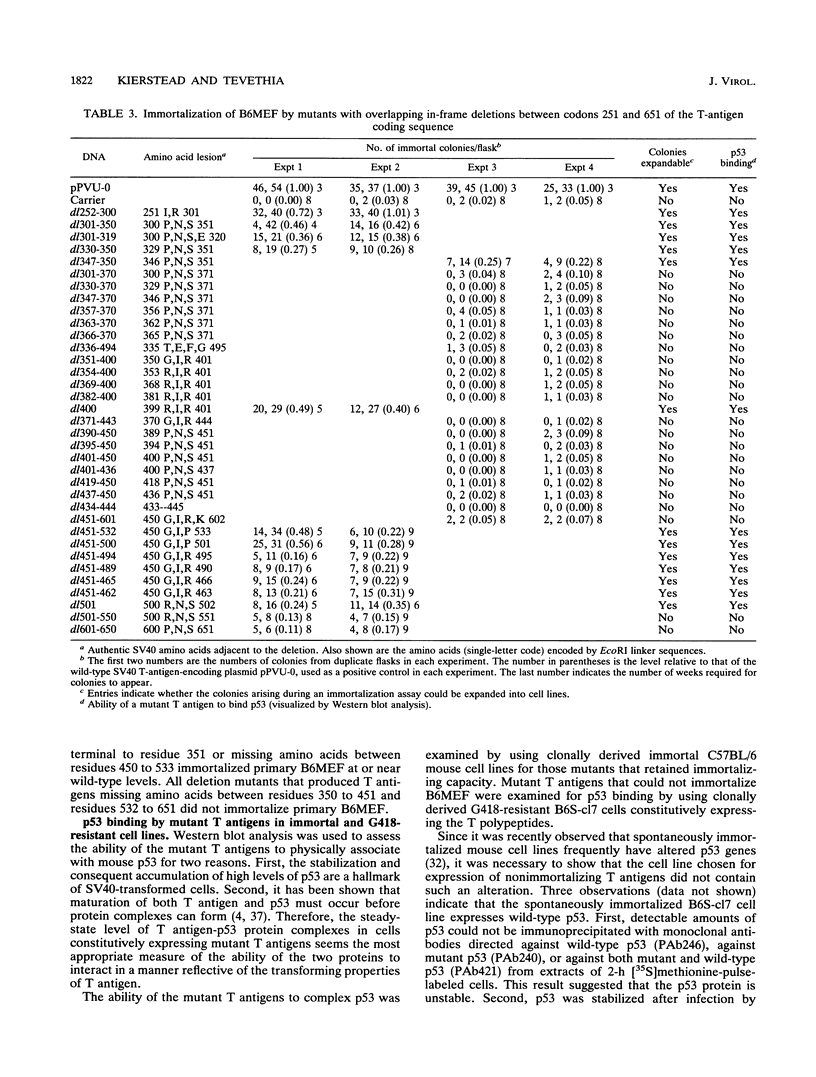
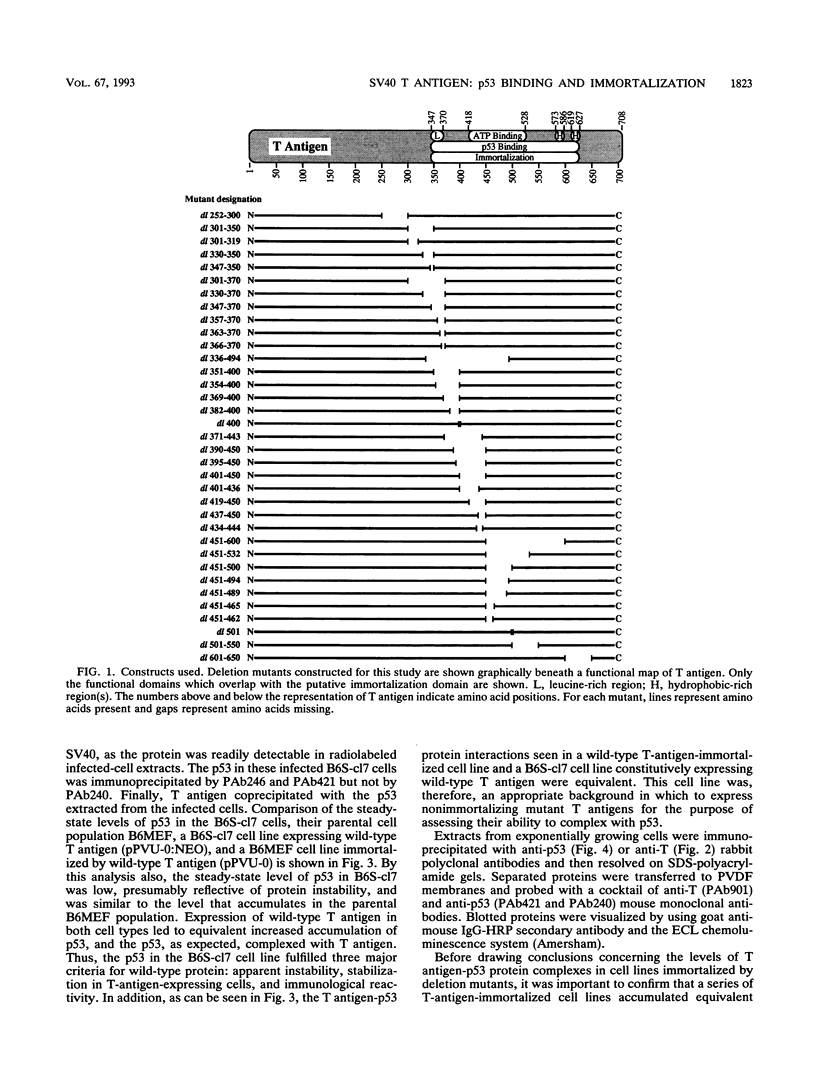
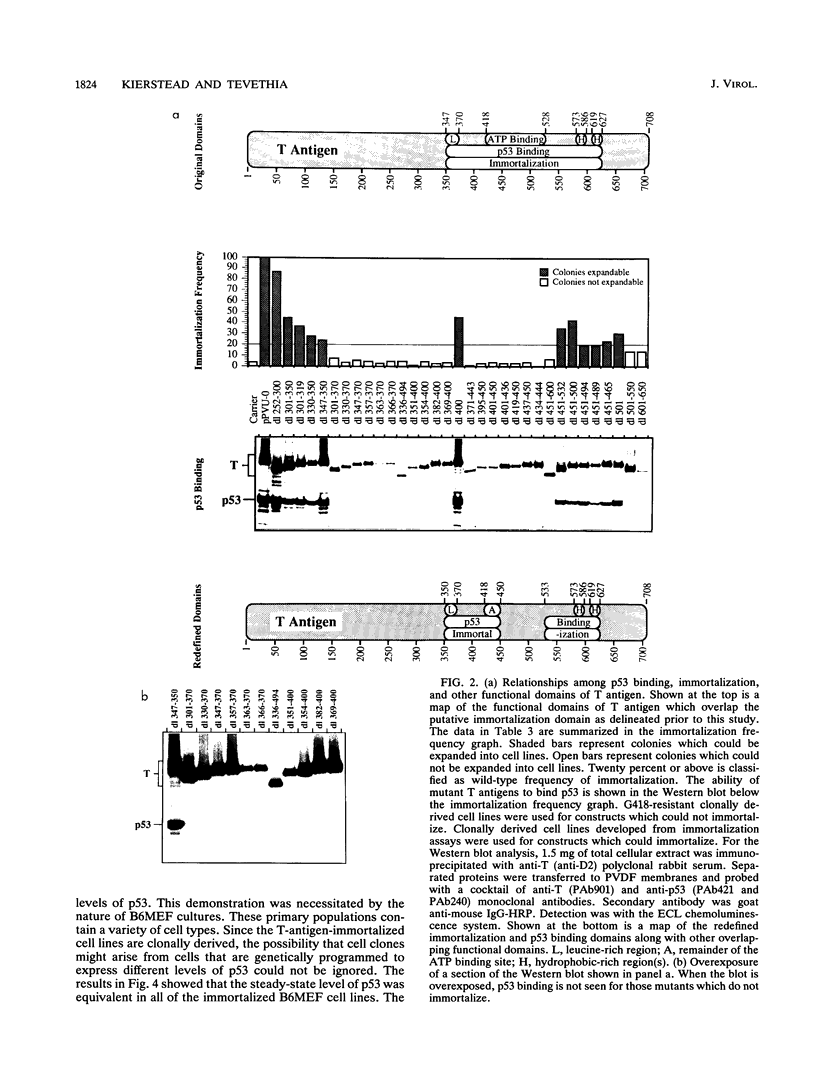
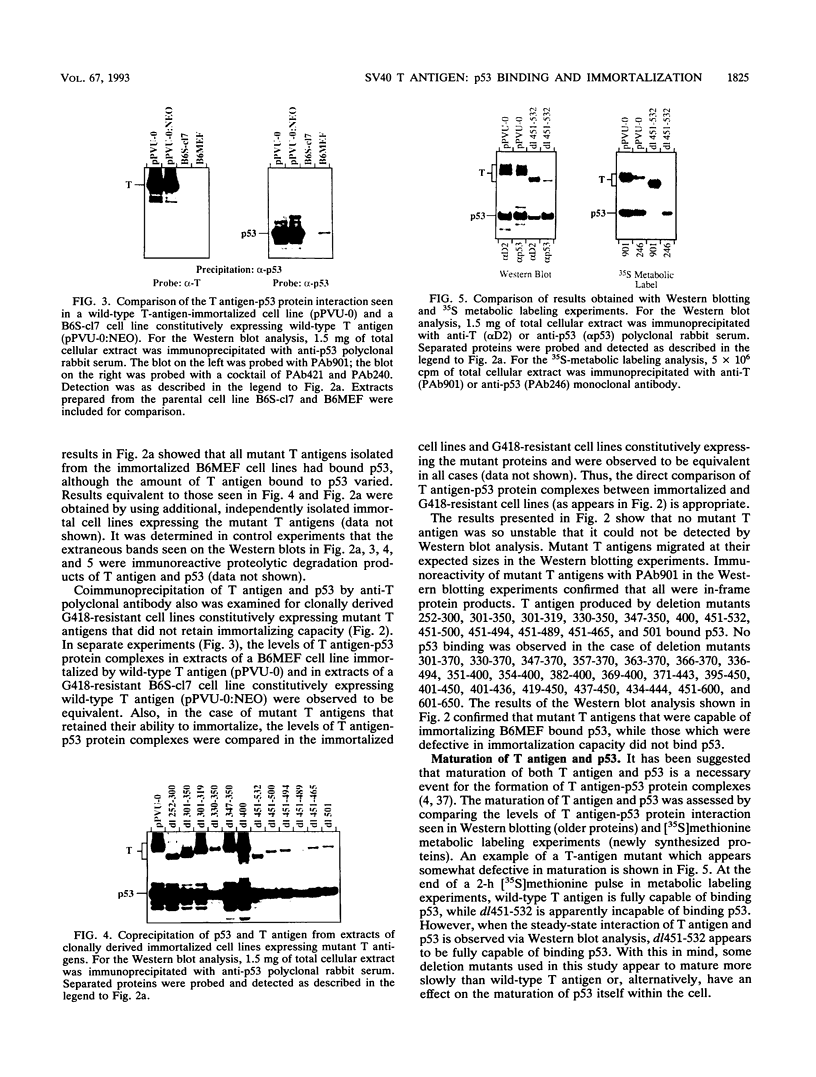
To more precisely map the immortalization and p53 binding domains of T antigen, a large series of overlapping deletion mutations were created between codons 251 to 651 by utilizing a combination of Bal 31 deletion and oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Immortalization assay results indicated that amino acids (aa) 252 to 350, 400, and 451 to 532 could be removed without seriously compromising immortalization, although the appearance of immortal colonies was delayed in some cases. Western immunoblotting experiments indicated that the p53 binding capacities of T antigen produced by mutants missing aa 252 to 300, 301 to 350, 400, or 451 to 532 were only slightly reduced relative to that of wild-type T antigen. Within the limits of this deletion analysis, the immortalization and p53 binding domains appear to be colinear and, in fact, may represent two aspects of the same domain. This deletion analysis eliminates the entire zinc finger domain (aa 302 to 320), a small portion of the leucine-rich region (aa 345 to 350), and a large portion of the ATP binding domain (aa 451 to 528) as participants in p53 binding or in the immortalization process. The results also show that removal of T antigen amino acids within the region 451 to 532 appears to alter the capacity of newly synthesized but not older T antigen and p53 molecules to form complexes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthur A. K., Höss A., Fanning E. Expression of simian virus 40 T antigen in Escherichia coli: localization of T-antigen origin DNA-binding domain to within 129 amino acids. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1999–2006. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1999-2006.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselin C., Bastin M. Sequences from polyomavirus and simian virus 40 large T genes capable of immortalizing primary rat embryo fibroblasts. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):958–968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.958-968.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley M. K., Smith T. F., Lathrop R. H., Livingston D. M., Webster T. A. Consensus topography in the ATP binding site of the simian virus 40 and polyomavirus large tumor antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4026–4030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. B., Gurney E. G. Time-dependent maturation of the simian virus 40 large T antigen-p53 complex studied by using monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):565–573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.565-573.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S., Paucha E. Identification of a region of simian virus 40 large T antigen required for cell transformation. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3350–3357. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3350-3357.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherington V., Brown M., Paucha E., St Louis J., Spiegelman B. M., Roberts T. M. Separation of simian virus 40 large-T-antigen-transforming and origin-binding functions from the ability to block differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1380–1384. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R., Lane D. P., Tjian R. Use of monoclonal antibodies as probes of simian virus 40 T antigen ATPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11854–11858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R., Peden K., Pipas J. M., Nathans D., Tjian R. Biochemical activities of T-antigen proteins encoded by simian virus 40 A gene deletion mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):220–228. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Tornow J., Clark R., Tjian R. Properties of the simian virus 40 (SV40) large T antigens encoded by SV40 mutants with deletions in gene A. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):539–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.539-546.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Lynch D., Furukawa Y., Griffin J., Piwnica-Worms H., Huang C. M., Livingston D. M. The product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene has properties of a cell cycle regulatory element. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1085–1095. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90507-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Sal G., Manfioletti G., Schneider C. The CTAB-DNA precipitation method: a common mini-scale preparation of template DNA from phagemids, phages or plasmids suitable for sequencing. Biotechniques. 1989 May;7(5):514–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Haug M. Evidence for free and metabolically stable p53 protein in nuclear subfractions of simian virus 40-transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2233–2240. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Haug M., Steinmayer T. Modulation of p53 protein expression during cellular transformation with simian virus 40. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4453–4463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Steinmayer T., Richter W. Cooperation of SV40 large T antigen and the cellular protein p53 in maintenance of cell transformation. Oncogene. 1989 Sep;4(9):1103–1110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornreiter I., Höss A., Arthur A. K., Fanning E. SV40 T antigen binds directly to the large subunit of purified DNA polymerase alpha. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3329–3336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07533.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Buchkovich K., Whyte P., Harlow E. The cellular 107K protein that binds to adenovirus E1A also associates with the large T antigens of SV40 and JC virus. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90839-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Ludlow J. W., Marsilio E., DeCaprio J. A., Millikan R. C., Cheng S. H., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. An N-terminal transformation-governing sequence of SV40 large T antigen contributes to the binding of both p110Rb and a second cellular protein, p120. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90840-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Xing Y. G., Lawrence J. B., Livingston D. M. Molecular cloning, chromosomal mapping, and expression of the cDNA for p107, a retinoblastoma gene product-related protein. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1155–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90038-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Knippers R. Structure and function of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:55–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E. Simian virus 40 large T antigen: the puzzle, the pieces, and the emerging picture. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1289–1293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1289-1293.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Tan T. H., Eliyahu D., Oren M., Levine A. J. Activating mutations for transformation by p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc70-p53 complex with an altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., Wewerka-Lutz Y., Levine A. S., Sambrook J., Sharp P. A. Adenovirus transcription. II. RNA sequences complementary to simian virus 40 and adenovirus 2DNA in AD2+ND1- and AD2+ND3-infected cells. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):662–673. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.662-673.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flyer D. C., Burakoff S. J., Faller D. V. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte recognition of transfected cells expressing a cloned retroviral gene. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):815–818. doi: 10.1038/305815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Greaves R., Iggo R., Lane D. P. Activating mutations in p53 produce a common conformational effect. A monoclonal antibody specific for the mutant form. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1595–1602. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 and DNA polymerase alpha compete for binding to SV40 T antigen. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):456–458. doi: 10.1038/329456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicker T., Anderson C., Sharp P. A., Sambrook J. Conditional lethal mutants of adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrids. I. Host range mutants of Ad2+ND1. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1237–1244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1237-1244.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guizani I., Clertant P., Cuzin F. Biochemical properties associated with the immortalizing domain of the large T protein of polyoma virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):973–979. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey D. M., Levine A. J. p53 alteration is a common event in the spontaneous immortalization of primary BALB/c murine embryo fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2375–2385. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Richardson W. D., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):33–38. doi: 10.1038/311033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Smith A. E. In vitro mutagenesis of a putative DNA binding domain of SV40 large-T. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):109–137. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohrman D. C., Imperiale M. J. Simian virus 40 large T antigen stably complexes with a 185-kilodalton host protein. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1752–1760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1752-1760.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraiss S., Quaiser A., Oren M., Montenarh M. Oligomerization of oncoprotein p53. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4737–4744. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4737-4744.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. J., Upson R. H., Simmons D. T. Nonspecific DNA binding activity of simian virus 40 large T antigen: evidence for the cooperation of two regions for full activity. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5443–5452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5443-5452.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. Y., Simmons D. T. Stable T-p53 complexes are not required for replication of simian virus 40 in culture or for enhanced phosphorylation of T antigen and p53. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):2066–2072. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.2066-2072.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. Y., Simmons D. T. The ability of large T antigen to complex with p53 is necessary for the increased life span and partial transformation of human cells by simian virus 40. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6447–6453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6447-6453.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Levine A. J. Characterization of a 54K dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston D. M., Bradley M. K. The simian virus 40 large T antigen. A lot packed into a little. Mol Biol Med. 1987 Apr;4(2):63–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeber G., Tevethia M. J., Schwedes J. F., Tegtmeyer P. Temperature-sensitive mutants identify crucial structural regions of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4426–4430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4426-4430.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W., DeCaprio J. A., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large T antigen binds preferentially to an underphosphorylated member of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product family. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90983-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manfredi J. J., Prives C. Binding of p53 and p105-RB is not sufficient for oncogenic transformation by a hybrid polyomavirus-simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5250–5259. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5250-5259.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael-Michalovitz D., Yehiely F., Gottlieb E., Oren M. Simian virus 40 can overcome the antiproliferative effect of wild-type p53 in the absence of stable large T antigen-p53 binding. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4160–4168. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4160-4168.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mole S. E., Gannon J. V., Ford M. J., Lane D. P. Structure and function of SV40 large-T antigen. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Dec 15;317(1187):455–469. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1987.0072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E. A region of SV40 large T antigen can substitute for a transforming domain of the adenovirus E1A products. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):168–170. doi: 10.1038/334168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Lerman L. S., Maniatis T. A general method for saturation mutagenesis of cloned DNA fragments. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):242–247. doi: 10.1126/science.2990046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamaye K. L., Eckstein F. Inhibition of restriction endonuclease Nci I cleavage by phosphorothioate groups and its application to oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9679–9698. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Srinivasan A., Farber J. M., Pipas J. M. Mutants with changes within or near a hydrophobic region of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen are defective for binding cellular protein p53. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C. The replication functions of SV40 T antigen are regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):735–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90179-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawai E. T., Butel J. S. Association of a cellular heat shock protein with simian virus 40 large T antigen in transformed cells. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3961–3973. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3961-3973.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieg F. I., Simmons D. T. Characterization of the in vitro interaction between SV40 T antigen and p53: mapping the p53 binding site. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):132–140. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90628-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheen J. Y., Seed B. Electrolyte gradient gels for DNA sequencing. Biotechniques. 1988 Nov-Dec;6(10):942–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Tjian R. Inhibition of simian virus 40 DNA replication by specific modification of T-antigen with oxidized ATP. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14369–14372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L., Danna K. J. The amino-terminal 147 amino acids of SV40 large T antigen transform secondary rat embryo fibroblasts. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):412–415. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90516-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprano K. J., Galanti N., Jonak G. J., McKercher S., Pipas J. M., Peden K. W., Baserga R. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 T antigen: stimulation of cellular DNA synthesis and activation of rRNA genes by mutants with deletions in the T-antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):214–219. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan A., Peden K. W., Pipas J. M. The large tumor antigen of simian virus 40 encodes at least two distinct transforming functions. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5459–5463. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5459-5463.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Dröge P., Knippers R. DNA helicase activity of SV40 large tumor antigen. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1939–1944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen C. W., Lane D. P. Mutant conformation of p53. Precise epitope mapping using a filamentous phage epitope library. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 5;225(3):577–583. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90386-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Addison C., Jenkins J. R. Characterization of mutant p53-hsp72/73 protein-protein complexes by transient expression in monkey COS cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3740–3747. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack L. C., Cartwright C. A., Wright J. H., Eckhart W., Peden K. W., Srinivasan A., Pipas J. M. Properties of a simian virus 40 mutant T antigen substituted in the hydrophobic region: defective ATPase and oligomerization activities and altered phosphorylation accompany an inability to complex with cellular p53. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3362–3367. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3362-3367.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Schmidt W., Cosstick R., Okruszek A., Eckstein F. The use of phosphorothioate-modified DNA in restriction enzyme reactions to prepare nicked DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8749–8764. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia M. J. Immortalization of primary mouse embryo fibroblasts with SV40 virions, viral DNA, and a subgenomic DNA fragment in a quantitative assay. Virology. 1984 Sep;137(2):414–421. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia M. J., Pipas J. M., Kierstead T., Cole C. Requirements for immortalization of primary mouse embryo fibroblasts probed with mutants bearing deletions in the 3' end of SV40 gene A. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):76–89. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90396-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. L., Kalderon D., Smith A. E., Tevethia M. J. Dissociation of Rb-binding and anchorage-independent growth from immortalization and tumorigenicity using SV40 mutants producing N-terminally truncated large T antigens. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):15–34. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90375-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornow J., Polvino-Bodnar M., Santangelo G., Cole C. N. Two separable functional domains of simian virus 40 large T antigen: carboxyl-terminal region of simian virus 40 large T antigen is required for efficient capsid protein synthesis. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):415–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.415-424.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. Monoclonal antibody analysis of p53 expression in normal and transformed cells. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):444–452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.444-452.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J. Y., Abate M., Rice P. W., Cole C. N. The ability of simian virus 40 large T antigen to immortalize primary mouse embryo fibroblasts cosegregates with its ability to bind to p53. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6872–6880. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6872-6880.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J., Rice P. W., Gorsch L., Abate M., Cole C. N. Transformation of a continuous rat embryo fibroblast cell line requires three separate domains of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2780–2791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2780-2791.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]