Abstract
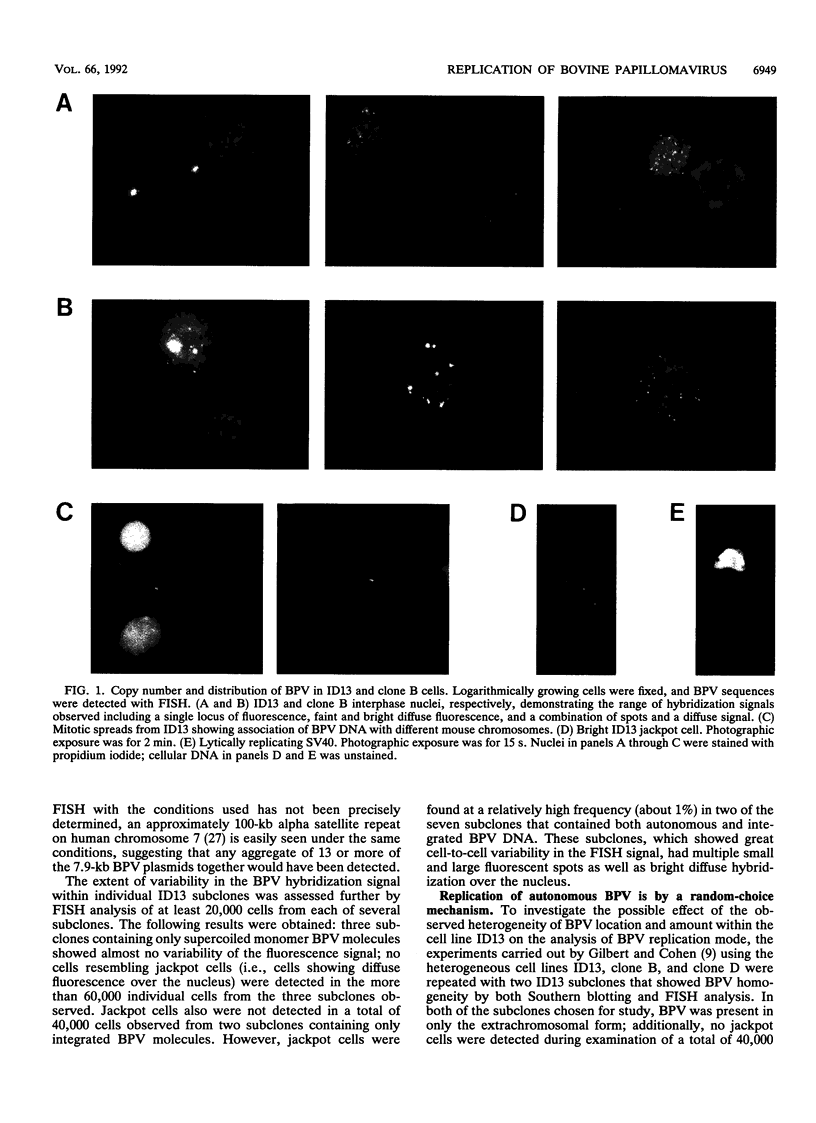
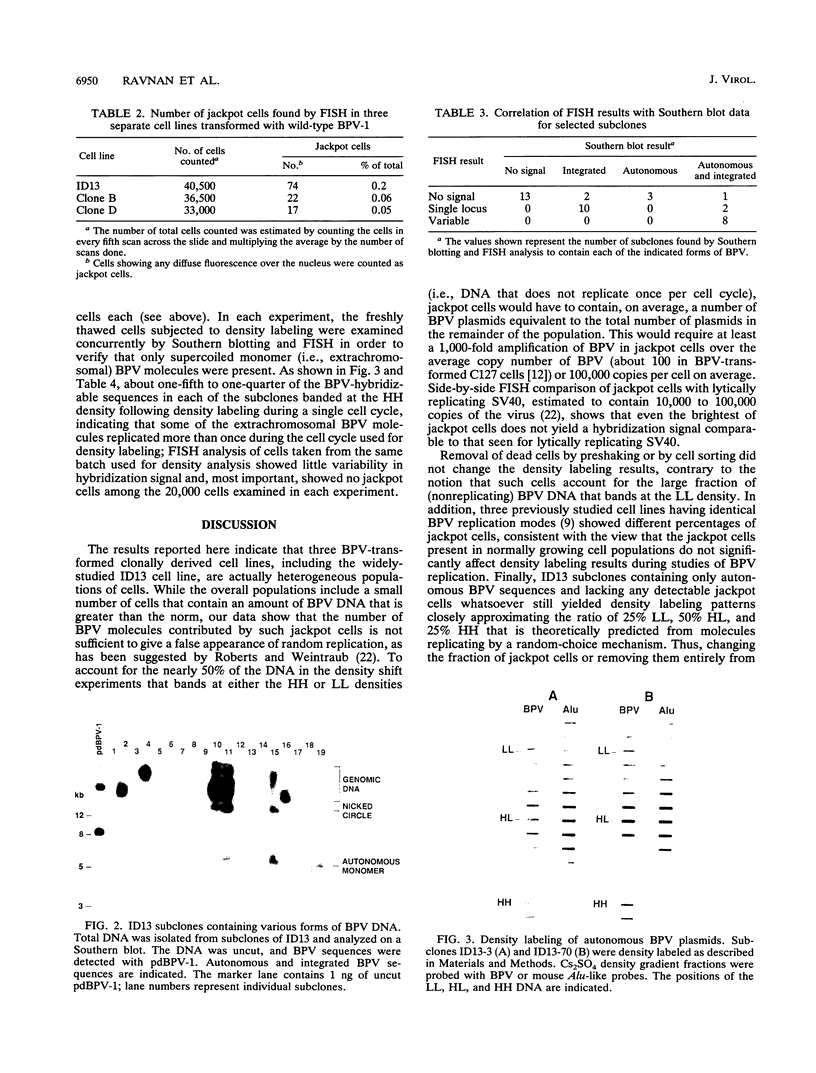
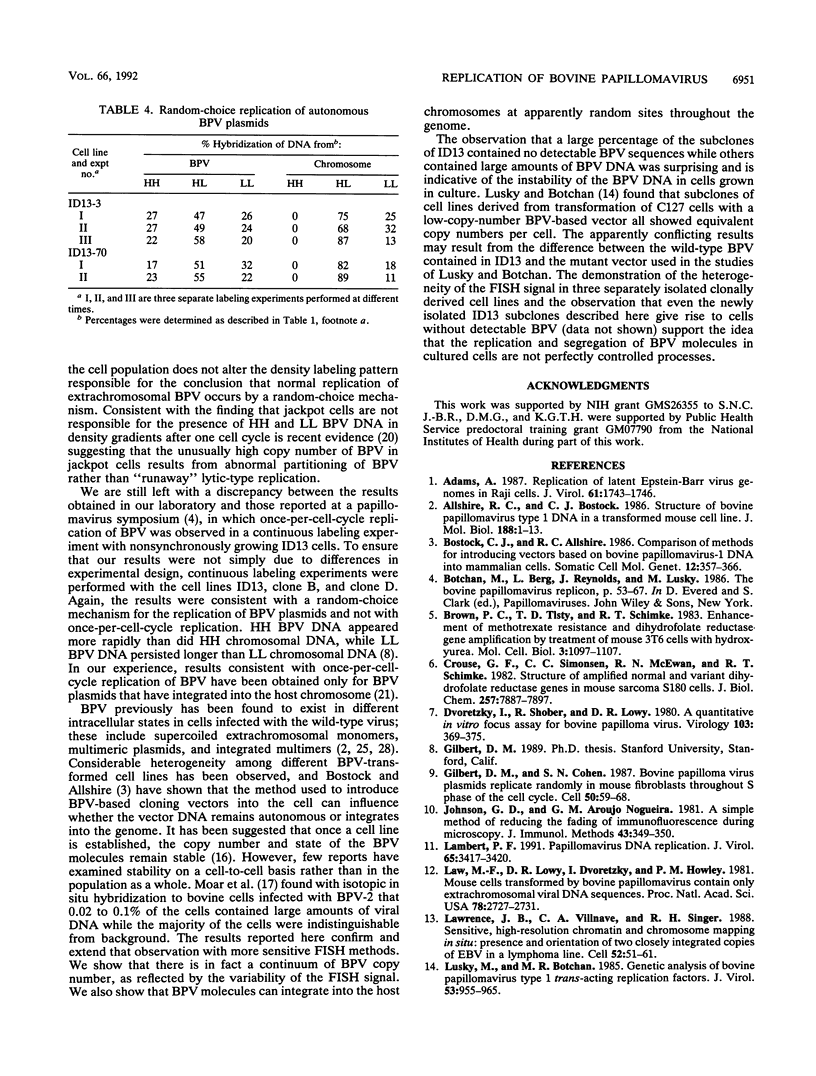
Using fluorescence in situ hybridization and Southern blot analysis, we show that three clonally derived cell lines transformed with bovine papillomavirus (BPV), including ID13, the cell line commonly employed for BPV replication studies, are heterogeneous populations having extensive cell-to-cell variation in both the distribution and amount of BPV DNA. Different subclones of ID13 were found to differ in the form and amount of BPV DNA they contain. Most subclones showed no detectable BPV sequences; some contained either extrachromosomal BPV molecules distributed throughout the nucleus or BPV sequences integrated at discrete chromosomal sites, while others contained both integrated and plasmid forms. The results of density gradient analysis of BPV DNA from individual homogeneous subclones showed replication of the extrachromosomal BPV plasmids in a random-choice mode. In all cell lines studied, the presence after one round of chromosomal DNA replication of unreplicated BPV DNA and of BPV DNA having two postreplicative strands was independent of the presence of high-BPV-copy-number ("jackpot") cells. Our results substantiate the earlier conclusion that extrachromosomal BPV molecules replicate randomly and not according to a once-per-cell-cycle mechanism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A. Replication of latent Epstein-Barr virus genomes in Raji cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1743–1746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1743-1746.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allshire R. C., Bostock C. J. Structure of bovine papillomavirus type 1 DNA in a transformed mouse cell line. J Mol Biol. 1986 Mar 5;188(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90475-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostock C. J., Allshire R. C. Comparison of methods for introducing vectors based on bovine papillomavirus-1 DNA into mammalian cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Jul;12(4):357–366. doi: 10.1007/BF01570730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Berg L., Reynolds J., Lusky M. The bovine papillomavirus replicon. Ciba Found Symp. 1986;120:53–67. doi: 10.1002/9780470513309.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. C., Tlsty T. D., Schimke R. T. Enhancement of methotrexate resistance and dihydrofolate reductase gene amplification by treatment of mouse 3T6 cells with hydroxyurea. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1097–1107. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., Simonsen C. C., McEwan R. N., Schimke R. T. Structure of amplified normal and variant dihydrofolate reductase genes in mouse sarcoma S180 cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7887–7897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretzky I., Shober R., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R. A quantitative in vitro focus assay for bovine papilloma virus. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. M., Cohen S. N. Bovine papilloma virus plasmids replicate randomly in mouse fibroblasts throughout S phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90662-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Nogueira Araujo G. M. A simple method of reducing the fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy. J Immunol Methods. 1981;43(3):349–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F. Papillomavirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3417–3420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3417-3420.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. F., Lowy D. R., Dvoretzky I., Howley P. M. Mouse cells transformed by bovine papillomavirus contain only extrachromosomal viral DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2727–2731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Villnave C. A., Singer R. H. Sensitive, high-resolution chromatin and chromosome mapping in situ: presence and orientation of two closely integrated copies of EBV in a lymphoma line. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90530-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. R. Genetic analysis of bovine papillomavirus type 1 trans-acting replication factors. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):955–965. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.955-965.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecsas J., Sugden B. Replication of plasmids derived from bovine papilloma virus type 1 and Epstein-Barr virus in cells in culture. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:87–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moar M. H., Campo M. S., Laird H., Jarrett W. F. Persistence of non-integrated viral DNA in bovine cells transformed in vitro by bovine papillomavirus type 2. Nature. 1981 Oct 29;293(5835):749–751. doi: 10.1038/293749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Straume T., Gray J. W. Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2934–2938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. M., Weintraub H. Cis-acting negative control of DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):397–404. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rownd R. Replication of a bacterial episome under relaxed control. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):387–402. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. Transformation and replication in mouse cells of a bovine papillomavirus--pML2 plasmid vector that can be rescued in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7147–7151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schvartzman J. B., Adolph S., Martín-Parras L., Schildkraut C. L. Evidence that replication initiates at only some of the potential origins in each oligomeric form of bovine papillomavirus type 1 DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3078–3086. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens P. E., Hentschel C. C. The bovine papillomavirus genome and its uses as a eukaryotic vector. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):1–11. doi: 10.1042/bj2480001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., England S. B., Willard H. F. Genomic organization of alpha satellite DNA on human chromosome 7: evidence for two distinct alphoid domains on a single chromosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):349–356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Botchan M. Replication of bovine papillomavirus type 1 DNA initiates within an E2-responsive enhancer element. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5903–5911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5903-5911.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Guan N. Epstein-Barr virus-derived plasmids replicate only once per cell cycle and are not amplified after entry into cells. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):483–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.483-488.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]