Abstract
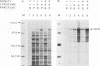
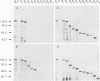
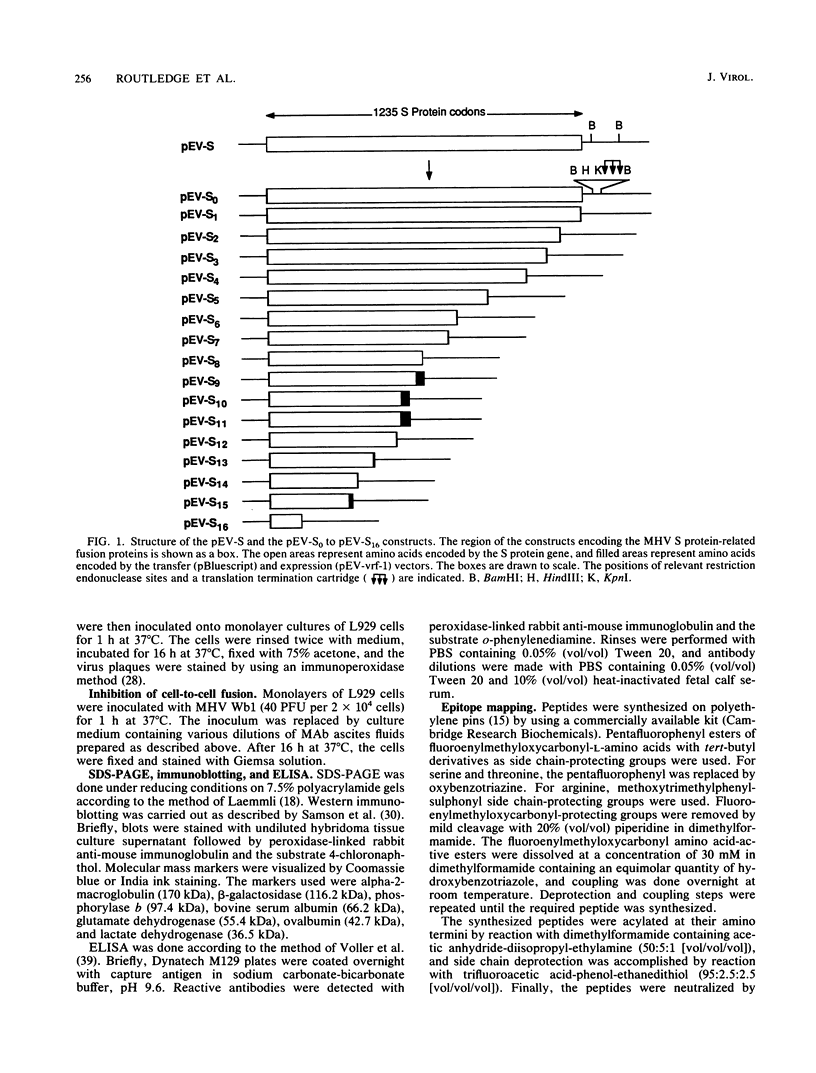
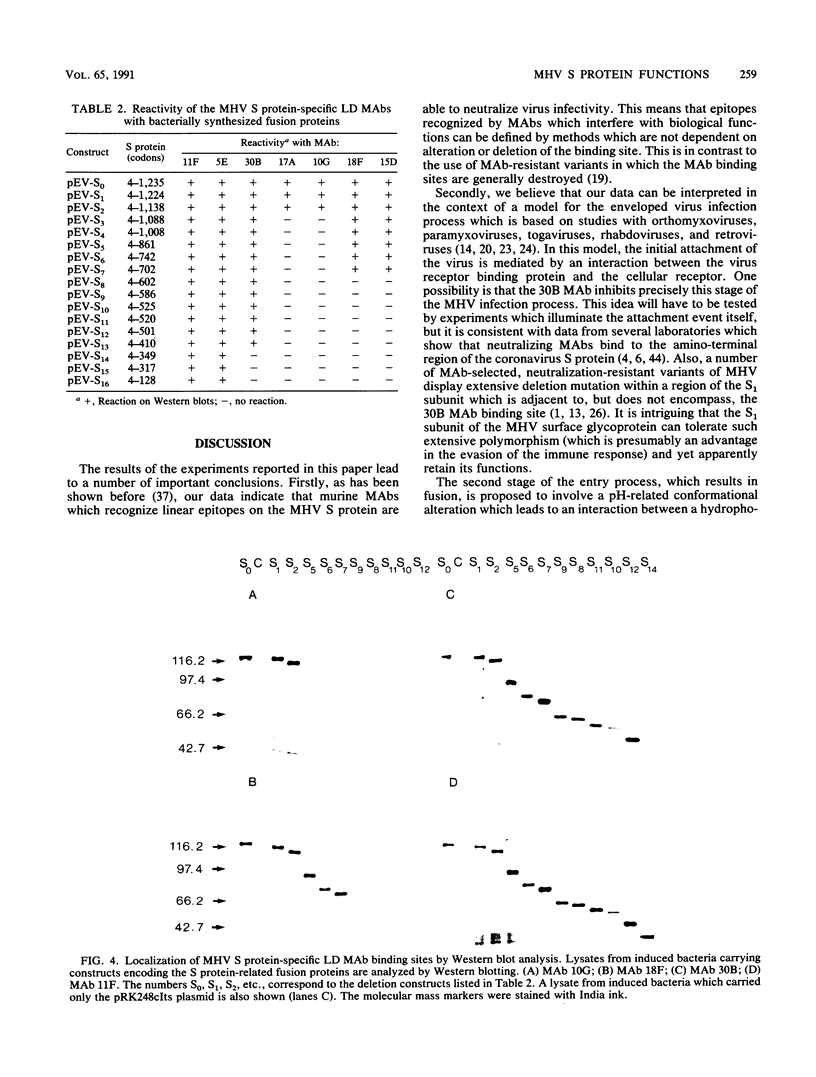
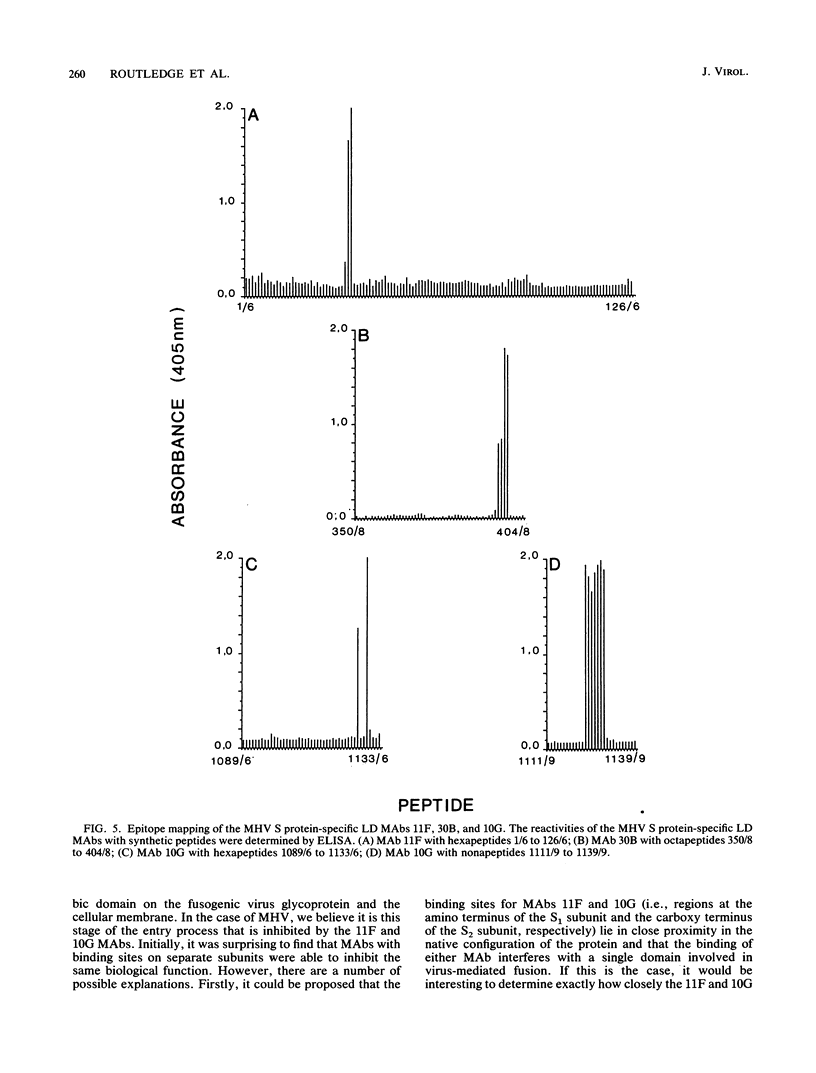
The murine coronavirus surface glycoprotein gene was expressed as a fusion protein in bacteria, and the expressed protein was used to generate S protein-specific monoclonal antibodies (MAbs). Three of the MAbs, 11F, 30B, and 10G, were able to neutralize virus infectivity, and two of them, 11F and 10G, were able to block virus-induced, cell-to-cell fusion. The binding sites of the 11F, 30B, and 10G MAbs were determined by Western immunoblotting and epitope mapping. The 11F and 30B MAbs bound to sites located, respectively, between amino acids 33 to 40 and 395 to 406 in the amino-terminal (S1) subunit of the S protein, and the 10G MAb bound to a site located between amino acids 1123 and 1137 in the carboxy-terminal (S2) subunit. These data define more precisely the interactions between the S1 and S2 subunits of the murine coronavirus S protein and provide further insights into its structure and function.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banner L. R., Keck J. G., Lai M. M. A clustering of RNA recombination sites adjacent to a hypervariable region of the peplomer gene of murine coronavirus. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):548–555. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90439-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard H. U., Helinski D. R. Use of the lambda phage promoter PL to promote gene expression in hybrid plasmid cloning vehicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:482–492. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh D. Coronavirus IBV: structural characterization of the spike protein. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2577–2583. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh D., Davis P. J., Darbyshire J. H., Peters R. W. Coronavirus IBV: virus retaining spike glycopolypeptide S2 but not S1 is unable to induce virus-neutralizing or haemagglutination-inhibiting antibody, or induce chicken tracheal protection. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jul;67(Pt 7):1435–1442. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-7-1435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A. R., Knobler R. L., Powell H., Buchmeier M. J. Monoclonal antibodies to murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM) define the viral glycoprotein responsible for attachment and cell--cell fusion. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):358–371. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90095-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa I., Gebauer F., Bullido M. J., Suñ C., Baay M. F., Zwaagstra K. A., Posthumus W. P., Lenstra J. A., Enjuanes L. Localization of antigenic sites of the E2 glycoprotein of transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus. J Gen Virol. 1990 Feb;71(Pt 2):271–279. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-2-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowl R., Seamans C., Lomedico P., McAndrew S. Versatile expression vectors for high-level synthesis of cloned gene products in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90200-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel R. G., Lampert P. W., Talbot P. J., Buchmeier M. J. Site-specific alteration of murine hepatitis virus type 4 peplomer glycoprotein E2 results in reduced neurovirulence. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):463–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.463-471.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels R. S., Downie J. C., Hay A. J., Knossow M., Skehel J. J., Wang M. L., Wiley D. C. Fusion mutants of the influenza virus hemagglutinin glycoprotein. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):431–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90157-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Helenius A. Quaternary structure of influenza virus hemagglutinin after acid treatment. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):833–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.833-839.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frana M. F., Behnke J. N., Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V. Proteolytic cleavage of the E2 glycoprotein of murine coronavirus: host-dependent differences in proteolytic cleavage and cell fusion. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):912–920. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.912-920.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher T. M., Parker S. E., Buchmeier M. J. Neutralization-resistant variants of a neurotropic coronavirus are generated by deletions within the amino-terminal half of the spike glycoprotein. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):731–741. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.731-741.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Meloen R. H., Barteling S. J. Use of peptide synthesis to probe viral antigens for epitopes to a resolution of a single amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumanishi T. Brain tumors induced with Rous sarcoma virus, Schmidt-Ruppin strain. I. Induction of brain tumors in adult mice with Rous chicken sarcoma cells. Jpn J Exp Med. 1967 Oct;37(5):461–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Air G. M., Webster R. G., Smith-Gill S. J. Epitopes on protein antigens: misconceptions and realities. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):553–556. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90464-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz T. L. The recognition event between virus and host cell receptor: a target for antiviral agents. J Gen Virol. 1990 Apr;71(Pt 4):751–766. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-4-751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luytjes W., Geerts D., Posthumus W., Meloen R., Spaan W. Amino acid sequence of a conserved neutralizing epitope of murine coronaviruses. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1408–1412. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1408-1412.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luytjes W., Sturman L. S., Bredenbeek P. J., Charite J., van der Zeijst B. A., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. Primary structure of the glycoprotein E2 of coronavirus MHV-A59 and identification of the trypsin cleavage site. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):479–487. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90142-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Virus entry into animal cells. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:107–151. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60583-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachuk C. J., Bredenbeek P. J., Zoltick P. W., Spaan W. J., Weiss S. R. Molecular cloning of the gene encoding the putative polymerase of mouse hepatitis coronavirus, strain A59. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90520-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker S. E., Gallagher T. M., Buchmeier M. J. Sequence analysis reveals extensive polymorphism and evidence of deletions within the E2 glycoprotein gene of several strains of murine hepatitis virus. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):664–673. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90579-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasschaert D., Laude H. The predicted primary structure of the peplomer protein E2 of the porcine coronavirus transmissible gastroenteritis virus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jul;68(Pt 7):1883–1890. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-7-1883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge E. G., Willcocks M. M., Samson A. C., Morgan L., Scott R., Anderson J. J., Toms G. L. The purification of four respiratory syncytial virus proteins and their evaluation as protective agents against experimental infection in BALB/c mice. J Gen Virol. 1988 Feb;69(Pt 2):293–303. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-2-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson A. C., Willcocks M. M., Routledge E. G., Morgan L. A., Toms G. L. A neutralizing monoclonal antibody to respiratory syncytial virus which binds to both F1 and F2 components of the fusion protein. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jul;67(Pt 7):1479–1483. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-7-1479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt I., Skinner M., Siddell S. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the surface projection glycoprotein of coronavirus MHV-JHM. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):47–56. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz B., Routledge E., Siddell S. G. Murine coronavirus nonstructural protein ns2 is not essential for virus replication in transformed cells. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4784–4791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4784-4791.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S. G. Coronavirus JHM: tryptic peptide fingerprinting of virion proteins and intracellular polypeptides. J Gen Virol. 1982 Oct;62(Pt 2):259–269. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-2-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S. G., Wege H., Barthel A., ter Meulen V. Coronavirus JHM: cell-free synthesis of structural protein p60. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):10–17. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.10-17.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W., Cavanagh D., Horzinek M. C. Coronaviruses: structure and genome expression. J Gen Virol. 1988 Dec;69(Pt 12):2939–2952. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-12-2939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot P. J., Salmi A. A., Knobler R. L., Buchmeier M. J. Topographical mapping of epitopes on the glycoproteins of murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM): correlation with biological activities. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):250–260. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90032-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennema H., Heijnen L., Zijderveld A., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. Intracellular transport of recombinant coronavirus spike proteins: implications for virus assembly. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):339–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.339-346.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Siddell S., ter Meulen V. The biology and pathogenesis of coronaviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;99:165–200. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68528-6_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Winter J., Meyermann R. The peplomer protein E2 of coronavirus JHM as a determinant of neurovirulence: definition of critical epitopes by variant analysis. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):87–98. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland E., Mussgay M., Weiland F. Nonproducer malignant tumor cells with rescuable sarcoma virus genome isolated from a recurrent Moloney sarcoma. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):408–423. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weismiller D. G., Sturman L. S., Buchmeier M. J., Fleming J. O., Holmes K. V. Monoclonal antibodies to the peplomer glycoprotein of coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus identify two subunits and detect a conformational change in the subunit released under mild alkaline conditions. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3051–3055. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3051-3055.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. J., Luytjes W., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A., Spaan W. J., Lenstra J. A. Evidence for a coiled-coil structure in the spike proteins of coronaviruses. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):963–966. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90422-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]