Abstract
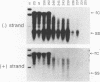
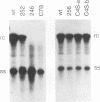
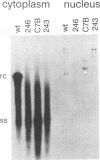
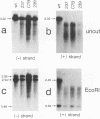
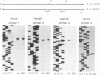
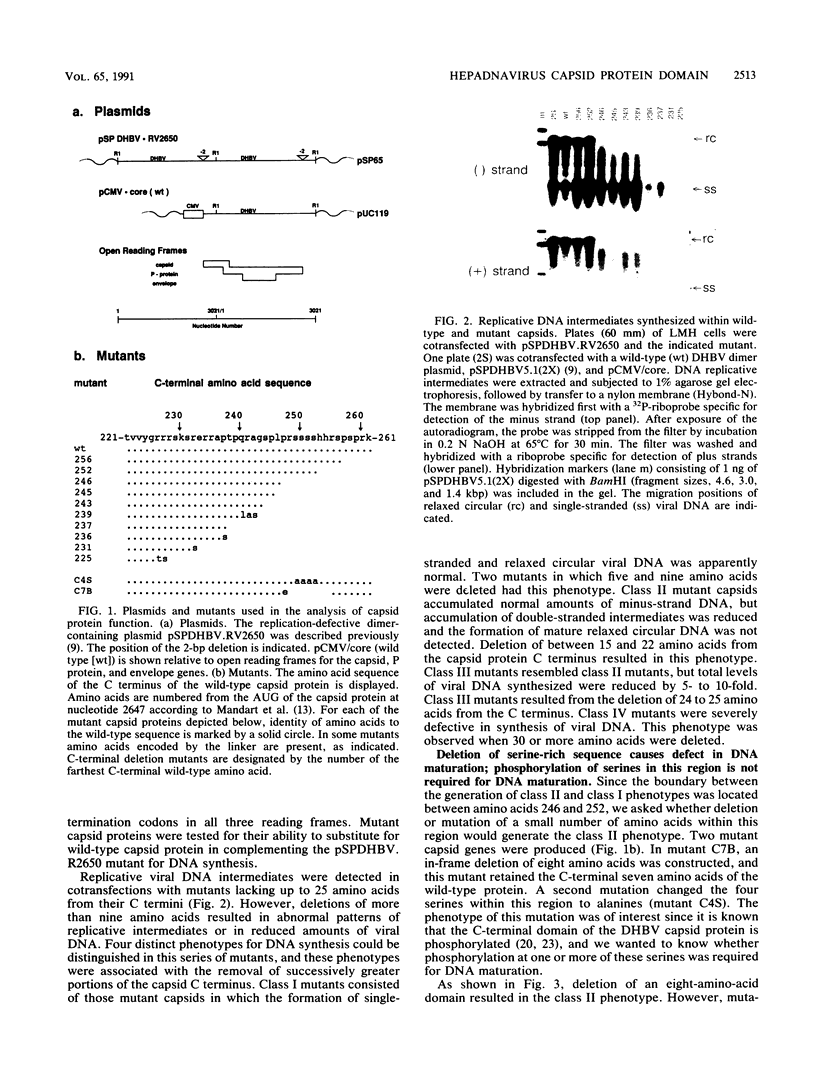
Mutations introduced into the capsid gene of duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) were tested for their effects on viral DNA synthesis and assembly of enveloped viruses. Four classes of mutant phenotypes were observed among a series of deletions of covering the 3' end of the capsid open reading frame. Class I mutant capsids were able to support normal single-stranded and relaxed circular viral DNA synthesis; class II mutant capsids supported normal single-stranded DNA synthesis but not relaxed circular DNA synthesis; class III mutant capsids resembled class II capsids, but viral DNA synthesis was inhibited 5- to 10-fold; and class IV capsids were severely restricted in their ability to support viral DNA synthesis. Class I capsids were assembled into enveloped virions, but class II, III, and IV capsids were not. Viral DNA synthesized inside class II capsids was normal with respect to minus-strand DNA initiation, plus-strand DNA initiation, and circularization of the DNA, but plus strands failed to be elongated to mature 3-kb DNA. The results suggest that a function of the capsid protein specifically required for viral DNA maturation is also required for assembly of nucleocapsids into envelopes. Thus, class II mutants appear to be defective in the appearance of the "packaging signal" for virus assembly (J. Summers and W. Mason, Cell 29:403-415, 1982).
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartenschlager R., Junker-Niepmann M., Schaller H. The P gene product of hepatitis B virus is required as a structural component for genomic RNA encapsidation. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5324–5332. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5324-5332.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartenschlager R., Schaller H. The amino-terminal domain of the hepadnaviral P-gene encodes the terminal protein (genome-linked protein) believed to prime reverse transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4185–4192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03315.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum F., Nassal M. Hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid assembly: primary structure requirements in the core protein. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3319–3330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3319-3330.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch V., Bartenschlager R., Radziwill G., Schaller H. The duck hepatitis B virus P-gene codes for protein strongly associated with the 5'-end of the viral DNA minus strand. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):475–485. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90518-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. J., Hirsch R. C., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Effects of insertional and point mutations on the functions of the duck hepatitis B virus polymerase. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5553–5558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5553-5558.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus occurs via a bimodal mechanism. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dane D. S., Cameron C. H., Briggs M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet. 1970 Apr 4;1(7649):695–698. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90926-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R. C., Lavine J. E., Chang L. J., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Polymerase gene products of hepatitis B viruses are required for genomic RNA packaging as wel as for reverse transcription. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):552–555. doi: 10.1038/344552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A. L., Furtak K., Pugh J., Summers J. Synthesis of hepadnavirus particles that contain replication-defective duck hepatitis B virus genomes in cultured HuH7 cells. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):642–650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.642-650.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi T., Nomura K., Hirayama Y., Kitagawa T. Establishment and characterization of a chicken hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, LMH. Cancer Res. 1987 Aug 15;47(16):4460–4464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lien J. M., Petcu D. J., Aldrich C. E., Mason W. S. Initiation and termination of duck hepatitis B virus DNA synthesis during virus maturation. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3832–3840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3832-3840.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandart E., Kay A., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned duck hepatitis B virus genome: comparison with woodchuck and human hepatitis B virus sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):782–792. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.782-792.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L., Oshiro L. S., Regnery D. C., Scullard G. H., Robinson W. S. A virus in Beechey ground squirrels that is related to hepatitis B virus of humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2941–2945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Aldrich C., Summers J., Taylor J. M. Asymmetric replication of duck hepatitis B virus DNA in liver cells: Free minus-strand DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3997–4001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Halpern M. S., England J. M., Seal G., Egan J., Coates L., Aldrich C., Summers J. Experimental transmission of duck hepatitis B virus. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90505-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Seal G., Summers J. Virus of Pekin ducks with structural and biological relatedness to human hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):829–836. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.829-836.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnar-Kimber K. L., Summers J. W., Mason W. S. Mapping of the cohesive overlap of duck hepatitis B virus DNA and of the site of initiation of reverse transcription. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):181–191. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.181-191.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto H., Ferchmin P. A., Bennett E. L. Spectrophotometric analysis of RNA and DNA using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Anal Biochem. 1974 Dec;62(2):436–448. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh J., Zweidler A., Summers J. Characterization of the major duck hepatitis B virus core particle protein. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1371–1376. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1371-1376.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziwill G., Tucker W., Schaller H. Mutational analysis of the hepatitis B virus P gene product: domain structure and RNase H activity. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):613–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.613-620.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Opazo N., Chakraborty P. R., Shafritz D. A. Evidence for supercoiled hepatitis B virus DNA in chimpanzee liver and serum Dane particles: possible implications in persistent HBV infection. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Bartenschlager R., Schaller H. The duck hepatitis B virus core protein contains a highly phosphorylated C terminus that is essential for replication but not for RNA packaging. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2995–3000. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2995-3000.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel R., Kaleta E. F., Will H. Isolation and characterization of a hepatitis B virus endemic in herons. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3832–3839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3832-3839.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Mason W. S. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B--like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):403–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smith P. M., Horwich A. L. Hepadnavirus envelope proteins regulate covalently closed circular DNA amplification. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2819–2824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2819-2824.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smith P. M., Huang M. J., Yu M. S. Morphogenetic and regulatory effects of mutations in the envelope proteins of an avian hepadnavirus. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1310–1317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1310-1317.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smolec J. M., Snyder R. A virus similar to human hepatitis B virus associated with hepatitis and hepatoma in woodchucks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4533–4537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttleman J. S., Pourcel C., Summers J. Formation of the pool of covalently closed circular viral DNA in hepadnavirus-infected cells. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90602-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]