Abstract
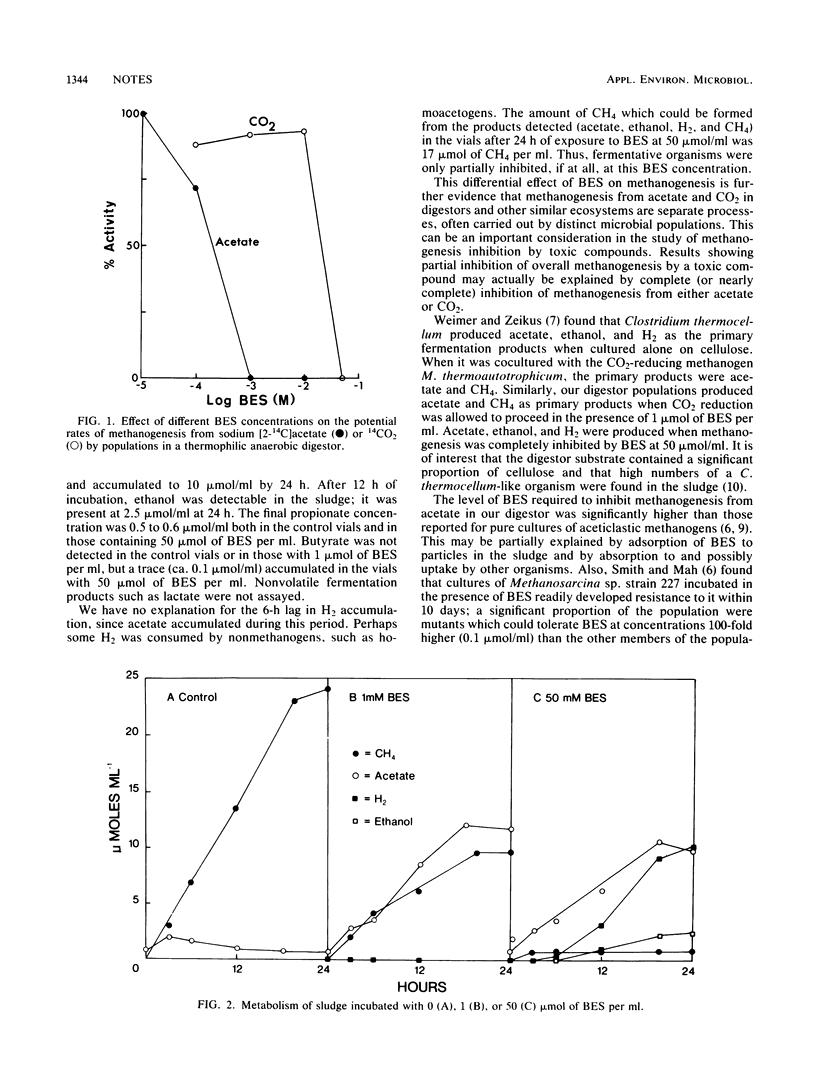
The effects of 2-bromoethanesulfonate, an inhibitor of methanogenesis, on metabolism in sludge from a thermophilic (58°C) anaerobic digestor were studied. It was found from short-term experiments that 1 μmol of 2-bromoethanesulfonate per ml completely inhibited methanogenesis from 14CH3COO−, whereas 50 μmol/ml was required for complete inhibition of 14CO2 reduction. When 1 μmol of 2-bromoethanesulfonate per ml was added to actively metabolizing sludge which was then incubated for 24 h. it caused a 60% reduction in methanogenesis and a corresponding increase in acetate accumulation; at 50 μmol/ml it caused complete inhibition of methanogenesis and accumulation of acetate. H2, and ethanol.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S. Transport of coenzyme M (2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid) in Methanobacterium ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):264–273. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.264-273.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouwer E. J., McCarty P. L. Effects of 2-bromoethanesulfonic Acid and 2- chloroethanesulfonic Acid on acetate utilization in a continuous-flow methanogenic fixed-film column. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1408–1410. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1408-1410.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P., Romesser J. A., Wolfe R. S. Preparation of coenzyme M analogues and their activity in the methyl coenzyme M reductase system of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2374–2377. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy J. B., Young L. Y., Reinhard M. Methanogenic decomposition of ferulic Acid, a model lignin derivative. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):436–444. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.436-444.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimer P. J., Zeikus J. G. Fermentation of cellulose and cellobiose by Clostridium thermocellum in the absence of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):289–297. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.289-297.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehnder A. J., Brock T. D. Anaerobic methane oxidation: occurrence and ecology. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):194–204. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.194-204.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehnder A. J., Huser B. A., Brock T. D., Wuhrmann K. Characterization of an acetate-decarboxylating, non-hydrogen-oxidizing methane bacterium. Arch Microbiol. 1980 Jan;124(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00407022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinder S. H., Cardwell S. C., Anguish T., Lee M., Koch M. Methanogenesis in a Thermophilic (58 degrees C) Anaerobic Digestor: Methanothrix sp. as an Important Aceticlastic Methanogen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Apr;47(4):796–807. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.4.796-807.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


