Abstract
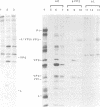
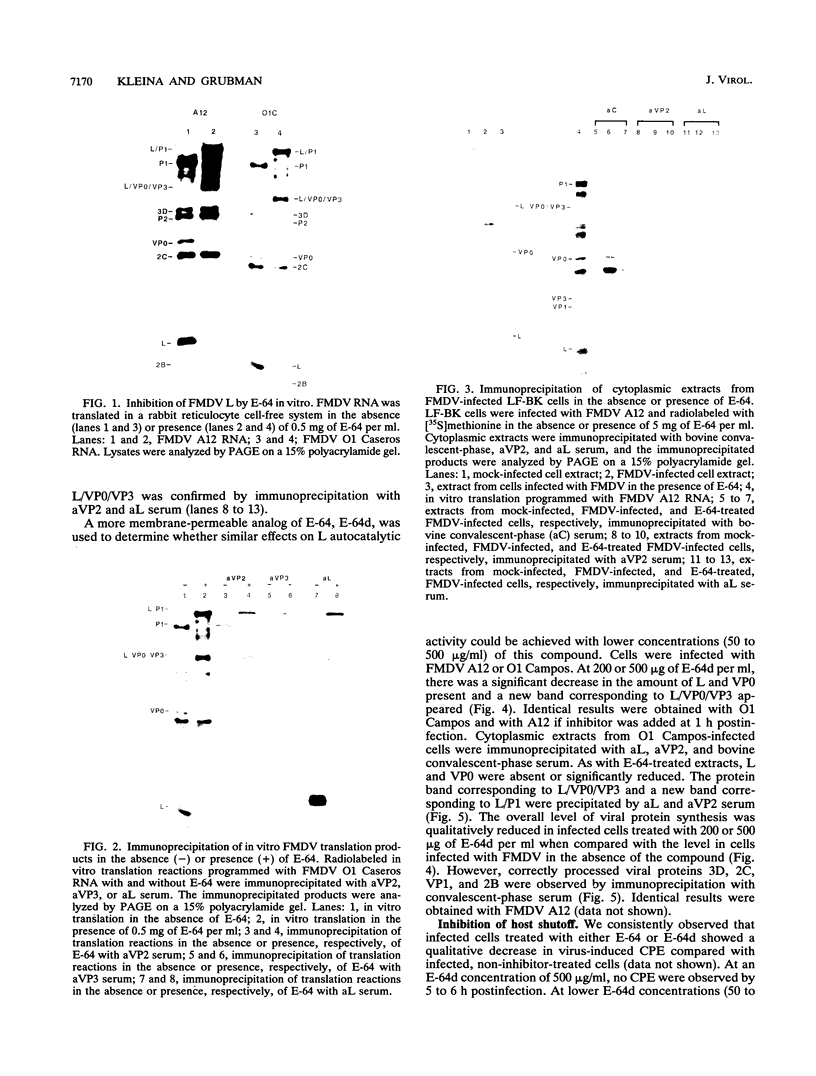
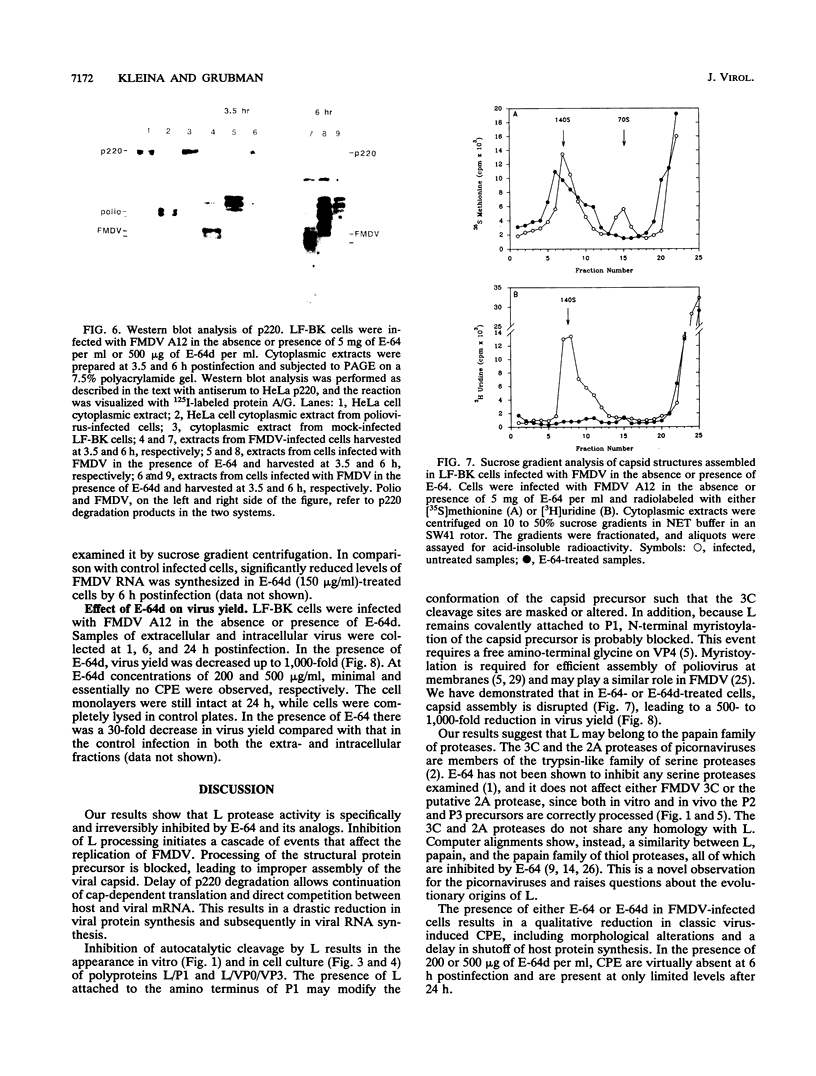
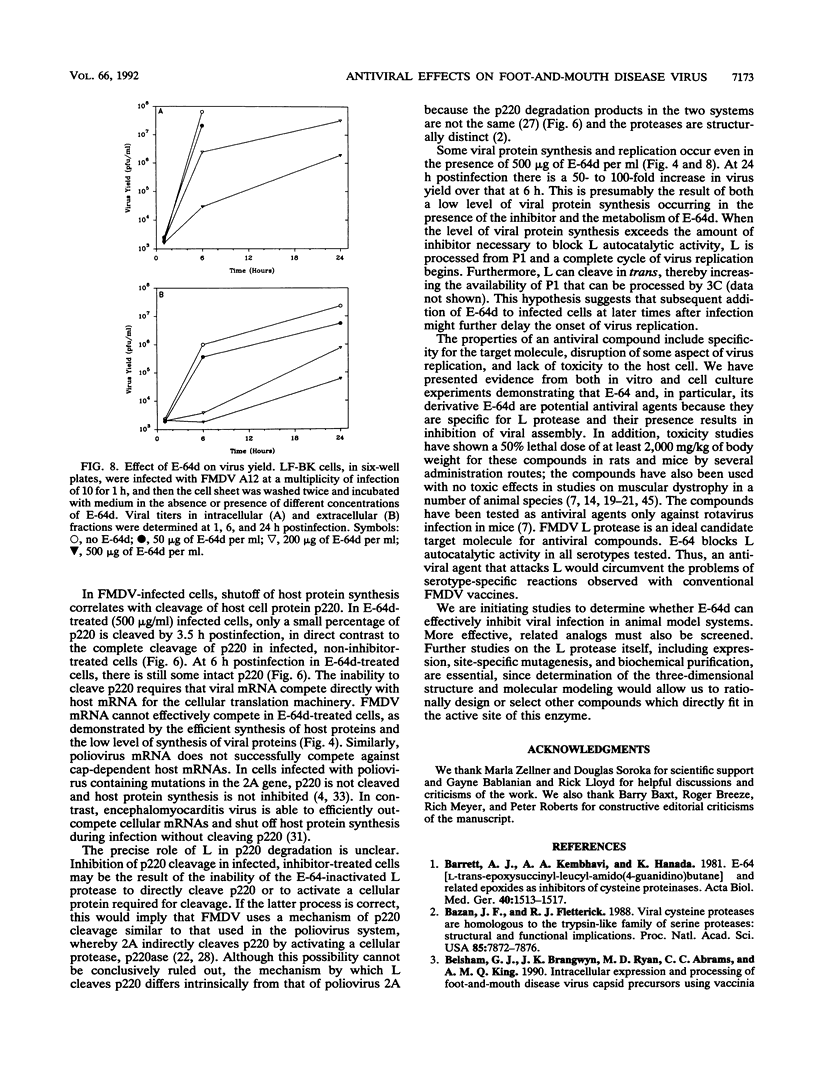
The thiol protease inhibitor E-64 specifically blocks autocatalytic activity of the leader protease of foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) and interferes with cleavage of the structural protein precursor in an in vitro translation assay programmed with virion RNA. Experiments with FMDV-infected cells and E-64 or a membrane-permeable analog, E-64d, have confirmed these results and demonstrated interference in virus assembly, causing a reduction in virus yield. In addition, there is a lag in the appearance of virus-induced cellular morphologic alterations, a delay in cleavage of host cell protein p220 and in shutoff of host protein synthesis, and a decrease in viral protein and RNA synthesis. The implications of using E-64-based compounds as potential antiviral agents for FMDV are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett A. J., Kembhavi A. A., Hanada K. E-64 [L-trans-epoxysuccinyl-leucyl-amido(4-guanidino)butane] and related epoxides as inhibitors of cysteine proteinases. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1981;40(10-11):1513–1517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J. Viral cysteine proteases are homologous to the trypsin-like family of serine proteases: structural and functional implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7872–7876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that does not selectively inhibit host cell protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2913–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Newman J. F., Filman D., Hogle J. M., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Myristylation of picornavirus capsid protein VP4 and its structural significance. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):482–486. doi: 10.1038/327482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaney M. A., Vakharia V. N., Lloyd R. E., Ehrenfeld E., Grubman M. J. Leader protein of foot-and-mouth disease virus is required for cleavage of the p220 component of the cap-binding protein complex. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4407–4409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4407-4409.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina T., Tsukada K. Protease inhibitors prevent the development of human rotavirus-induced diarrhea in suckling mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1991;35(7):583–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1991.tb01589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Milburn S. C., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Hershey J. W. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis following poliovirus infection correlates with the proteolysis of a 220,000-dalton polypeptide associated with eucaryotic initiation factor 3 and a cap binding protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14806–14810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Lai M. M. Putative papain-related thiol proteases of positive-strand RNA viruses. Identification of rubi- and aphthovirus proteases and delineation of a novel conserved domain associated with proteases of rubi-, alpha- and coronaviruses. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 19;288(1-2):201–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81034-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman M. J., Baxt B. Translation of foot-and-mouth disease virion RNA and processing of the primary cleavage products in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate. Virology. 1982 Jan 15;116(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90399-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman M. J., Morgan D. O., Kendall J., Baxt B. Capsid intermediates assembled in a foot-and-mouth disease virus genome RNA-programmed cell-free translation system and in infected cells. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):120–126. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.120-126.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman M. J., Robertson B. H., Morgan D. O., Moore D. M., Dowbenko D. Biochemical map of polypeptides specified by foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):579–586. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.579-586.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
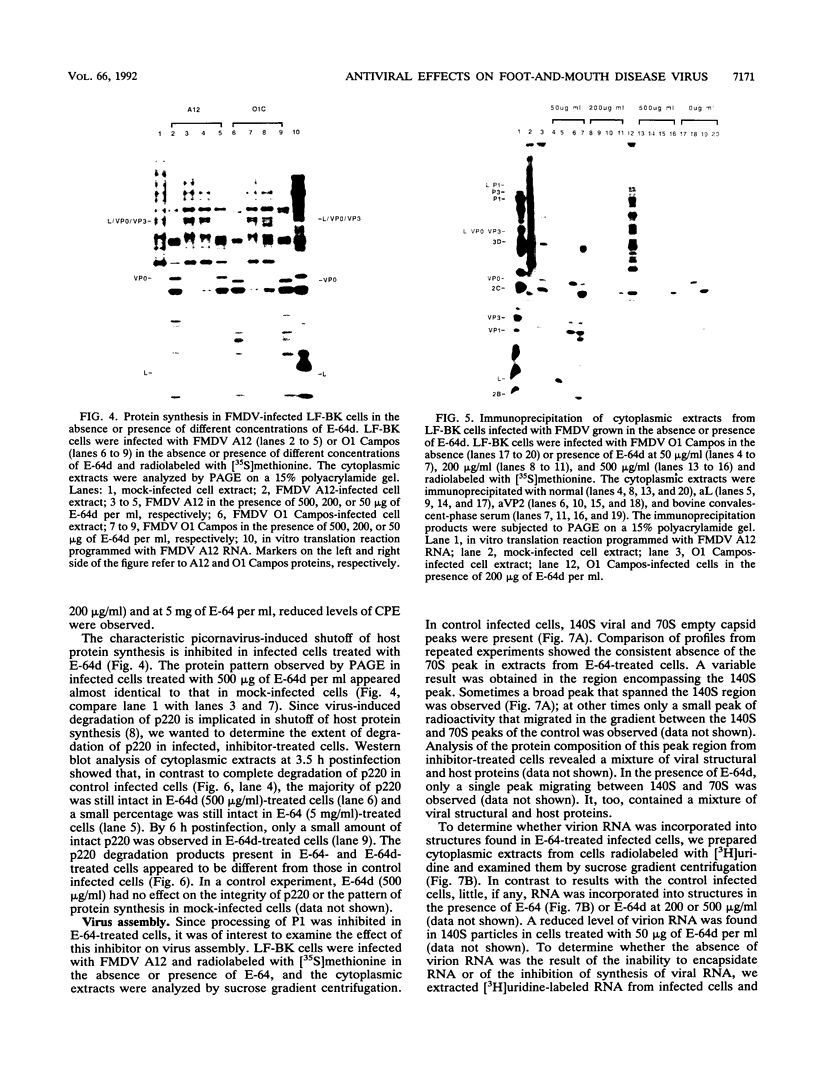
- Grubman M. J., Zellner M., Wagner J. Antigenic comparison of the polypeptides of foot-and-mouth disease virus serotypes and other picornaviruses. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90246-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudecki M. S., Pollina C. M., Heffner R. R. Limited benefit to genetically dystrophic chickens from a synthetic proteinase inhibitor: Ep475. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Jul;60(1):55–66. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiura S., Hanada K., Tamai M., Kashiwagi K., Sugita H. The effect of an in vivo-injected thiol protease inhibitor, E-64-c, on the calcium-induced degeneration of myofilaments. J Biochem. 1981 Nov;90(5):1557–1560. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu K., Inazuki K., Hosoya J., Satoh S. Beneficial effect of new thiol protease inhibitors, epoxide derivatives, on dystrophic mice. Exp Neurol. 1986 Jan;91(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(86)90022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Toyoda H., Etchison D., Wimmer E. Poliovirus proteinase 2A induces cleavage of eucaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide p220. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2711–2718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2711-2718.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Wimmer E. Viral proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:701–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Morgan D. O., Grubman M. J. Expression, processing, and assembly of foot-and-mouth disease virus capsid structures in heterologous systems: induction of a neutralizing antibody response in guinea pigs. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6572–6580. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6572-6580.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. E., Grubman M. J., Ehrenfeld E. Relationship of p220 cleavage during picornavirus infection to 2A proteinase sequencing. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4216–4223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4216-4223.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. E., Toyoda H., Etchison D., Wimmer E., Ehrenfeld E. Cleavage of the cap binding protein complex polypeptide p220 is not effected by the second poliovirus protease 2A. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):299–303. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90291-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc D., Girard M., van der Werf S. A Gly1 to Ala substitution in poliovirus capsid protein VP0 blocks its myristoylation and prevents viral assembly. J Gen Virol. 1991 May;72(Pt 5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-5-1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdi S. Cell-penetrating inhibitors of calpain. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Apr;16(4):150–153. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosenkis J., Daniels-McQueen S., Janovec S., Duncan R., Hershey J. W., Grifo J. A., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. Shutoff of host translation by encephalomyocarditis virus infection does not involve cleavage of the eucaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide that accompanies poliovirus infection. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):643–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.643-645.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill R. E., Racaniello V. R. Inhibition of translation in cells infected with a poliovirus 2Apro mutant correlates with phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eucaryotic initiation factor 2. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5069–5075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5069-5075.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C. Proteolytic processing of picornaviral polyprotein. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:603–623. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.003131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks G. D., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C. Encephalomyocarditis virus 3C protease: efficient cell-free expression from clones which link viral 5' noncoding sequences to the P3 region. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.376-384.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. H., Grubman M. J., Weddell G. N., Moore D. M., Welsh J. D., Fischer T., Dowbenko D. J., Yansura D. G., Small B., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide and amino acid sequence coding for polypeptides of foot-and-mouth disease virus type A12. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):651–660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.651-660.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. D., Belsham G. J., King A. M. Specificity of enzyme-substrate interactions in foot-and-mouth disease virus polyprotein processing. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):35–45. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. D., King A. M., Thomas G. P. Cleavage of foot-and-mouth disease virus polyprotein is mediated by residues located within a 19 amino acid sequence. J Gen Virol. 1991 Nov;72(Pt 11):2727–2732. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-11-2727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G. Structure, function and evolution of picornaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71(Pt 11):2483–2501. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-11-2483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strebel K., Beck E. A second protease of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):893–899. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.893-899.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strebel K., Beck E., Strohmaier K., Schaller H. Characterization of foot-and-mouth disease virus gene products with antisera against bacterially synthesized fusion proteins. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):983–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.983-991.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaney L. M. A continuous bovine kidney cell line for routine assays of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Vet Microbiol. 1988 Sep;18(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamai M., Hanada K., Adachi T., Oguma K., Kashiwagi K., Omura S., Ohzeki M. Papain inhibitions by optically active E-64 analogs. J Biochem. 1981 Jul;90(1):255–257. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamai M., Omura S., Kimura M., Hanada K., Sugita H. Prolongation of life span of dystrophic hamster by cysteine proteinase inhibitor, loxistation (EST). J Pharmacobiodyn. 1987 Nov;10(11):678–681. doi: 10.1248/bpb1978.10.678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vakharia V. N., Devaney M. A., Moore D. M., Dunn J. J., Grubman M. J. Proteolytic processing of foot-and-mouth disease virus polyproteins expressed in a cell-free system from clone-derived transcripts. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3199–3207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3199-3207.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yafal A. G., Palma E. L. Morphogenesis of foot-and-mouth disease virus. I. Role of procapsids as virion Precursors. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):643–649. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.643-649.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. F., Lloyd R. E. Identification of essential amino acid residues in the functional activity of poliovirus 2A protease. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):615–625. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90602-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]