Abstract
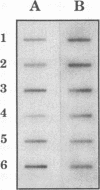
Polar packaging of adenovirus DNA into virions is dependent on the presence of cis-acting sequences at the left end of the viral genome. Our previous analyses demonstrated that the adenovirus type 5 (Ad5) packaging domain (nucleotides 194 to 358) is composed of at least five elements that are functionally redundant. A repeated sequence, termed the A repeat, was associated with packaging function. Here we report a more detailed analysis of the requirements for the selective packaging of Ad5 DNA. By introducing site-directed point mutations into specific A repeat sequences, we demonstrate that the A repeats represent cis-acting functional components of the packaging signal. Additional elements, located outside the originally defined packaging domain boundaries and that resemble the A repeat consensus sequence, also are capable of promoting the packaging of viral DNA. The cis-acting components of the packaging signal appear to be subject to certain spatial constraints for function, possibly reflecting a necessity for the coordinate binding of packaging proteins to these sites. In agreement with this idea, we present evidence that the interaction of a limiting trans-acting factor(s) with the packaging domain in vivo is required for efficient encapsidation of the Ad5 genome.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruder J. T., Hearing P. Nuclear factor EF-1A binds to the adenovirus E1A core enhancer element and to other transcriptional control regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5143–5153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee-Sheung C. C., Ginsberg H. S. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive fiber mutant of type 5 adenovirus and effect of the mutation on virion assembly. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):932–950. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.932-950.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Halluin J. C., Martin G. R., Torpier G., Boulanger P. A. Adenovirus type 2 assembly analyzed by reversible cross-linking of labile intermediates. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):357–363. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.357-363.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Halluin J. C., Milleville M., Boulanger P. A., Martin G. R. Temperature-sensitive mutant of adenovirus type 2 blocked in virion assembly: accumulation of light intermediate particles. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):344–356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.344-356.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Halluin J. C., Milleville M., Boulanger P. Effects of novobiocin on adenovirus DNA synthesis and encapsidation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 11;8(7):1625–1641. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.7.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Halluin J. C., Milleville M., Martin G. R., Boulanger P. Morphogenesis of human adenovirus type 2 studied with fiber- and fiber and penton base-defective temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):88–99. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.88-99.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniell E. Genome structure of incomplete particles of adenovirus. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):685–708. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.685-708.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Deb S., Partin K., Tegtmeyer P. Functional interactions of the simian virus 40 core origin of replication with flanking regulatory sequences. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.138-144.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Casjens S. R. DNA packaging by the double-stranded DNA bacteriophages. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):319–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckdahl T. T., Anderson J. N. Bent DNA is a conserved structure in an adenovirus control region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2346–2346. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvardsson B., Everitt E., Jörnvall H., Prage L., Philipson L. Intermediates in adenovirus assembly. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):533–547. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.533-547.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvardsson B., Ustacelebi S., Williams J., Philipson L. Assembly intermediates among adenovirus type 5 temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1978 Feb;25(2):641–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.2.641-651.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gräble M., Hearing P. Adenovirus type 5 packaging domain is composed of a repeated element that is functionally redundant. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2047–2056. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2047-2056.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarskjöld M. L., Winberg G. Encapsidation of adenovirus 16 DNA is directed by a small DNA sequence at the left end of the genome. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):787–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90325-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasson T. B., Soloway P. D., Ornelles D. A., Doerfler W., Shenk T. Adenovirus L1 52- and 55-kilodalton proteins are required for assembly of virions. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3612–3621. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3612-3621.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Samulski R. J., Wishart W. L., Shenk T. Identification of a repeated sequence element required for efficient encapsidation of the adenovirus type 5 chromosome. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2555–2558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2555-2558.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Shenk T. The adenovirus type 5 E1A enhancer contains two functionally distinct domains: one is specific for E1A and the other modulates all early units in cis. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):229–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90387-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Shenk T. The adenovirus type 5 E1A transcriptional control region contains a duplicated enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosturko L. D., Sharnick S. V., Tibbetts C. Polar encapsidation of adenovirus DNA: cloning and DNA sequence of the left end of adenovirus type 3. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1132–1137. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1132-1137.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Role of an adenovirus E2 promoter binding factor in E1A-mediated coordinate gene control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2180–2184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohyama T., Hashimoto S. Upstream half of adenovirus type 2 enhancer adopts a curved DNA conformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3845–3853. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson C. C., Tibbetts C. Polar encapsidation of adenovirus DNA: evolutionary variants reveal dispensable sequences near the left ends of Ad3 genomes. Virology. 1984 Sep;137(2):276–286. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Cloning of a DNA fragment from the left-hand terminus of the adenovirus type 2 genome and its use in site-directed mutagenesis. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):171–180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.171-180.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist B., Everitt E., Philipson L., Hoglund S. Assembly of adenoviruses. J Virol. 1973 Mar;11(3):449–459. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.3.449-459.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbetts C. Viral DNA sequences from incomplete particles of human adenovirus type 7. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):243–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Silverstein S., Lee L. S., Pellicer A., Cheng Y. c., Axel R. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]