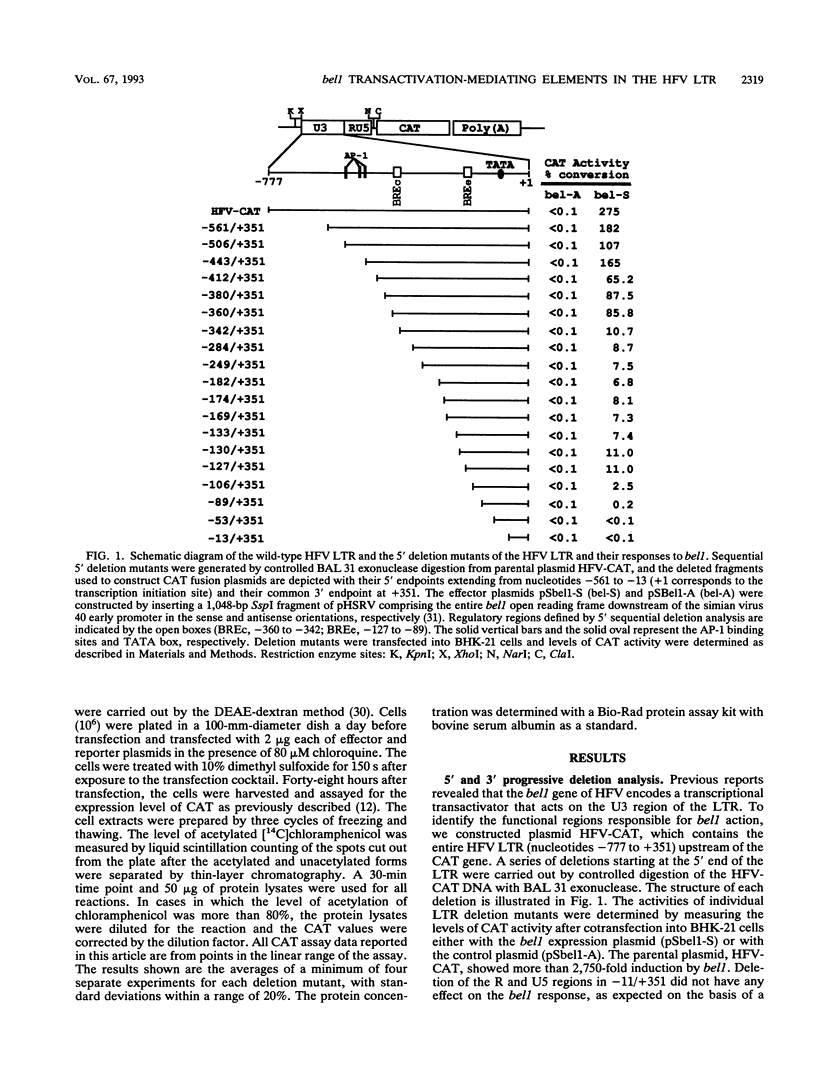
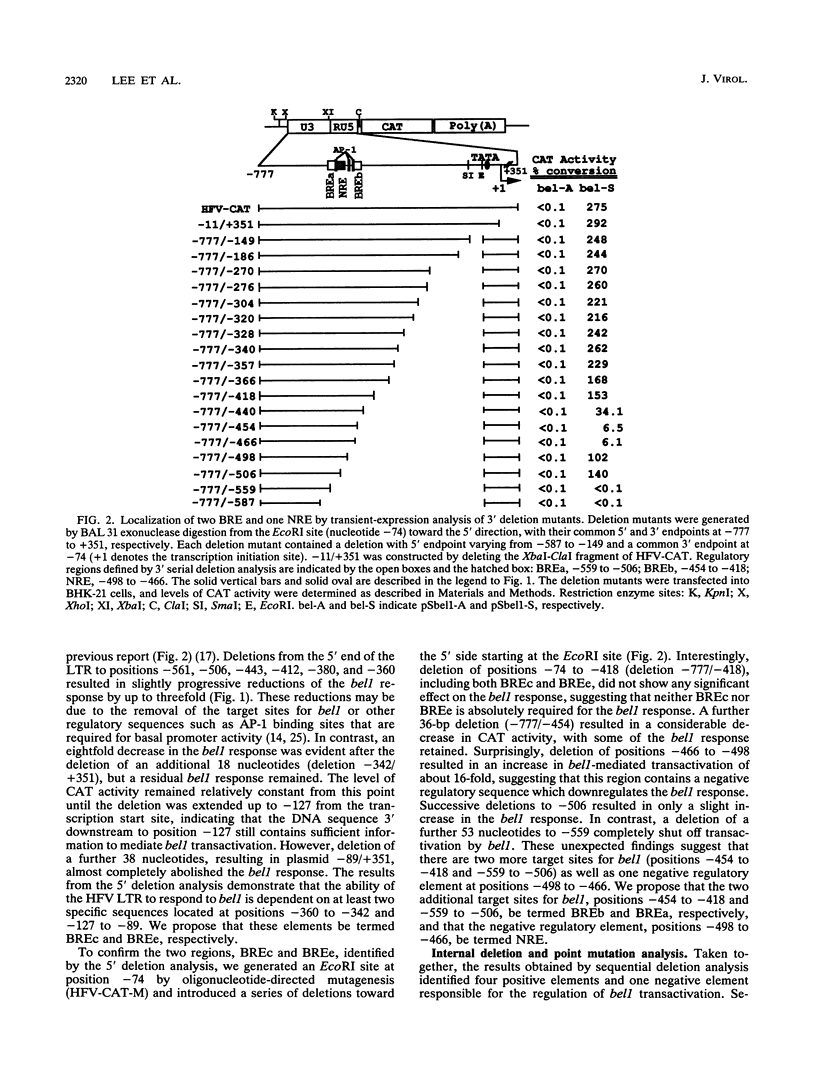
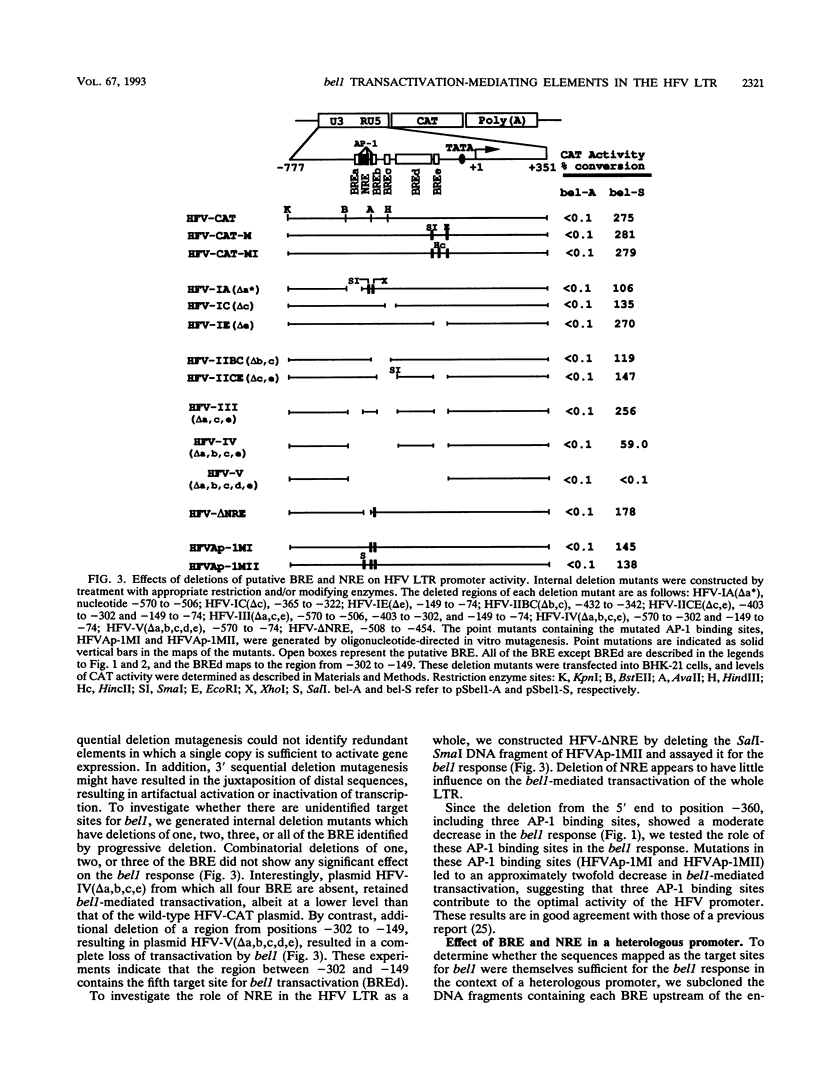
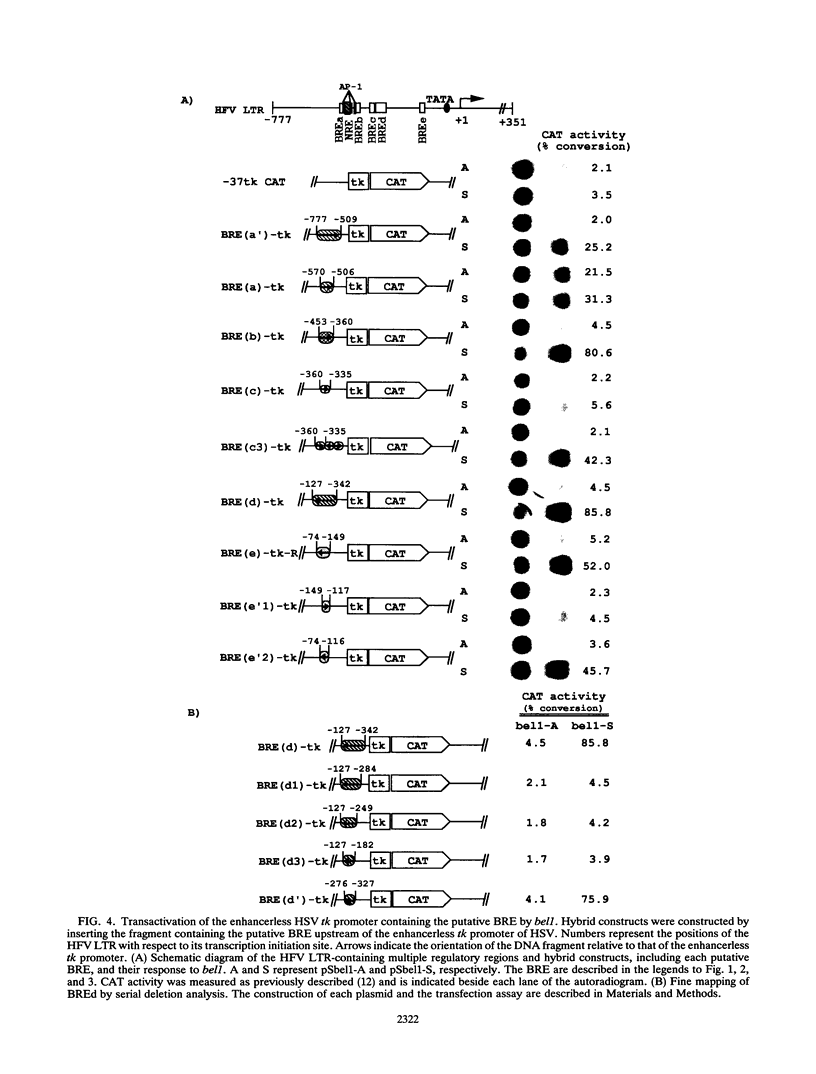
Abstract
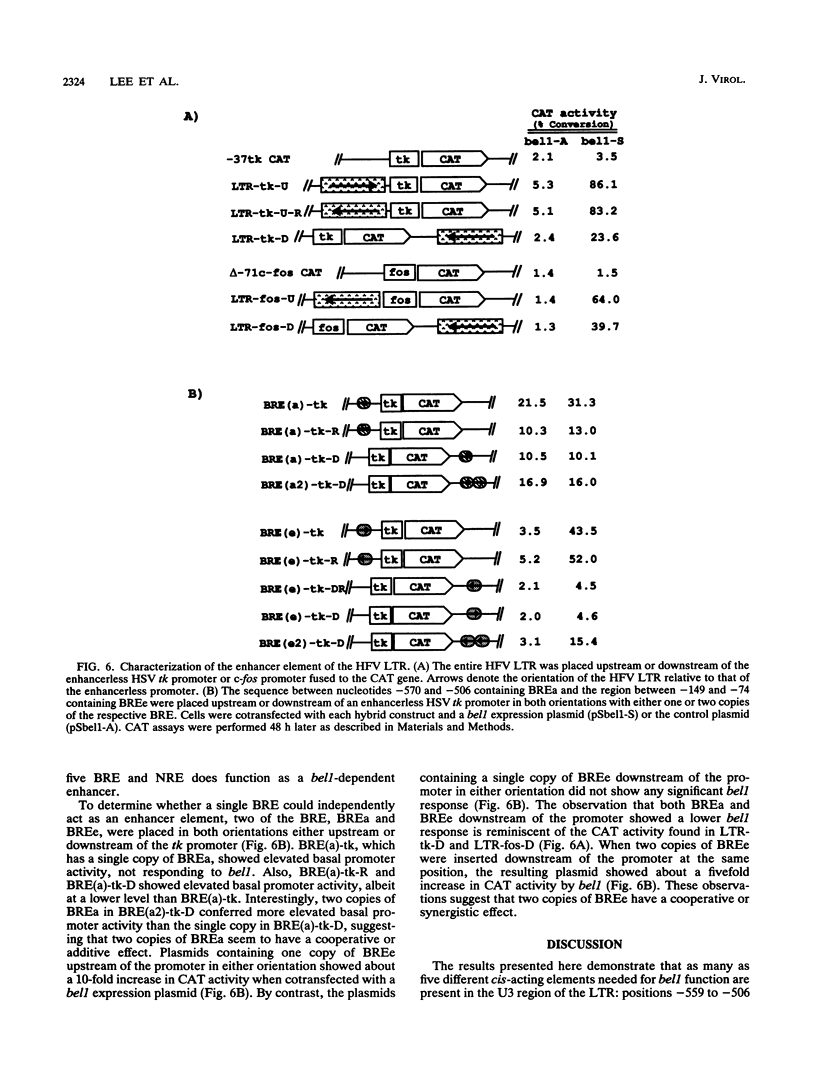
The bel1 protein of human foamy virus (HFV), a retrovirus, regulates expression of the gene linked to the HFV long terminal repeat (LTR) and is essential for viral gene expression. The mechanism of action of the bel1 protein is unknown, but its action is mediated through the U3 region of the LTR. To determine which U3 sequences are critical for transactivation by bel1, a series of hybrid vectors consisting of a mutant HFV LTR and the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene were constructed and tested for their responsiveness to the bel1 protein by using transient assays after transfection. The target sequences for transactivation by bel1 were mapped to five regions in the U3 domain of the LTR: nucleotides -559 to -506, -454 to -418, -360 to -342, -327 to -284, and -116 to -89 (+1 represents the transcription initiation site). No significant sequence similarity was identified among the five target sites. The observation that the multiple distinct elements in the HFV LTR are the targets for bel1 transactivation is different from observations with other human retroviral systems. The regulation mechanism of HFV bel1 protein-mediated transactivation appears to be analogous to that of some DNA virus transactivators that increase transcription from numerous different viral promoters with little sequence similarity shared among them. We demonstrated that multiple bel1-responsive elements (BRE) can act as bel1-dependent enhancer elements, while a single copy of one BRE, BREe, can serve as an upstream activating element in both orientations. In addition, the region between -466 and -498 was identified as responsible for the downregulation of gene expression directed by BREa, which requires its upstream sequence element to act as a bel1-dependent enhancer element in a heterologous promoter.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achong B. G., Mansell P. W., Epstein M. A., Clifford P. An unusual virus in cultures from a human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Feb;46(2):299–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arya S. K., Guo C., Josephs S. F., Wong-Staal F. Trans-activator gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III). Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):69–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2990040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Jeang K. T., Duvall J., Khoury G. Identification of p40x-responsive regulatory sequences within the human T-cell leukemia virus type I long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2175–2181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2175-2181.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron K. R., Birchall S. M., Moses M. A. Isolation of foamy virus from patient with dialysis encephalopathy. Lancet. 1978 Oct 7;2(8093):796–796. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92691-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 Tat protein: an RNA sequence-specific processivity factor? Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):655–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel R. M., Rethwilm A., Maurer B., Darai G. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the env gene and its flanking regions of the human spumaretrovirus reveals two novel genes. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2077–2084. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02473.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa J., Toita M., Yoshimura T., Yoshida M. The indirect association of human T-cell leukemia virus tax protein with DNA results in transcriptional activation. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4525–4528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4525-4528.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gdovin S. L., Clements J. E. Molecular mechanisms of visna virus Tat: identification of the targets for transcriptional activation and evidence for a post-transcriptional effect. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):438–450. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90497-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Mutational analysis of the trans-activation-responsive region of the human immunodeficiency virus type I long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):673–679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.673-679.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. L., Small J. A., Clements J. E. Sequences in the visna virus long terminal repeat that control transcriptional activity and respond to viral trans-activation: involvement of AP-1 sites in basal activity and trans-activation. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3001–3015. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3001-3015.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller A., Partin K. M., Löchelt M., Bannert H., Flügel R. M., Cullen B. R. Characterization of the transcriptional trans activator of human foamy retrovirus. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2589–2594. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2589-2594.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. E1A transcription induction: enhanced binding of a factor to upstream promoter sequences. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):719–722. doi: 10.1126/science.2935935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Identification of a cellular transcription factor involved in E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong K., Brunet L., Berk A. J. Factors responsible for the higher transcriptional activity of extracts of adenovirus-infected cells fractionate with the TATA box transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1765–1774. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löchelt M., Zentgraf H., Flügel R. M. Construction of an infectious DNA clone of the full-length human spumaretrovirus genome and mutagenesis of the bel 1 gene. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90820-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott S. J., Boros I., Duvall J. F., Brady J. N. Indirect binding of human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax1 to a responsive element in the viral long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4152–4160. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Bannert H., Darai G., Flügel R. M. Analysis of the primary structure of the long terminal repeat and the gag and pol genes of the human spumaretrovirus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1590–1597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1590-1597.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Serfling E., ter Meulen V., Rethwilm A. Transcription factor AP-1 modulates the activity of the human foamy virus long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6353–6357. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6353-6357.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyborg J. K., Dynan W. S., Chen I. S., Wachsman W. Binding of host-cell factors to DNA sequences in the long terminal repeat of human T-cell leukemia virus type I: implications for viral gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1457–1461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. W., Lenardo M., Baltimore D. Oligonucleotide that binds nuclear factor NF-kappa B acts as a lymphoid-specific and inducible enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1482–1486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Huima T., Williams B. A., Bardina L., Brotman B. Isolation of a virus from chimpanzee liver cell cultures inoculated with sera containing the agent of non-A, non-B hepatitis. Lancet. 1984 Nov 10;2(8411):1071–1075. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethwilm A., Erlwein O., Baunach G., Maurer B., ter Meulen V. The transcriptional transactivator of human foamy virus maps to the bel 1 genomic region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):941–945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):813–823. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby M. J., Bain E. S., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Structure, sequence, and position of the stem-loop in tar determine transcriptional elongation by tat through the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):547–558. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Takano M., Teruuchi T., Miwa M. Requirement of multiple copies of a 21-nucleotide sequence in the U3 regions of human T-cell leukemia virus type I and type II long terminal repeats for trans-acting activation of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8112–8116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SivaRaman L., Thimmappaya B. Two promoter-specific host factors interact with adjacent sequences in an EIA-inducible adenovirus promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6112–6116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Rosen C., Goh W. C., Haseltine W. A transcriptional activator protein encoded by the x-lor region of the human T-cell leukemia virus. Science. 1985 Jun 21;228(4706):1430–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2990028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stancek D., Stanceková-Gressnerová M., Janotka M., Hnilica P., Oravec D. Isolation and some serological and epidemiological data on the viruses recovered from patients with subacute thyroiditis de Quervain. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1975;161(2):133–144. doi: 10.1007/BF02121755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh L. K., Theodorakis P. A., Chinnadurai G. Distinct cis-acting regions in U3 regulate trans-activation of the human spumaretrovirus long terminal repeat by the viral bel1 gene product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3661–3666. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A. Foamy retroviruses. A virus in search of a disease. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):497–498. doi: 10.1038/333497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner J., Gelderblom H. Isolation of foamy virus from patients with de Quervain thyroiditis. Lancet. 1979 Aug 4;2(8136):258–259. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Rosser D. S., Schmidt M. C., Berk A. A TATA box implicated in E1A transcriptional activation of a simple adenovirus 2 promoter. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):512–515. doi: 10.1038/326512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D., Samuels J., Clarke J. K. A foamy virus of possible human origin isolated in BHK-21 cells. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;42(3):228–234. doi: 10.1007/BF01265647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




