Abstract
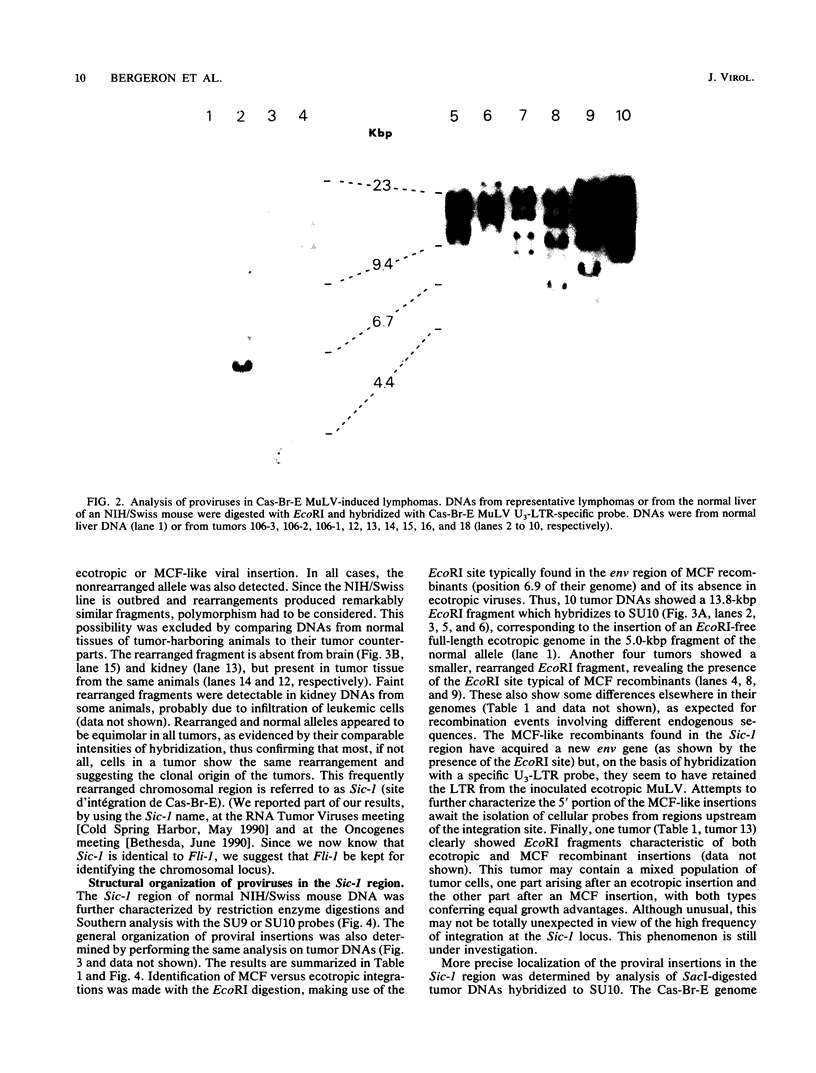
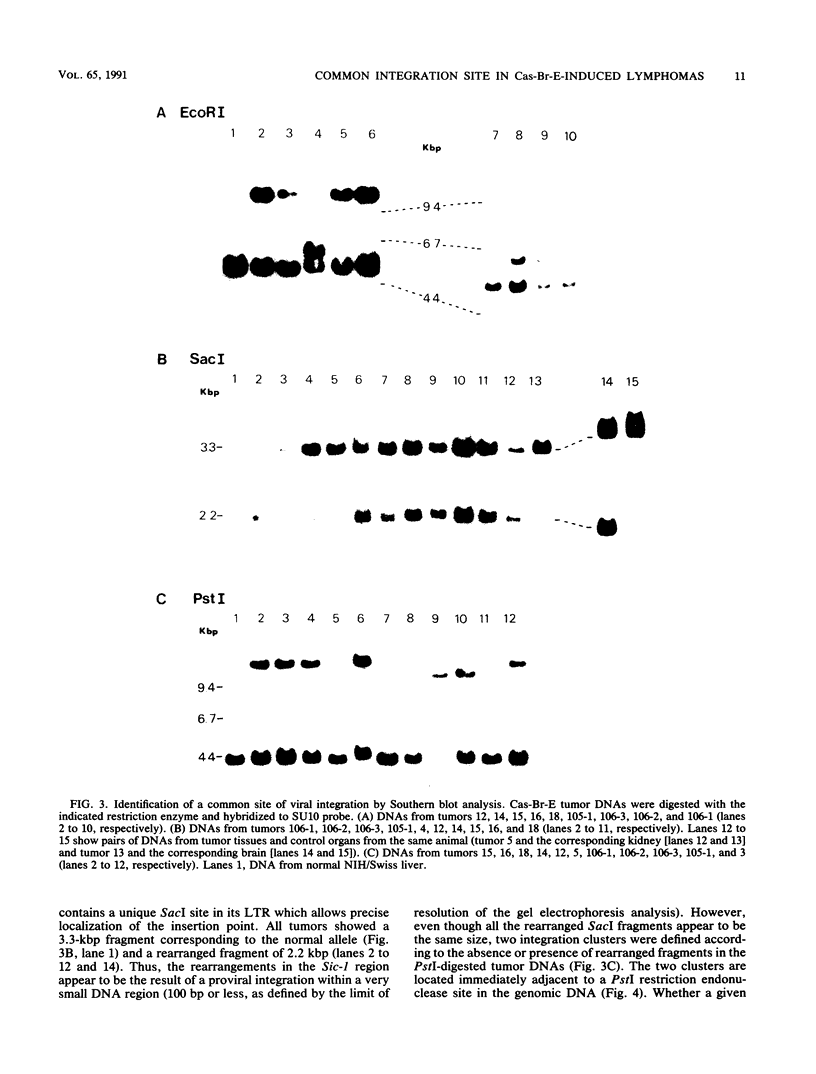
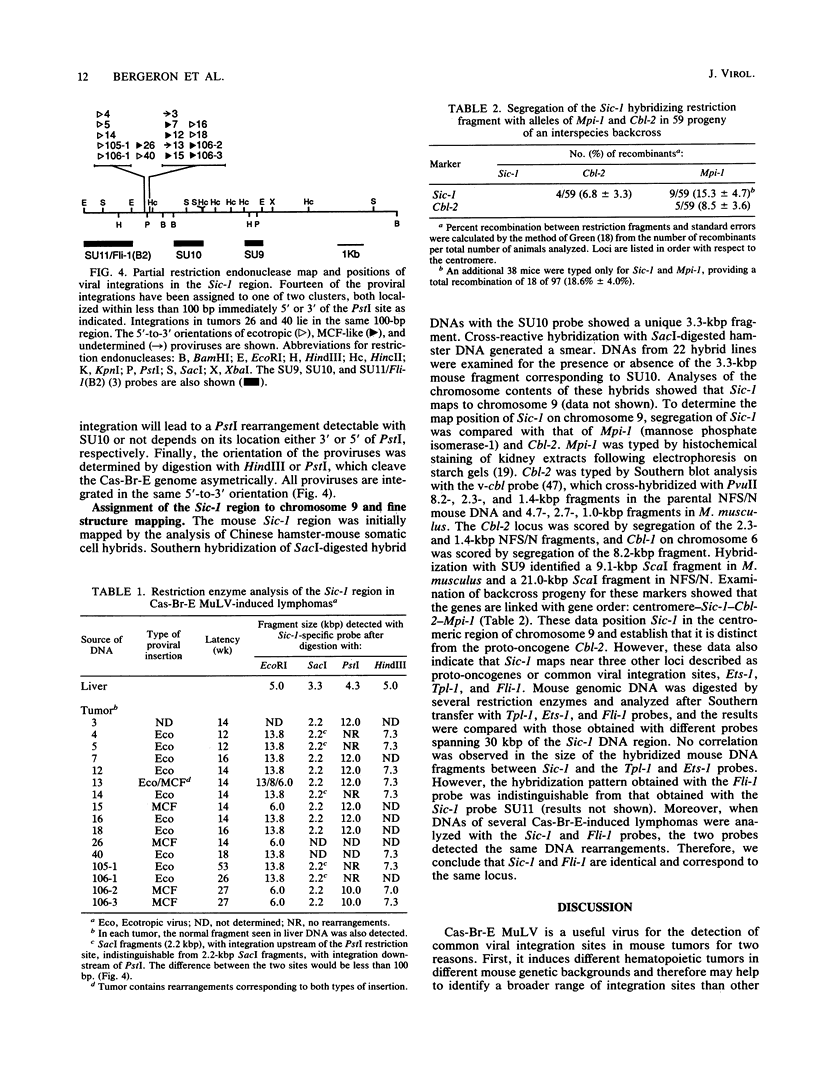
The Cas-Br-E murine leukemia virus is a nondefective retrovirus that induces non-T-, non-B-cell lymphomas in susceptible NIH/Swiss mice. By using a DNA probe derived from Cas-Br-E provirus-flanking sequences, we identified a DNA region, originally called Sic-1, rearranged in 16 of 24 tumors analyzed (67%). All proviruses were integrated in a DNA segment smaller than 100 bp and were in the same 5'-to-3' orientation. Ecotropic as well as mink cell focus-forming virus types were found integrated in that specific DNA region. On the basis of Southern blot analysis of somatic cell hybrids and progeny of an interspecies backcross, the Sic-1 region was localized on mouse chromosome 9 near the previously described proto-oncogenes or common viral integration sites: Ets-1, Cbl-2, Tpl-1, and Fli-1. Restriction map analysis shows that this region is identical to the Fli-1 locus identified in Friend murine leukemia virus-induced erythroleukemia cell lines and thus may contain sequences also responsible for the development of mouse non-T-, non-B-cell lymphomas.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Rosenberg N., Casanova R. J., Thomas E., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain expression and class switching in a murine leukaemia cell line. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):325–331. doi: 10.1038/296325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear S. E., Bellacosa A., Lazo P. A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Hanson C., Levan G., Tsichlis P. N. Provirus insertion in Tpl-1, an Ets-1-related oncogene, is associated with tumor progression in Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced rat thymic lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7495–7499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-David Y., Giddens E. B., Bernstein A. Identification and mapping of a common proviral integration site Fli-1 in erythroleukemia cells induced by Friend murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1332–1336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuer M. L., Cuypers H. T., Berns A. Evidence for the involvement of pim-2, a new common proviral insertion site, in progression of lymphomas. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):743–748. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. L., Scott J. L., Pal B. K., Estes J. D., Gardner M. B. Immunopathology of natural and experimental lymphomas induced by wild mouse leukemia virus. Am J Pathol. 1981 Sep;104(3):272–282. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caccia N., Kronenberg M., Saxe D., Haars R., Bruns G. A., Goverman J., Malissen M., Willard H., Yoshikai Y., Simon M. The T cell receptor beta chain genes are located on chromosome 6 in mice and chromosome 7 in humans. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1091–1099. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90443-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Baroudy B. M., Holmes K. L., Fredrickson T. N., Lander M. R., Morse H. C., 3rd, Hartley J. W. Biologic and molecular genetic characteristics of a unique MCF virus that is highly leukemogenic in ecotropic virus-negative mice. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):90–100. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90407-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Adams J. M., Dunn A. R., Cory S. Murine T lymphomas in which the cellular myc oncogene has been activated by retroviral insertion. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90306-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G., Quint W., Zijlstra M., Maandag E. R., Boelens W., van Wezenbeek P., Melief C., Berns A. Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolcetti R., Rizzo S., Viel A., Maestro R., De Re V., Feriotto G., Boiocchi M. N-myc activation by proviral insertion in MCF 247-induced murine T-cell lymphomas. Oncogene. 1989 Aug;4(8):1009–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson T. N., Langdon W. Y., Hoffman P. M., Hartley J. W., Morse H. C., 3rd Histologic and cell surface antigen studies of hematopoietic tumors induced by Cas-Br-M murine leukemia virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 Feb;72(2):447–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallahan D., Kozak C., Callahan R. A new common integration region (int-3) for mouse mammary tumor virus on mouse chromosome 17. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):218–220. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.218-220.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M., Wellinger R., Vessaz A., Diggelmann H. A new site of integration for mouse mammary tumor virus proviral DNA common to BALB/cf(C3H) mammary and kidney adenocarcinomas. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):127–134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B. Type C viruses of wild mice: characterization and natural history of amphotropic, ecotropic, and xenotropic MuLv. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;79:215–259. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66853-1_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gisselbrecht S., Fichelson S., Sola B., Bordereaux D., Hampe A., André C., Galibert F., Tambourin P. Frequent c-fms activation by proviral insertion in mouse myeloblastic leukaemias. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):259–261. doi: 10.1038/329259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Naturally occurring murine leukemia viruses in wild mice: characterization of a new "amphotropic" class. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):19–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.19-25.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. M., Davidson W. F., Ruscetti S. K., Chused T. M., Morse H. C., 3rd Wild mouse ecotropic murine leukemia virus infection of inbred mice: dual-tropic virus expression precedes the onset of paralysis and lymphoma. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):597–602. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.597-602.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoggan M. D., Halden N. F., Buckler C. E., Kozak C. A. Genetic mapping of the mouse c-fms proto-oncogene to chromosome 18. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):1055–1056. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.1055-1056.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. L., Langdon W. Y., Fredrickson T. N., Coffman R. L., Hoffman P. M., Hartley J. W., Morse H. C., 3rd Analysis of neoplasms induced by Cas-Br-M MuLV tumor extracts. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):679–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Smith-White B., Sisson B., Parker D., Blair D. G., Schultz A., Kozak C., Lunsford R. D., Askew D., Weinstein Y. Activation of the c-H-ras proto-oncogene by retrovirus insertion and chromosomal rearrangement in a Moloney leukemia virus-induced T-cell leukemia. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2959–2966. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2959-2966.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P., DesGroseillers L. Neurotropic Cas-BR-E murine leukemia virus harbors several determinants of leukemogenicity mapping in different regions of the genome. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):639–643. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.639-643.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P., Nicolaiew N., DesGroseillers L., Rassart E. Molecular cloning of infectious viral DNA from ecotropic neurotropic wild mouse retrovirus. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1159–1163. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1159-1163.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley D. M., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. A molecular genetic linkage map of mouse chromosome 9 with regional localizations for the Gsta, T3g, Ets-1 and Ldlr loci. Genetics. 1989 Sep;123(1):165–172. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehne C. F., Lazo P. A., Alves K., Lee J. S., Tsichlis P. N., O'Donnell P. V. The Mlvi-1 locus involved in the induction of rat T-cell lymphomas and the pvt-1/Mis-1 locus are identical. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2366–2369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2366-2369.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langdon W. Y., Hartley J. W., Klinken S. P., Ruscetti S. K., Morse H. C., 3rd v-cbl, an oncogene from a dual-recombinant murine retrovirus that induces early B-lineage lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1168–1172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau-Gachelin F., Tavitian A., Tambourin P. Spi-1 is a putative oncogene in virally induced murine erythroleukaemias. Nature. 1988 Jan 21;331(6153):277–280. doi: 10.1038/331277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita K., Parker D. S., Mucenski M. L., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Ihle J. N. Retroviral activation of a novel gene encoding a zinc finger protein in IL-3-dependent myeloid leukemia cell lines. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):831–840. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mucenski M. L., Gilbert D. J., Taylor B. A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Common sites of viral integration in lymphomas arising in AKXD recombinant inbred mouse strains. Oncogene Res. 1987;2(1):33–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mucenski M. L., Taylor B. A., Ihle J. N., Hartley J. W., Morse H. C., 3rd, Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Identification of a common ecotropic viral integration site, Evi-1, in the DNA of AKXD murine myeloid tumors. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):301–308. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau J. H. Maps of linkage and synteny homologies between mouse and man. Trends Genet. 1989 Mar;5(3):82–86. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel B. G., Hayward W. S., Robinson H. L., Fang J., Astrin S. M. Avian leukosis virus-induced tumors have common proviral integration sites and synthesize discrete new RNAs: oncogenesis by promoter insertion. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil J. C., Forrest D. Mechanisms of retrovirus-induced leukaemia: selected aspects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 20;907(1):71–91. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(87)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn M. F., Seeburg P. H., Moscovici C., Duesberg P. H. Tripartite structure of the avian erythroblastosis virus E26 transforming gene. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):391–395. doi: 10.1038/306391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., Varmus H. E. Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90409-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattengale P. K., Taylor C. R. Experimental models of lymphoproliferative disease. The mouse as a model for human non-Hodgkin's lymphomas and related leukemias. Am J Pathol. 1983 Nov;113(2):237–265. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Lee A. E., Dickson C. Concerted activation of two potential proto-oncogenes in carcinomas induced by mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):628–631. doi: 10.1038/320628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier Y., Jolicoeur P. Distinct helper virus requirements for Abelson murine leukemia virus-induced pre-B- and T-cell lymphomas. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2088–2098. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2088-2098.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier Y., Kozak C., Jolicoeur P. Identification of a common helper provirus integration site in Abelson murine leukemia virus-induced lymphoma DNA. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3985–3992. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3985-3992.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quint W., Quax W., van der Putten H., Berns A. Characterization of AKR murine leukemia virus sequences in AKR mouse substrains and structure of integrated recombinant genomes in tumor tissues. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):1–10. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.1-10.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in avian leukosis virus-induced erythroblastosis: clustered integration sites and the arrangement of provirus in the c-erbB alleles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2287–2291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassart E., DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. Molecular cloning of B- and N-tropic endogenous BALB/c murine leukemia virus circular DNA intermediates: isolation and characterization of infectious recombinant clones. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):162–171. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.162-171.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassart E., Nelbach L., Jolicoeur P. Cas-Br-E murine leukemia virus: sequencing of the paralytogenic region of its genome and derivation of specific probes to study its origin and the structure of its recombinant genomes in leukemic tissues. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):910–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.910-919.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regnier D. C., Kozak C. A., Kingsley D. M., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Langdon W. Y., Morse H. C., 3rd Identification of two murine loci homologous to the v-cbl oncogene. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3678–3682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3678-3682.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohdewohld H., Weiher H., Reik W., Jaenisch R., Breindl M. Retrovirus integration and chromatin structure: Moloney murine leukemia proviral integration sites map near DNase I-hypersensitive sites. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):336–343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.336-343.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi A. Y., Lalley P. A., Zabel B. U., Ellis R. W., Scolnick E. M., Naylor S. L. Chromosome assignments of four mouse cellular homologs of sarcoma and leukemia virus oncogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):525–529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherdin U., Rhodes K., Breindl M. Transcriptionally active genome regions are preferred targets for retrovirus integration. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):907–912. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.907-912.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Boelens W., Robanus-Maandag E., Verbeek J., Domen J., van Beveren C., Berns A. The primary structure of the putative oncogene pim-1 shows extensive homology with protein kinases. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):603–611. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90886-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Wolff L. Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced myeloid tumors in adult BALB/c mice: requirement of c-myb activation but lack of v-abl involvement. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3721–3725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3721-3725.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C. C., Stoye J. P., Coffin J. M. Highly preferred targets for retrovirus integration. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):531–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90569-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Kozak C. Common proviral integration region on mouse chromosome 7 in lymphomas and myelogenous leukemias induced by Friend murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):526–533. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.526-533.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sola B., Fichelson S., Bordereaux D., Tambourin P. E., Gisselbrecht S. fim-1 and fim-2: two new integration regions of Friend murine leukemia virus in myeloblastic leukemias. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):718–725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.718-725.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sola B., Simon D., Mattéi M. G., Fichelson S., Bordereaux D., Tambourin P. E., Guenet J. L., Gisselbrecht S. Fim-1, Fim-2/c-fms, and Fim-3, three common integration sites of Friend murine leukemia virus in myeloblastic leukemias, map to mouse chromosomes 13, 18, and 3, respectively. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3973–3978. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3973-3978.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Shepherd B. M., Bear S. E. Activation of the Mlvi-1/mis1/pvt-1 locus in Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5487–5491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Lohse M. A. Concerted DNA rearrangements in Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced thymomas: a potential synergistic relationship in oncogenesis. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):258–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.258-267.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijaya S., Steffen D. L., Kozak C., Robinson H. L. Dsi-1, a region with frequent proviral insertions in Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced rat thymomas. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1164–1170. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1164-1170.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijaya S., Steffen D. L., Robinson H. L. Acceptor sites for retroviral integrations map near DNase I-hypersensitive sites in chromatin. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):683–692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.683-692.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villemur R., Monczak Y., Rassart E., Kozak C., Jolicoeur P. Identification of a new common provirus integration site in gross passage A murine leukemia virus-induced mouse thymoma DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):512–522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., McWilliams-Smith M. J., Kozak C., Reeves R., Gearhart J., Nunn M. F., Nash W., Fowle J. R., 3rd, Duesberg P., Papas T. S. Conserved chromosomal positions of dual domains of the ets protooncogene in cats, mice, and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1792–1796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein Y., Cleveland J. L., Askew D. S., Rapp U. R., Ihle J. N. Insertion and truncation of c-myb by murine leukemia virus in a myeloid cell line derived from cultures of normal hematopoietic cells. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2339–2343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2339-2343.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein Y., Ihle J. N., Lavu S., Reddy E. P. Truncation of the c-myb gene by a retroviral integration in an interleukin 3-dependent myeloid leukemia cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5010–5014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff L., Koller R. Regions of the Moloney murine leukemia virus genome specifically related to induction of promonocytic tumors. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):155–160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.155-160.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lohuizen M., Breuer M., Berns A. N-myc is frequently activated by proviral insertion in MuLV-induced T cell lymphomas. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):133–136. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]