Abstract
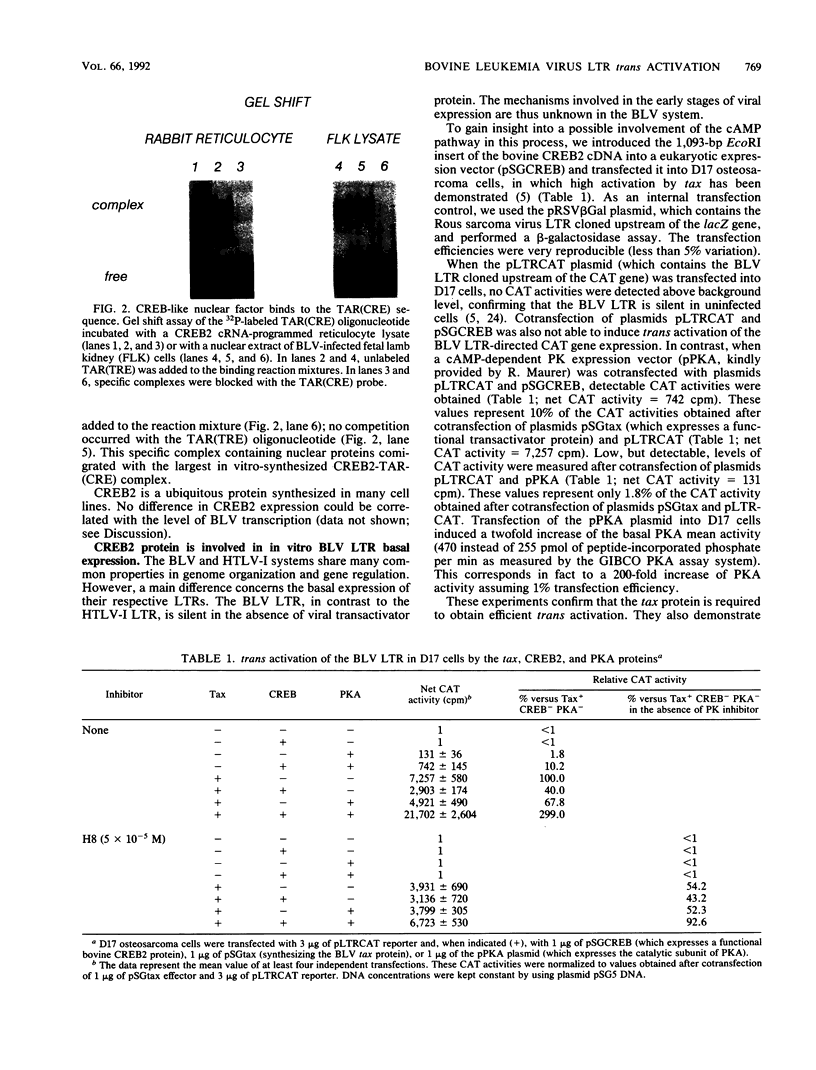
To gain insight into the cellular regulation of bovine leukemia virus (BLV) trans activation, a lambda-gt11 cDNA library was constructed with mRNA isolated from a BLV-induced tumor and the recombinant proteins were screened with an oligonucleotide corresponding to the tax activation-responsive element (TAR). Two clones (called TAR-binding protein) were isolated from 750,000 lambda-gt11 plaques. The binding specificity was confirmed by Southwestern (DNA-protein) and gel retardation assays. Nucleotide sequence analysis revealed that TAR-binding protein is very similar to the CREB2 protein. It contains a leucine zipper structure required for dimerization, a basic amino acid domain, and multiple potential phosphorylation sites. A vector expressing CREB2 was transfected into D17 osteosarcoma cells. In the absence of the tax transactivator, the CREB2 protein and the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A activate the BLV long terminal repeat at a basal expression level: trans activation reached 10% of the values obtained in the presence of tax alone. These data demonstrate that CREB2 is a cellular factor able to induce BLV long terminal repeat expression in the absence of tax protein and could thus be involved in the early stages of viral infection. In addition, we observed that in vitro tax-induced trans activation can be activated or inhibited by CREB2 depending on the presence or absence of protein kinase A. These data suggest that the cyclic AMP pathway plays a role in the regulation of viral expression in BLV-infected animals.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman R., Harrich D., Garcia J. A., Gaynor R. B. Human T-cell leukemia virus types I and II exhibit different DNase I protection patterns. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1339–1346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1339-1346.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weih F., Schmidt A., Fournier R. E., Schütz G. A cyclic AMP response element mediates repression of tyrosine aminotransferase gene transcription by the tissue-specific extinguisher locus Tse-1. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):905–916. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90201-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brash D. E., Reddel R. R., Quanrud M., Yang K., Farrell M. P., Harris C. C. Strontium phosphate transfection of human cells in primary culture: stable expression of the simian virus 40 large-T-antigen gene in primary human bronchial epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):2031–2034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burny A., Cleuter Y., Kettmann R., Mammerickx M., Marbaix G., Portetelle D., Van den Broeke A., Willems L., Thomas R. Bovine leukaemia: facts and hypotheses derived from the study of an infectious cancer. Cancer Surv. 1987;6(1):139–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D. Bovine leukemia virus transcription is controlled by a virus-encoded trans-acting factor and by cis-acting response elements. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2462–2471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2462-2471.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa J., Toita M., Yoshida M. A unique enhancer element for the trans activator (p40tax) of human T-cell leukemia virus type I that is distinct from cyclic AMP- and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-responsive elements. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3234–3239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3234-3239.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giam C. Z., Xu Y. L. HTLV-I tax gene product activates transcription via pre-existing cellular factors and cAMP responsive element. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15236–15241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Montminy M. R. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K., Fischer W. H., Karr D., Menzel P., Biggs W., 3rd, Vale W. W., Montminy M. R. A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):749–752. doi: 10.1038/337749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P., Ferrer J. F. Expression of bovine leukemia virus genome is blocked by a nonimmunoglobulin protein in plasma from infected cattle. Science. 1982 Jan 22;215(4531):405–407. doi: 10.1126/science.6276975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffler J. P., Meyer T. E., Yun Y., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP-responsive DNA-binding protein: structure based on a cloned placental cDNA. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1430–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.2974179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Boros I., Brady J., Radonovich M., Khoury G. Characterization of cellular factors that interact with the human T-cell leukemia virus type I p40x-responsive 21-base-pair sequence. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4499–4509. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4499-4509.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh I., Yoshinaka Y., Ikawa Y. Bovine leukemia virus trans-activator p38tax activates heterologous promoters with a common sequence known as a cAMP-responsive element or the binding site of a cellular transcription factor ATF. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):497–503. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03403.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Niki M., Ohtani K., Sugamura K. Differential activation of the 21-base-pair enhancer element of human T-cell leukemia virus type I by its own trans-activator and cyclic AMP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5207–5221. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyborg J. K., Dynan W. S., Chen I. S., Wachsman W. Binding of host-cell factors to DNA sequences in the long terminal repeat of human T-cell leukemia virus type I: implications for viral gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1457–1461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyborg J. K., Dynan W. S. Interaction of cellular proteins with the human T-cell leukemia virus type I transcriptional control region. Purification of cellular proteins that bind the 21-base pair repeat elements. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8230–8236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Tsuzuku-Kawamura J., Nagayoshi-Aida M., Shimizu F., Imagawa K., Ikawa Y. Identification and some biochemical properties of the major XBL gene product of bovine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7879–7883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Molecular cloning of an enhancer binding protein: isolation by screening of an expression library with a recognition site DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):415–423. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto A., Nyunoya H., Morita T., Sato T., Shimotohno K. Isolation of cDNAs for DNA-binding proteins which specifically bind to a tax-responsive enhancer element in the long terminal repeat of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1420–1426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1420-1426.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Broeke A., Cleuter Y., Chen G., Portetelle D., Mammerickx M., Zagury D., Fouchard M., Coulombel L., Kettmann R., Burny A. Even transcriptionally competent proviruses are silent in bovine leukemia virus-induced sheep tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9263–9267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems L., Chen G., Burny A., Kettmann R. Expression in bacteria of beta-galactosidase fusion proteins carrying antigenic determinants of the two X gene products of bovine leukemia virus. Leukemia. 1988 Jan;2(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems L., Gegonne A., Chen G., Burny A., Kettmann R., Ghysdael J. The bovine leukemia virus p34 is a transactivator protein. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3385–3389. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02661.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems L., Heremans H., Chen G., Portetelle D., Billiau A., Burny A., Kettmann R. Cooperation between bovine leukaemia virus transactivator protein and Ha-ras oncogene product in cellular transformation. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1577–1581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems L., Kettmann R., Chen G., Portetelle D., Burny A., Derse D. Nucleotide sequence of the bovine cyclic-AMP responsive DNA binding protein (CREB2) cDNA. DNA Seq. 1991;1(6):415–417. doi: 10.3109/10425179109020800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M. Multiple cDNA clones encoding nuclear proteins that bind to the tax-dependent enhancer of HTLV-1: all contain a leucine zipper structure and basic amino acid domain. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2537–2542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]