Abstract
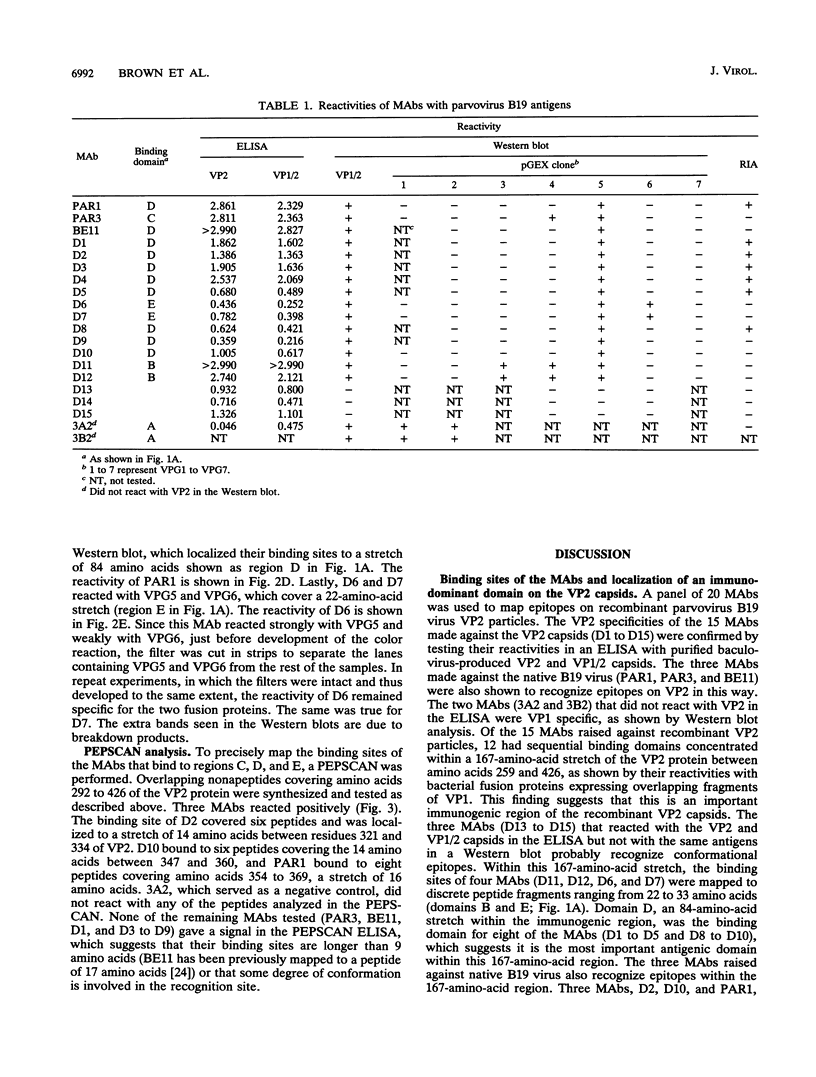
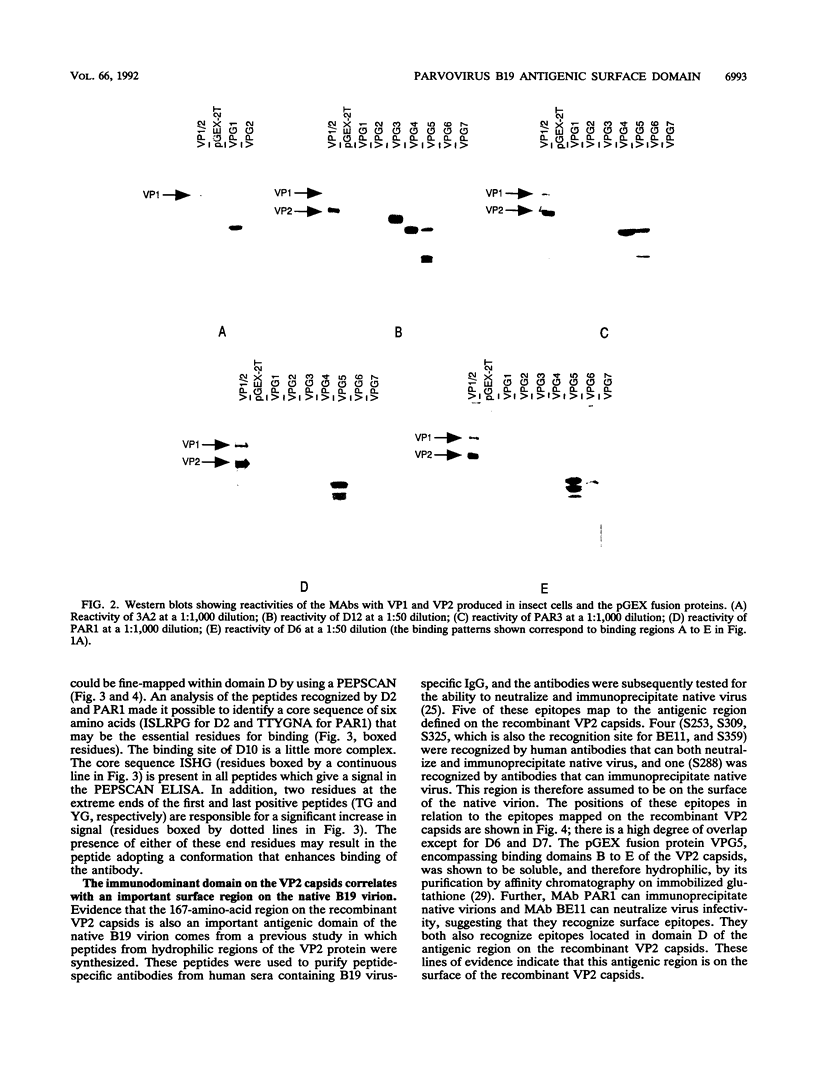
An immunodominant region on baculovirus-produced parvovirus B19 VP2 capsids was localized between amino acids 259 and 426 by mapping the binding sites of a panel of monoclonal antibodies which recognize determinants on the particles. The binding sites of three monoclonal antibodies were fine-mapped within this antigenic domain. Six VP2-specific monoclonal antibodies recognized determinants common to both the empty capsids and native parvovirus. The defined antigenic region is most probably exposed on the native B19 virion and corresponds to part of the threefold spike on the surface of canine parvovirus particles.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson L. J., Hurwitz E. S. Human parvovirus B19 and pregnancy. Clin Perinatol. 1988 Jun;15(2):273–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. L., Francis M. J., Hastings G. Z., Parry N. R., Barnett P. V., Rowlands D. J., Clarke B. E. Foreign epitopes in immunodominant regions of hepatitis B core particles are highly immunogenic and conformationally restricted. Vaccine. 1991 Aug;9(8):595–601. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(91)90248-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. S., Salimans M. M., Noteborn M. H., Weiland H. T. Antigenic parvovirus B19 coat proteins VP1 and VP2 produced in large quantities in a baculovirus expression system. Virus Res. 1990 Mar;15(3):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(90)90028-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. S., Van Lent J. W., Vlak J. M., Spaan W. J. Assembly of empty capsids by using baculovirus recombinants expressing human parvovirus B19 structural proteins. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2702–2706. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2702-2706.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke B. E., Newton S. E., Carroll A. R., Francis M. J., Appleyard G., Syred A. D., Highfield P. E., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Improved immunogenicity of a peptide epitope after fusion to hepatitis B core protein. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):381–384. doi: 10.1038/330381a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. J., Mortimer P. P., Pereira M. S. Diagnostic assays with monoclonal antibodies for the human serum parvovirus-like virus (SPLV). J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Aug;91(1):113–130. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. The autonomously replicating parvoviruses of vertebrates. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:91–174. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis M. J., Hastings G. Z., Brown A. L., Grace K. G., Rowlands D. J., Brown F., Clarke B. E. Immunological properties of hepatitis B core antigen fusion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2545–2549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Barteling S. J., Meloen R. H. Small peptides induce antibodies with a sequence and structural requirement for binding antigen comparable to antibodies raised against the native protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):178–182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Meloen R. H., Barteling S. J. Use of peptide synthesis to probe viral antigens for epitopes to a resolution of a single amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths J. C., Berrie E. L., Holdsworth L. N., Moore J. P., Harris S. J., Senior J. M., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J., Adams S. E. Induction of high-titer neutralizing antibodies, using hybrid human immunodeficiency virus V3-Ty viruslike particles in a clinically relevant adjuvant. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):450–456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.450-456.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajigaya S., Fujii H., Field A., Anderson S., Rosenfeld S., Anderson L. J., Shimada T., Young N. S. Self-assembled B19 parvovirus capsids, produced in a baculovirus system, are antigenically and immunogenically similar to native virions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4646–4650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajigaya S., Shimada T., Fujita S., Young N. S. A genetically engineered cell line that produces empty capsids of B19 (human) parvovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7601–7605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. Polyvalent recombinant antigens: a new vaccine strategy. Vaccine. 1988 Aug;6(4):304–306. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(88)90174-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori J., Beattie P., Melton D. W., Cohen B. J., Clewley J. P. Structure and mapping of the DNA of human parvovirus B19. J Gen Virol. 1987 Nov;68(Pt 11):2797–2806. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-11-2797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morinet F., Tratschin J. D., Perol Y., Siegl G. Comparison of 17 isolates of the human parvovirus B 19 by restriction enzyme analysis. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1986;90(1-2):165–172. doi: 10.1007/BF01314155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer P. P., Humphries R. K., Moore J. G., Purcell R. H., Young N. S. A human parvovirus-like virus inhibits haematopoietic colony formation in vitro. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):426–429. doi: 10.1038/302426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Hirata J., Furukawa M., Kuroda N., Shiraki H., Maeda Y., Okochi K. Identification of the region including the epitope for a monoclonal antibody which can neutralize human parvovirus B19. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1667–1672. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1667-1672.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Hirata J., Kuroda N., Shiraki H., Maeda Y., Okochi K. Identification and mapping of neutralizing epitopes of human parvovirus B19 by using human antibodies. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5485–5490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5485-5490.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schödel F., Moriarty A. M., Peterson D. L., Zheng J. A., Hughes J. L., Will H., Leturcq D. J., McGee J. S., Milich D. R. The position of heterologous epitopes inserted in hepatitis B virus core particles determines their immunogenicity. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):106–114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.106-114.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shade R. O., Blundell M. C., Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P., Astell C. R. Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of human parvovirus B19 isolated from the serum of a child during aplastic crisis. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):921–936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.921-936.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl S. J., Murray K. Immunogenicity of peptide fusions to hepatitis B virus core antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6283–6287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao J., Chapman M. S., Agbandje M., Keller W., Smith K., Wu H., Luo M., Smith T. J., Rossmann M. G., Compans R. W. The three-dimensional structure of canine parvovirus and its functional implications. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1456–1464. doi: 10.1126/science.2006420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Elsacker-Niele A. M., Salimans M. M., Weiland H. T., Vermey-Keers C., Anderson M. J., Versteeg J. Fetal pathology in human parvovirus B19 infection. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1989 Jul;96(7):768–775. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1989.tb03314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland H. T., Salimans M. M., Fibbe W. E., Kluin P. M., Cohen B. J. Prolonged parvovirus B19 infection with severe anaemia in a bone marrow transplant patient. Br J Haematol. 1989 Feb;71(2):300–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb04276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaegashi N., Tada K., Shiraishi H., Ishii T., Nagata K., Sugamura K. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human parvovirus B19. Microbiol Immunol. 1989;33(7):561–567. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1989.tb02006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young N., Harrison M., Moore J., Mortimer P., Humphries R. K. Direct demonstration of the human parvovirus in erythroid progenitor cells infected in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2024–2032. doi: 10.1172/JCI111625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young N. Hematologic and hematopoietic consequences of B19 parvovirus infection. Semin Hematol. 1988 Apr;25(2):159–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]