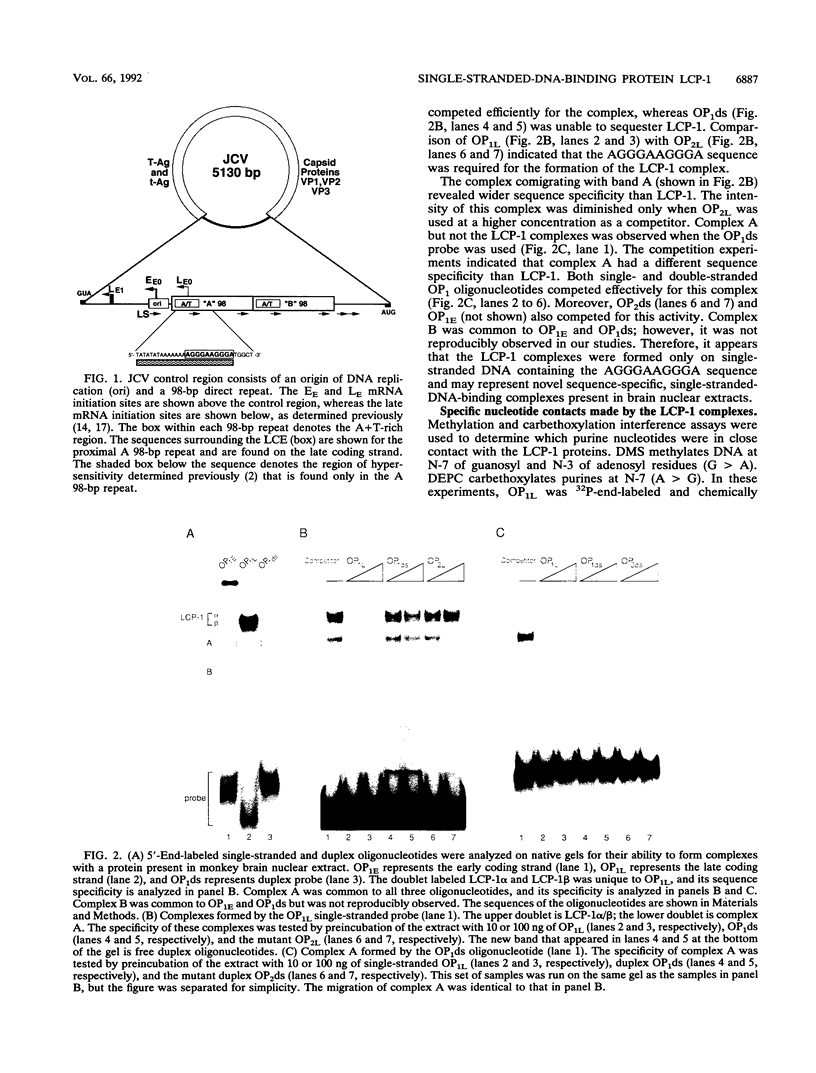
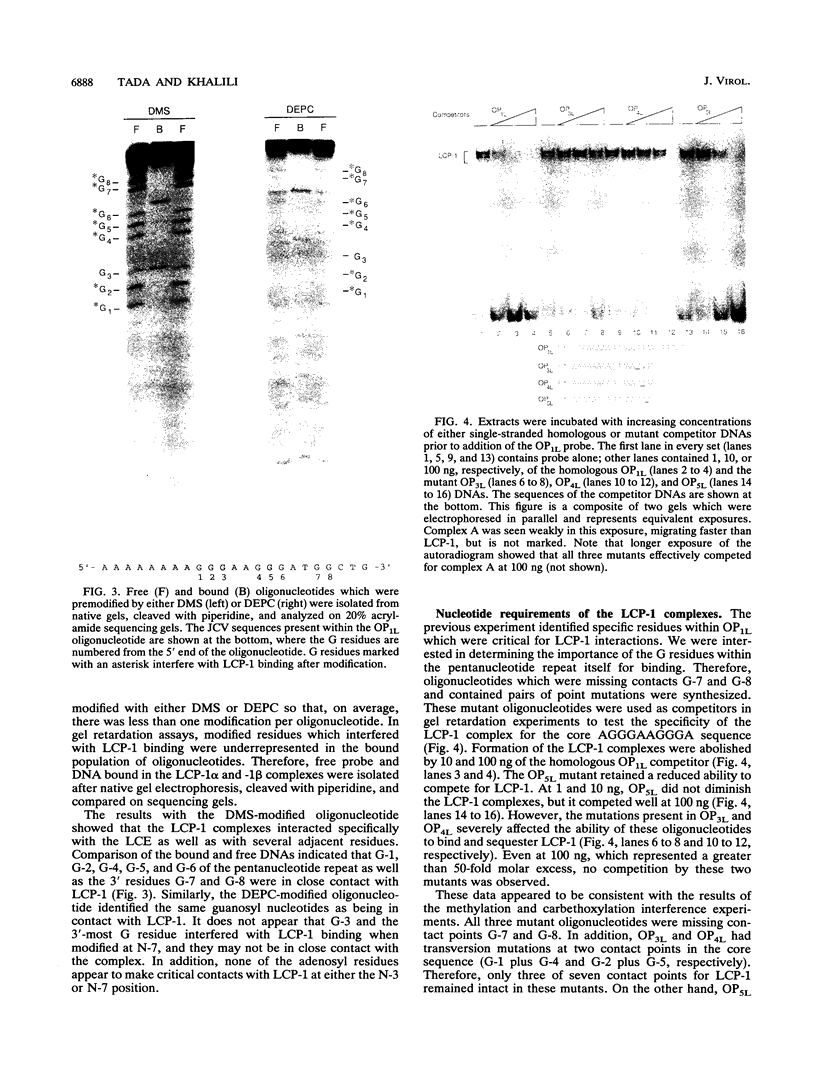
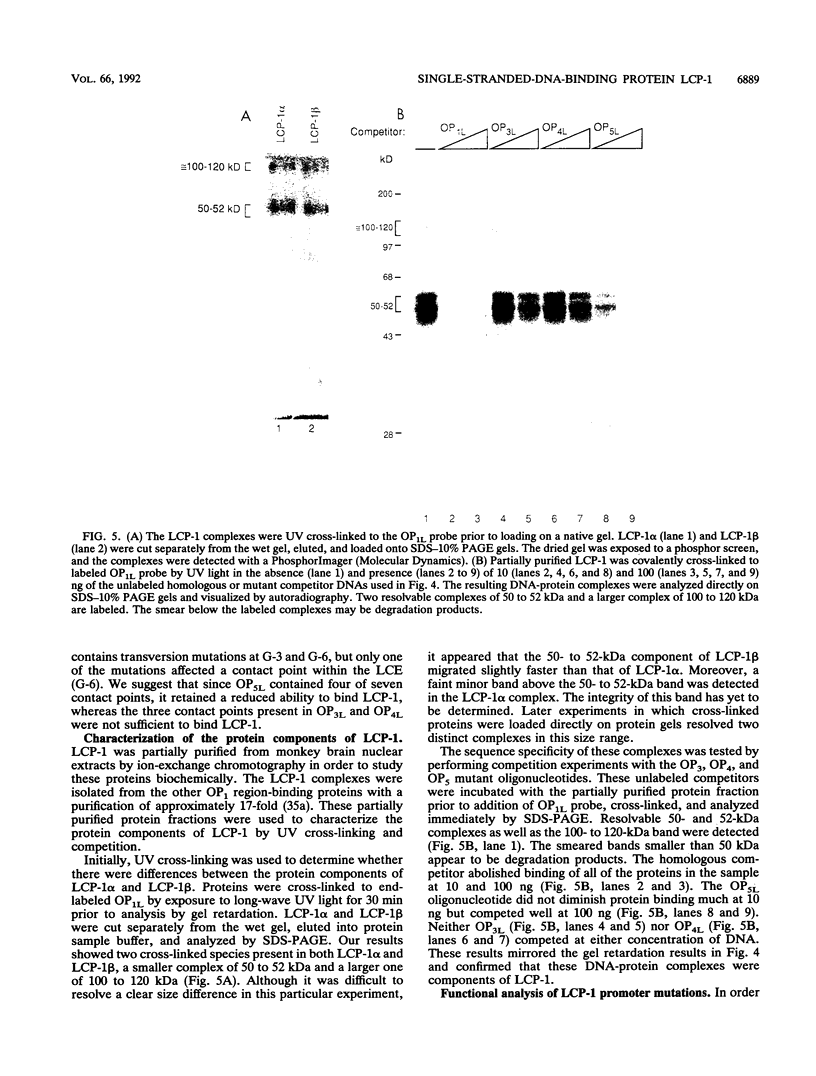
Abstract
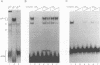
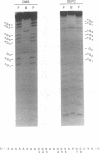
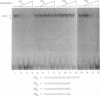
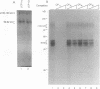
We have identified a novel brain-derived single-stranded-DNA-binding protein that interacts with a region of the human neurotropic JC virus enhancer designated the lytic control element (LCE). This nuclear factor, LCP-1 (for lytic control element-binding protein 1), specifically recognizes the LCE, as determined by gel retardation assays. Alkylation interference showed that specific nucleotides within the LCE were contacted by LCP-1. Subsequent experiments revealed that point mutations within the LCE differentially affected LCP-1 binding. UV cross-linking and competition analysis suggested that the LCP-1 DNA-protein complexes were 50 to 52 and 100 to 120 kDa in size. Promoter mutations that affected LCP-1 binding reduced early mRNA transcription during the early phase of the lytic cycle. However, upon DNA replication in the presence of JC virus T antigen, when early mRNA initiation shifts to new locations indicative of the late phase, the LCP-1 mutations had no effect. We suggest that the JC virus early transcription unit is differentially regulated by LCP-1 prior to but not after DNA replication, suggesting a novel mechanism by which DNA structure regulates eukaryotic gene expression.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed S., Rappaport J., Tada H., Kerr D., Khalili K. A nuclear protein derived from brain cells stimulates transcription of the human neurotropic virus promoter, JCVE, in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13899–13905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amirhaeri S., Wohlrab F., Major E. O., Wells R. D. Unusual DNA structure in the regulatory region of the human papovavirus JC virus. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):922–931. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.922-931.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beggs A. H., Frisque R. J., Scangos G. A. Extinction of JC virus tumor-antigen expression in glial cell--fibroblast hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7632–7636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Vecchio A. M., Steinman R. A., Ricciardi R. P. An element of the BK virus enhancer required for DNA replication. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1514–1524. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1514-1524.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl H. J., Schaich M., Budzinski R. M., Stoffel W. Individual exons encode the integral membrane domains of human myelin proteolipid protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9807–9811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigenbaum L., Khalili K., Major E., Khoury G. Regulation of the host range of human papovavirus JCV. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3695–3698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisque R. J., Rifkin D. B., Walker D. L. Transformation of primary hamster brain cells with JC virus and its DNA. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):265–269. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.265-269.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Rosenfeld M. G. Mechanisms of complex transcriptional regulation: implications for brain development. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):183–196. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90257-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. J., Munholland J. M., Wildeman A. G. Comeasurement of simian virus 40 early and late promoter activity in HeLa and 293 cells in the presence of T antigen. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):383–391. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.383-391.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Natarajan V., Salzman N. P. Mapping 5' termini of JC virus late RNA. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):216–219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.216-219.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Natarajan V., Strike D., Khoury G., Salzman N. P. JC virus enhancer-promoter active in human brain cells. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1337–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.6095453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr D., Khalili K. A recombinant cDNA derived from human brain encodes a DNA binding protein that stimulates transcription of the human neurotropic virus JCV. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15876–15881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalili K., Feigenbaum L., Khoury G. Evidence for a shift in 5'-termini of early viral RNA during the lytic cycle of JC virus. Virology. 1987 Jun;158(2):469–472. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalili K., Rappaport J., Khoury G. Nuclear factors in human brain cells bind specifically to the JCV regulatory region. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1205–1210. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02932.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latchman D. S. Eukaryotic transcription factors. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):281–289. doi: 10.1042/bj2700281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression of eukaryotic promoters. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch K. J., Frisque R. J. Identification of critical elements within the JC virus DNA replication origin. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5812–5822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5812-5822.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. New human papovaviruses. Prog Med Virol. 1976;22:1–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., ZuRhein G. M., Eckroade R. J., Dessel B. H. Cultivation of papova-like virus from human brain with progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy. Lancet. 1971 Jun 19;1(7712):1257–1260. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro I. M., Yi T. M., Walsh K. Identification of single-stranded-DNA-binding proteins that interact with muscle gene elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1944–1953. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A. M., Herterich S. U., Krauss G. A single-stranded DNA binding protein from S. cerevisiae specifically recognizes the T-rich strand of the core sequence of ARS elements and discriminates against mutant sequences. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):981–985. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma A. K., Kumar G. A 53 kDa protein binds to the negative regulatory region of JC virus early promoter. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):272–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80409-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. A., Khoury G., Jay G., Howley P. M., Scangos G. A. Early regions of JC virus and BK virus induce distinct and tissue-specific tumors in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8288–8292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. A., Scangos G. A., Cork L., Jay G., Khoury G. The early region of human papovavirus JC induces dysmyelination in transgenic mice. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90855-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spana C., Corces V. G. DNA bending is a determinant of binding specificity for a Drosophila zinc finger protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1505–1515. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Mechanisms for diversity in gene expression patterns. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90256-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R., Baumruker T., Franza B. R., Jr, Herr W. A 100-kD HeLa cell octamer binding protein (OBP100) interacts differently with two separate octamer-related sequences within the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1147–1160. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada H., Lashgari M. S., Khalili K. Regulation of JCVL promoter function: evidence that a pentanucleotide "silencer" repeat sequence AGGGAAGGGA down-regulates transcription of the JC virus late promoter. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):327–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90037-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada H., Lashgari M., Rappaport J., Khalili K. Cell type-specific expression of JC virus early promoter is determined by positive and negative regulation. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):463–466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.463-466.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada H., Rappaport J., Lashgari M., Amini S., Wong-Staal F., Khalili K. Trans-activation of the JC virus late promoter by the tat protein of type 1 human immunodeficiency virus in glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3479–3483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapp B. D., Small J. A., Pulley M., Khoury G., Scangos G. A. Dysmyelination in transgenic mice containing JC virus early region. Ann Neurol. 1988 Jan;23(1):38–48. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Chambon P. Transcription from the SV40 early-early and late-early overlapping promoters in the absence of DNA replication. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1605–1611. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G. Transactivation of both early and late simian virus 40 promoters by large tumor antigen does not require nuclear localization of the protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2123–2127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Ferra F., Engh H., Hudson L., Kamholz J., Puckett C., Molineaux S., Lazzarini R. A. Alternative splicing accounts for the four forms of myelin basic protein. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):721–727. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90245-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]