Abstract
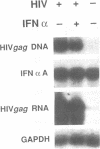
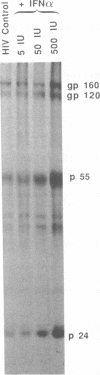
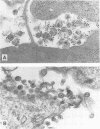
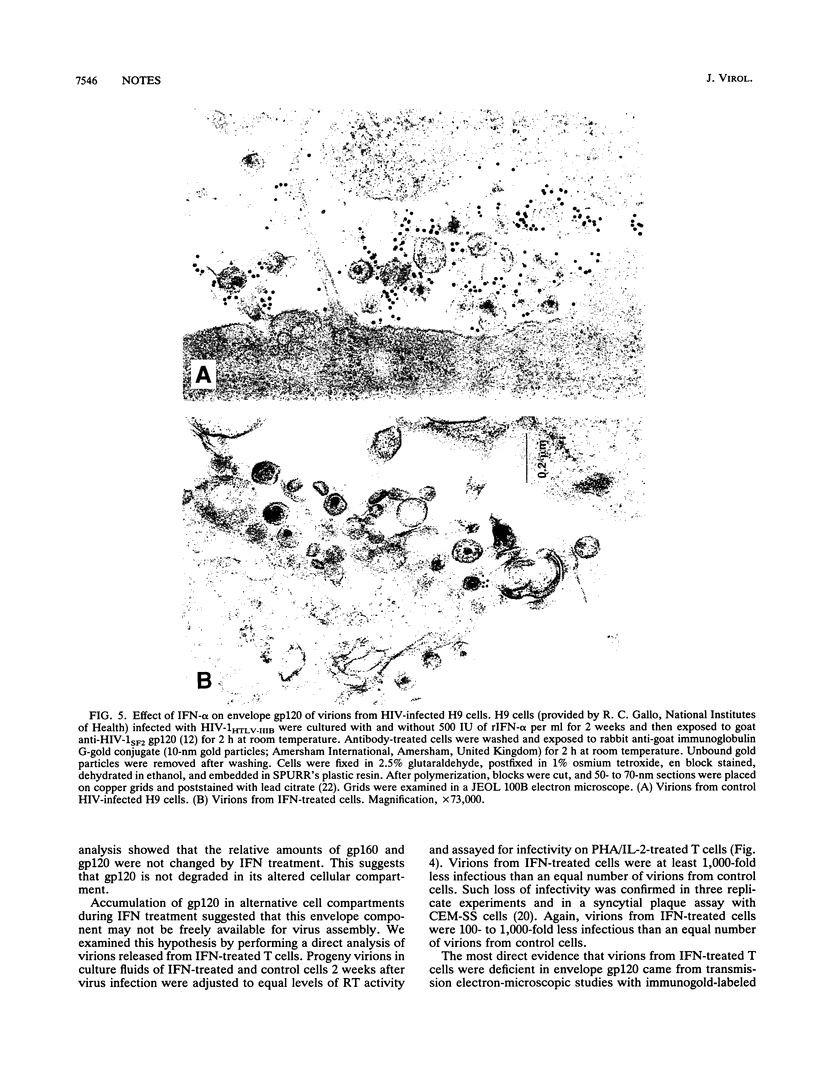
Levels of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) DNA, RNA, or p24 antigen and reverse transcriptase activity in T-cell cultures treated with 500 IU of recombinant alpha interferon (rIFN alpha) per ml were comparable to those in control cultures. Radioimmunoprecipitation analysis of proteins in lysates of IFN-treated T cells documented a marked accumulation of HIV proteins. Localization of gp120 by immunofluorescence showed a diffuse pattern in IFN-treated cells quite distinct from the ring pattern in untreated control cells. That large quantities of gp120 in aberrant cell compartments might affect HIV morphogenesis was confirmed in infectivity studies: virions from IFN-treated cells were 100- to 1,000-fold less infectious than an equal number of virions from control cells. Direct examination of IFN-treated and control HIV-infected cells by transmission electron microscopy showed little difference in the number or distribution of viral particles. However, quantitation of gp120 by immunogold particle analysis revealed a marked depletion of envelope glycoprotein in virions released from IFN-treated cells. This defect in gp120 assembly onto mature viral particles provides a molecular basis for this loss of infectivity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abb J., Zachoval R., Zachoval V., Deinhardt F. HIV antigen, HIV antibody and serum interferon in a patient with encephalopathy. Infection. 1987 Nov-Dec;15(6):425–426. doi: 10.1007/BF01647221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay A. K., Chang E. H., Levy C. C., Friedman R. M. Structural abnormalities in murine leukemia viruses produced by interferon-treated cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 27;87(4):983–988. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(79)80003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron S., Tyring S. K., Fleischmann W. R., Jr, Coppenhaver D. H., Niesel D. W., Klimpel G. R., Stanton G. J., Hughes T. K. The interferons. Mechanisms of action and clinical applications. JAMA. 1991 Sep 11;266(10):1375–1383. doi: 10.1001/jama.266.10.1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billiau A., Heremans H., Allens P. T., Baron S., de Somer P. Interferon inhibits C-type virus at a posttranscriptional, prerelease step. Arch Virol. 1978;57(3):205–220. doi: 10.1007/BF01315085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeStefano E., Friedman R. M., Friedman-Kien A. E., Goedert J. J., Henriksen D., Preble O. T., Sonnabend J. A., Vilcek J. Acid-labile human leukocyte interferon in homosexual men with Kaposi's sarcoma and lymphadenopathy. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):451–459. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedera D., Vander Heyden N., Ratner L. Attenuation of HIV-1 infectivity by an inhibitor of oligosaccharide processing. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Jun;6(6):785–794. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyster M. E., Goedert J. J., Poon M. C., Preble O. T. Acid-labile alpha interferon. A possible preclinical marker for the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in hemophilia. N Engl J Med. 1983 Sep 8;309(10):583–586. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198309083091003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernie B. F., Poli G., Fauci A. S. Alpha interferon suppresses virion but not soluble human immunodeficiency virus antigen production in chronically infected T-lymphocytic cells. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3968–3971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3968-3971.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Baca L. M., Turpin J., Kalter D. C., Hansen B., Orenstein J. M., Dieffenbach C. W., Friedman R. M., Meltzer M. S. Regulation of HIV replication in infected monocytes by IFN-alpha. Mechanisms for viral restriction. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2669–2676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay F. T., Dawood M. R., Friedman R. M. Interferon induces the production of membrane protein-deficient and infectivity-defective vesicular stomatitis virions through interference in the virion assembly process. J Gen Virol. 1983 Mar;64(Pt 3):707–712. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-3-707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth R. S., Oh P. S., Munis J. R., Cleveland P. H., Richman D. D. The role of interferons in the control of HIV replication in macrophages. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Feb;54(2):200–219. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Davey V., Kovacs J. A., Feinberg J., Metcalf J. A., Herpin B., Walker R., Deyton L., Davey R. T., Jr, Falloon J. Interferon-alpha in patients with asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Jun 1;112(11):805–811. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-11-805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layne S. P., Dembo M. The auto-regulation model: a unified concept of how HIV regulates its infectivity, pathogenesis and persistence. Int Rev Immunol. 1992;8(1):1–32. doi: 10.3109/08830189209056638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson A. R., Rutherford G. W., Jaffe H. W. The natural history of human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1360–1367. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari R. K., Demsey A. E., Mohanty S. B., Friedman R. M. Interferon-treated cells release vesicular stomatitis virus particles lacking glycoprotein spikes: correlation with biochemical data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2284–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari R. K., Friedman R. M. Effect of interferon treatment on vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV): release of unusual particles with low infectivity. Virology. 1980 Mar;101(2):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari R. K., Friedman R. M. Production of vesicular stomatitis virus with low infectivity by interferon-treated cells. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jul;44(1):261–264. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-1-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naso R. B., Wu Y. H., Edbauer C. A. Antiretroviral effect of interferon: proposed mechanism. J Interferon Res. 1982;2(1):75–96. doi: 10.1089/jir.1982.2.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein J. M., Meltzer M. S., Phipps T., Gendelman H. E. Cytoplasmic assembly and accumulation of human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 in recombinant human colony-stimulating factor-1-treated human monocytes: an ultrastructural study. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2578–2586. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2578-2586.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitha P. M. Multiple effects of interferon on HIV-1 replication. J Interferon Res. 1991 Dec;11(6):313–318. doi: 10.1089/jir.1991.11.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitha P. M., Wivel N. A., Fernie B. F., Harper H. P. Effect of interferon on murine leukaemia virus infection. IV. Formation of non-infectious virus in chronically infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1979 Mar;42(3):467–480. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-42-3-467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Orenstein J. M., Kinter A., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S. Interferon-alpha but not AZT suppresses HIV expression in chronically infected cell lines. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):575–577. doi: 10.1126/science.2470148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Antiviral actions of interferon. Interferon-regulated cellular proteins and their surprisingly selective antiviral activities. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90112-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Pinter A. Interferon-mediated inhibition of production of Gazdar murine sarcoma virus, a retrovirus lacking env proteins and containing an uncleaved gag precursor. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):403–407. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90492-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirazi Y., Pitha P. M. Alpha interferon inhibits early stages of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication cycle. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1321–1328. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1321-1328.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh V. K., Maheshwari R. K., Damewood G. P., 4th, Stephensen C. B., Oliver C., Friedman R. M. Interferon alters intracellular transport of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 1988 Apr-Jun;2(2):53–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. S., Thresher R. J., Pagano J. S. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 morphogenesis in T cells by alpha interferon. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):62–67. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadhan-Raj S., Wong G., Gnecco C., Cunningham-Rundles S., Krim M., Real F. X., Oettgen H. F., Krown S. E. Immunological variables as predictors of prognosis in patients with Kaposi's sarcoma and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Cancer Res. 1986 Jan;46(1):417–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey R. L., Bonifacino J. S., Potts B. J., Martin M. A., Klausner R. D. Biosynthesis, cleavage, and degradation of the human immunodeficiency virus 1 envelope glycoprotein gp160. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9580–9584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda Y., Miyake S., Kato S., Kita M., Kishida T., Kimura T., Ikuta K. Interferon-alpha treatment leads to accumulation of virus particles on the surface of cells persistently infected with the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(11):1046–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Sydow M., Sönnerborg A., Gaines H., Strannegård O. Interferon-alpha and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in serum of patients in various stages of HIV-1 infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Apr;7(4):375–380. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]