Abstract
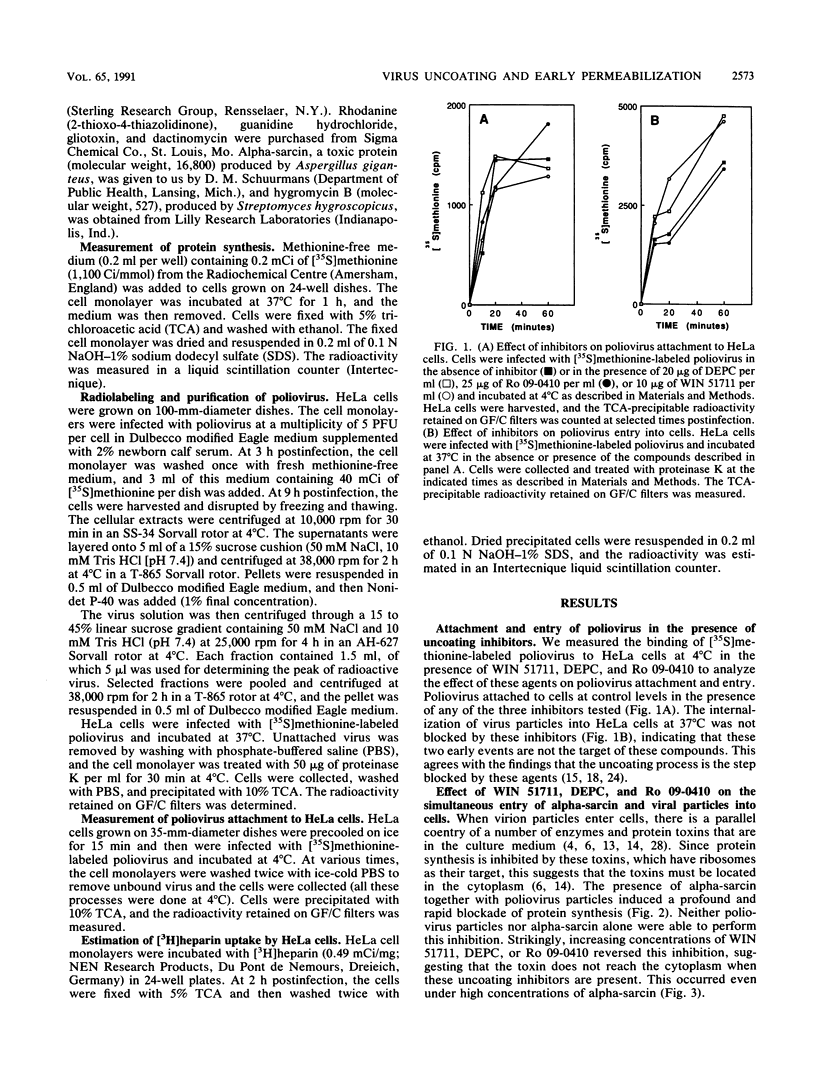
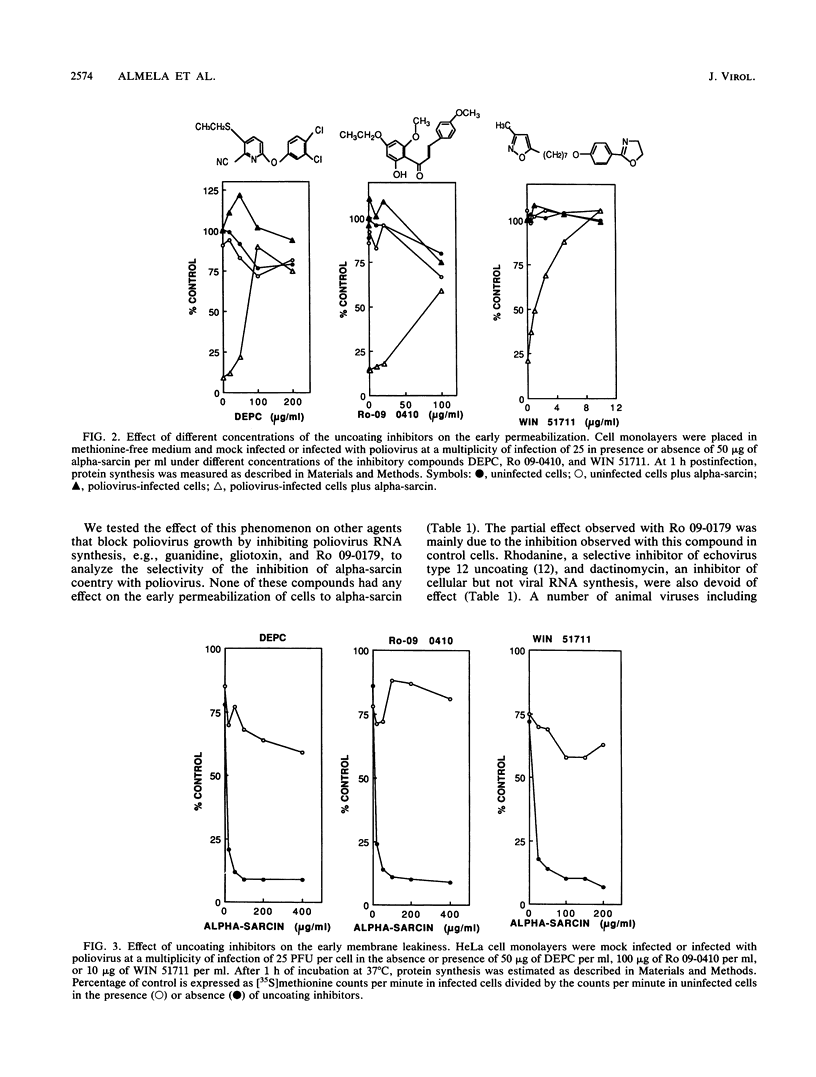
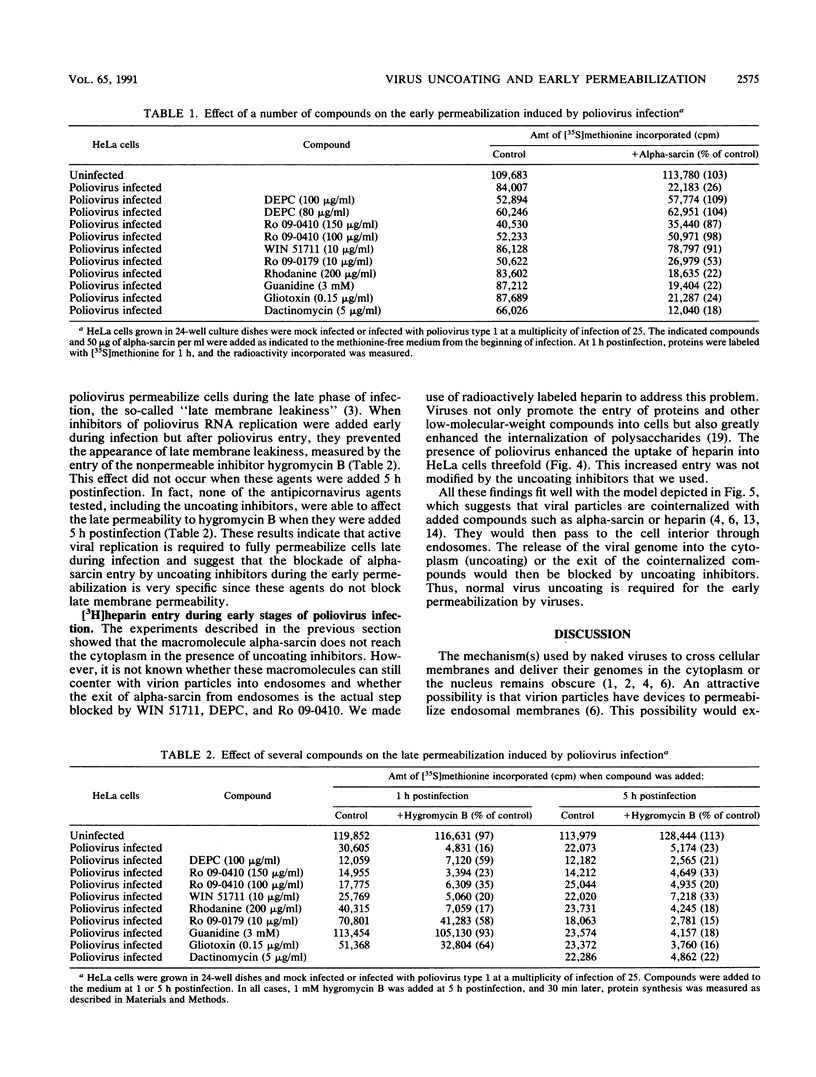
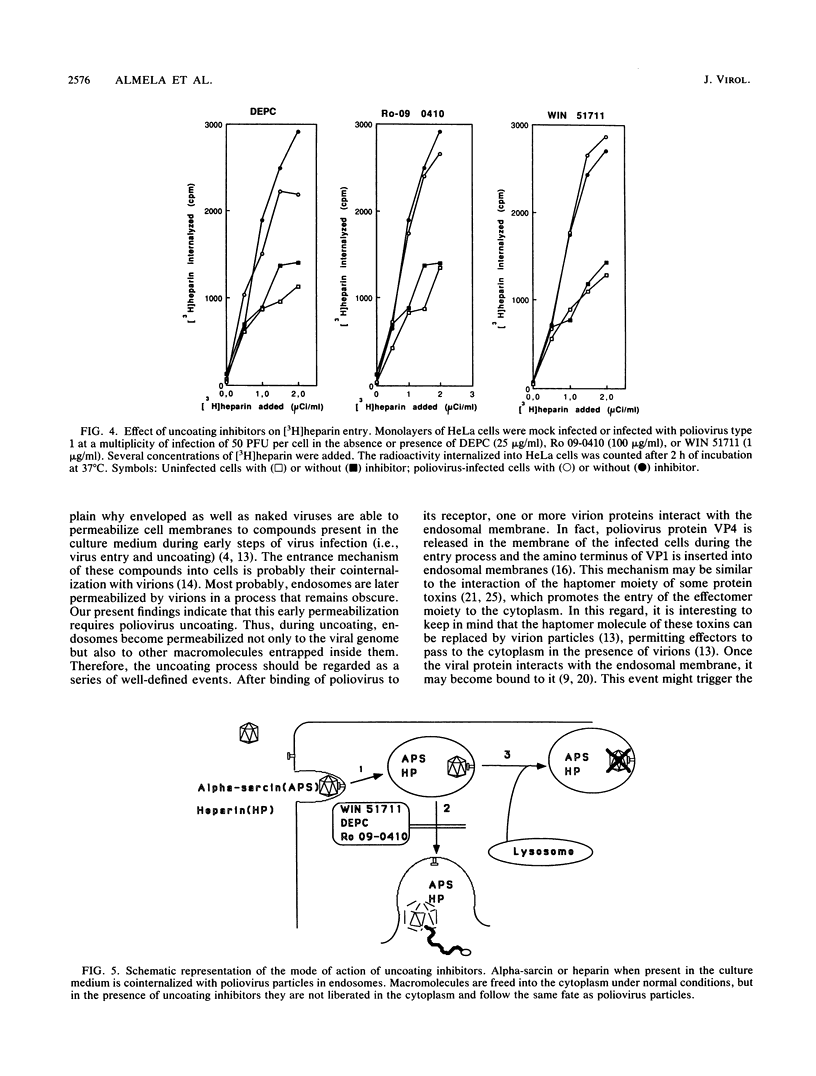
The entry of animal viruses into cells is associated with permeabilization of the infected cells to protein toxins such as alpha-sarcin (C. Fernández-Puentes and L. Carrasco, Cell 20:769-775, 1980). This phenomenon has been referred to as "the early permeabilization by animal viruses" (L. Carrasco, Virology 113:623-629, 1981). A number of inhibitors of poliovirus growth such as WIN 51711 6-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)-3-(ethylthio)-2-pyridincarbonitrile (DEPC) and Ro 09-0410 specifically block the uncoating step of poliovirus but have no effect on attachment or entry of poliovirus particles into cells. These agents are potent inhibitors of the early permeabilization induced by poliovirus to the toxin alpha-sarcin. Thus, the uncoating of poliovirus is required for the permeabilization of cell membranes to proteins. The increased entry of labeled heparin promoted by virus entry is not blocked by these agents, indicating that poliovirus binds to its receptor and is internalized along with heparin in endosomes in the presence of WIN 51711, DEPC, or Ro 09-0410. We conclude that the delivery to the cytoplasm of some molecules that coenter with virion particles does not take place if the uncoating process is hindered.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acharya R., Fry E., Stuart D., Fox G., Rowlands D., Brown F. The three-dimensional structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus at 2.9 A resolution. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):709–716. doi: 10.1038/337709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badger J., Minor I., Kremer M. J., Oliveira M. A., Smith T. J., Griffith J. P., Guerin D. M., Krishnaswamy S., Luo M., Rossmann M. G. Structural analysis of a series of antiviral agents complexed with human rhinovirus 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3304–3308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L., Esteban M. Modification of membrane permeability in vaccinia virus-infected cells. Virology. 1982 Feb;117(1):62–69. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90507-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L. Membrane leakiness after viral infection and a new approach to the development of antiviral agents. Nature. 1978 Apr 20;272(5655):694–699. doi: 10.1038/272694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L. Modification of membrane permeability induced by animal viruses early in infection. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):623–629. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L., Otero M. J., Castrillo J. L. Modification of membrane permeability by animal viruses. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;40(2):171–212. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Sena J., Mandel B. Studies on the in vitro uncoating of poliovirus. II. Characteristics of the membrane-modified particle. Virology. 1977 May 15;78(2):554–566. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diana G. D., Otto M. J., McKinlay M. A. Inhibitors of picornavirus uncoating as antiviral agents. Pharmacol Ther. 1985;29(3):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(85)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmock N. J. Review article initial stages in infection with animal viruses. J Gen Virol. 1982 Mar;59(Pt 1):1–22. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggers H. J., Koch M. A., Furst A., Daves G. D., Jr, Wilczynski J. J., Folkers K. Rhodanine: a selective inhibitor of the multiplication of echovirus 12. Science. 1970 Jan 16;167(3916):294–297. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3916.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Puentes C., Carrasco L. Viral infection permeabilizes mammalian cells to protein toxins. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):769–775. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald D. J., Padmanabhan R., Pastan I., Willingham M. C. Adenovirus-induced release of epidermal growth factor and pseudomonas toxin into the cytosol of KB cells during receptor-mediated endocytosis. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90480-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox M. P., Otto M. J., McKinlay M. A. Prevention of rhinovirus and poliovirus uncoating by WIN 51711, a new antiviral drug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jul;30(1):110–116. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricks C. E., Hogle J. M. Cell-induced conformational change in poliovirus: externalization of the amino terminus of VP1 is responsible for liposome binding. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):1934–1945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.1934-1945.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González M. E., Almela M. J., Yacout M., Carrasco L. 6-(3,4-Dichlorophenoxy)-3-(ethylthio)-2-pyridincarbonitrile inhibits poliovirus uncoating. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1259–1261. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González M. E., Carrasco L. Animal viruses promote the entry of polysaccharides with antiviral activity into cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 14;146(3):1303–1310. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90791-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttman N., Baltimore D. A plasma membrane component able to bind and alter virions of poliovirus type 1: studies on cell-free alteration using a simplified assay. Virology. 1977 Oct 1;82(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch D. H., Romero-Mira M., Ehrlich B. E., Finkelstein A., DasGupta B. R., Simpson L. L. Channels formed by botulinum, tetanus, and diphtheria toxins in planar lipid bilayers: relevance to translocation of proteins across membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1692–1696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D., Kok J. W. Entry mechanisms of enveloped viruses. Implications for fusion of intracellular membranes. Biosci Rep. 1989 Jun;9(3):273–305. doi: 10.1007/BF01114682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishitsuka H., Ninomiya Y. T., Ohsawa C., Fujiu M., Suhara Y. Direct and specific inactivation of rhinovirus by chalcone Ro 09-0410. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):617–621. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan B. L., Finkelstein A., Colombini M. Diphtheria toxin fragment forms large pores in phospholipid bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4950–4954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo M., Vriend G., Kamer G., Minor I., Arnold E., Rossmann M. G., Boege U., Scraba D. G., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C. The atomic structure of Mengo virus at 3.0 A resolution. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):182–191. doi: 10.1126/science.3026048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otero M. J., Carrasco L. Proteins are cointernalized with virion particles during early infection. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevear D. C., Fancher M. J., Felock P. J., Rossmann M. G., Miller M. S., Diana G., Treasurywala A. M., McKinlay M. A., Dutko F. J. Conformational change in the floor of the human rhinovirus canyon blocks adsorption to HeLa cell receptors. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2002–2007. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2002-2007.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Frankenberger E. A., Griffith J. P., Hecht H. J., Johnson J. E., Kamer G., Luo M., Mosser A. G. Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):145–153. doi: 10.1038/317145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Johnson J. E. Icosahedral RNA virus structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:533–573. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G. The structure of antiviral agents that inhibit uncoating when complexed with viral capsids. Antiviral Res. 1989 Feb;11(1):3–13. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(89)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth P., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Adenovirus-dependent release of 51Cr from KB cells at an acidic pH. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14350–14353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


