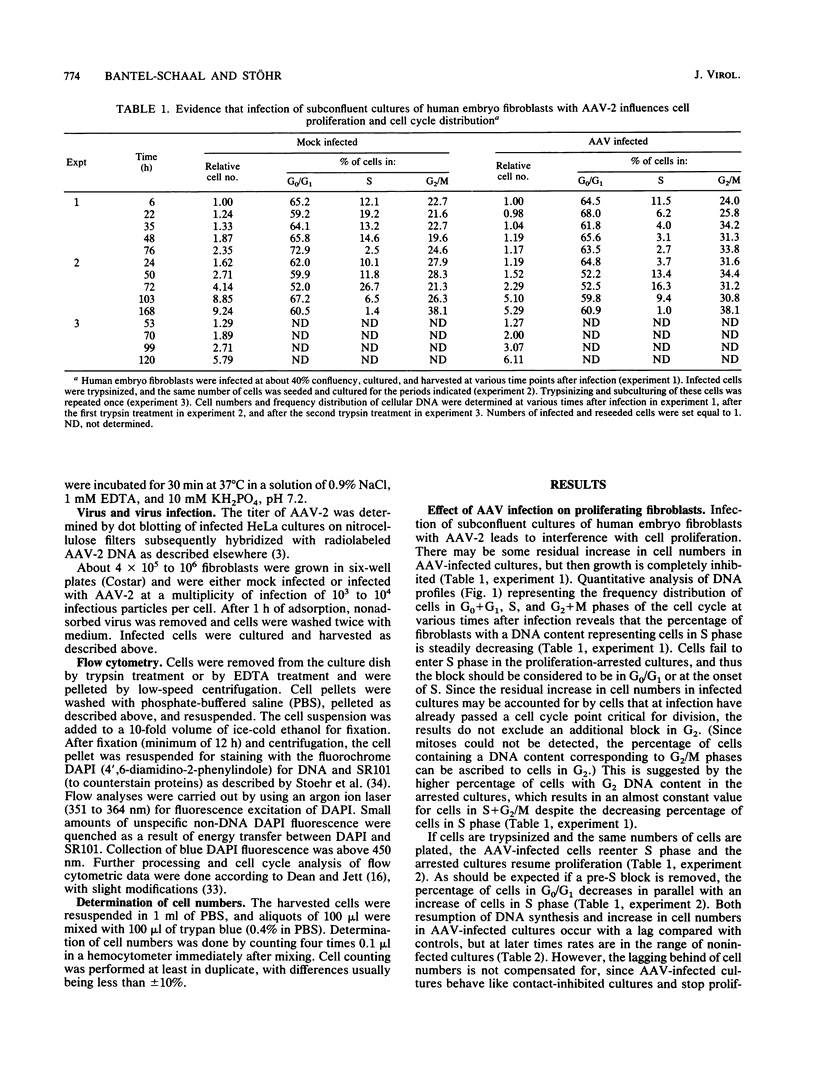
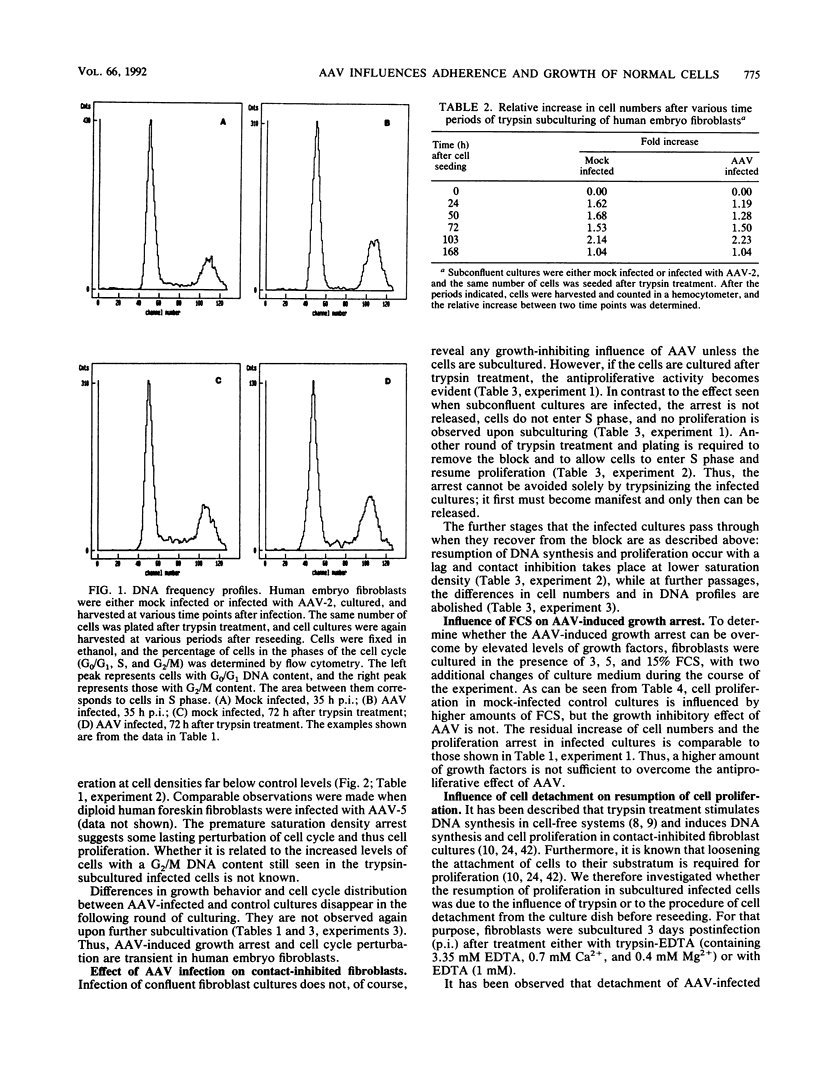
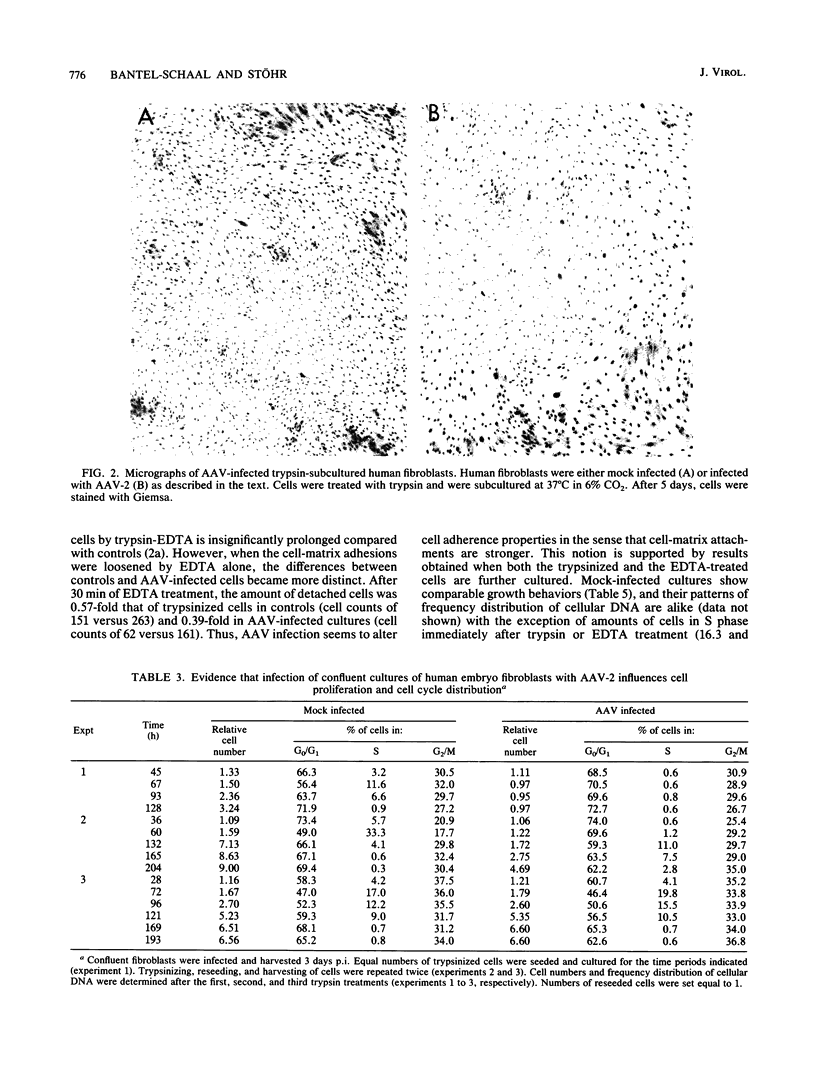
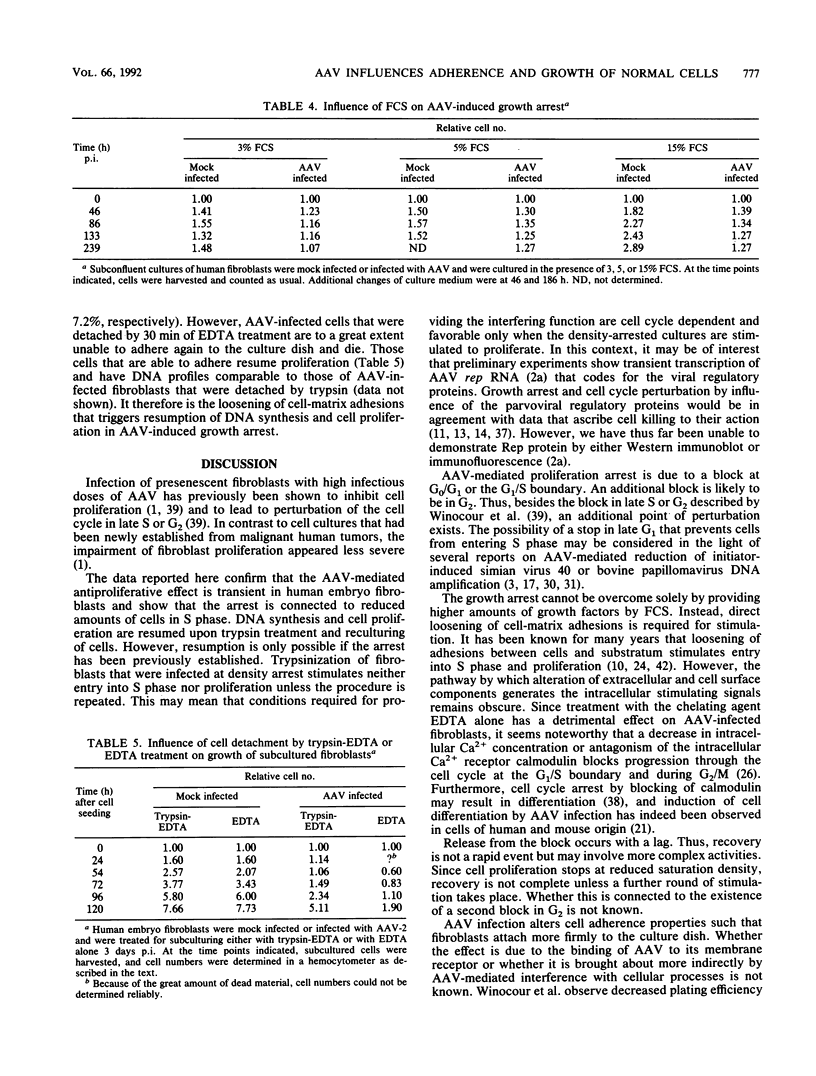
Abstract
It has been shown previously that infection of newly established cell cultures from malignant human tumors with adeno-associated parvovirus type 2 or type 5 results in growth arrest and cell death. Here we report that the additionally observed antiproliferative effect on diploid human fibroblasts is transient and is connected to a reduced number of cells in S phase. Progression through the cell cycle is disturbed either in G0/G1 or at the G1/S boundary, but an additional arrest in G2 cannot be excluded. DNA synthesis and cell proliferation are resumed when cells are recultured after loosening of cell-matrix adhesions by trypsin treatment. In contrast, they are not resumed by solely providing growth factors via higher amounts of fetal calf serum. The results suggest that cell adherence is altered in adeno-associated parvovirus-infected human embryo fibroblasts.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bantel-Schaal U. Adeno-associated parvoviruses inhibit growth of cells derived from malignant human tumors. Int J Cancer. 1990 Jan 15;45(1):190–194. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bantel-Schaal U. Infection with adeno-associated parvovirus leads to increased sensitivity of mammalian cells to stress. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):260–268. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90669-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bantel-Schaal U., zur Hausen H. Adeno-associated viruses inhibit SV40 DNA amplification and replication of herpes simplex virus in SV40-transformed hamster cells. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):64–74. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90620-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bantel-Schaal U., zur Hausen H. Dissociation of carcinogen-induced SV40 DNA-amplification and amplification of AAV DNA in a Chinese hamster cell line. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaton A., Palumbo P., Berns K. I. Expression from the adeno-associated virus p5 and p19 promoters is negatively regulated in trans by the rep protein. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4450–4454. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4450-4454.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns K. I., Bohenzky R. A. Adeno-associated viruses: an update. Adv Virus Res. 1987;32:243–306. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60479-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns K. I., Labow M. A. Parvovirus gene regulation. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):601–614. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. L., Clark R. W., Chiu J. F., Stubblefield E. Protease activation of G1 nuclei isolated from Chinese hamster fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Jan;104(1):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. L., Stubblefield E. Enhancement of DNA synthesis in a mammalian cell-free system by trypsin treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2432–2434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger M. M. Proteolytic enzymes initiating cell division and escape from contact inhibition of growth. Nature. 1970 Jul 11;227(5254):170–171. doi: 10.1038/227170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caillet-Fauquet P., Perros M., Brandenburger A., Spegelaere P., Rommelaere J. Programmed killing of human cells by means of an inducible clone of parvoviral genes encoding non-structural proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2989–2995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07491.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis J. J., Chen Y. Q., Spruyt N., Duponchel N., Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P., Rommelaere J. Susceptibility of human cells to killing by the parvoviruses H-1 and minute virus of mice correlates with viral transcription. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2537–2544. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2537-2544.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis J. J., Spruyt N., Spegelaere P., Guetta E., Darawshi T., Cotmore S. F., Tal J., Rommelaere J. Sensitization of transformed rat fibroblasts to killing by parvovirus minute virus of mice correlates with an increase in viral gene expression. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3438–3444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3438-3444.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. The autonomously replicating parvoviruses of vertebrates. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:91–174. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. N., Jett J. H. Mathematical analysis of DNA distributions derived from flow microfluorometry. J Cell Biol. 1974 Feb;60(2):523–527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.2.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilbronn R., Bürkle A., Stephan S., zur Hausen H. The adeno-associated virus rep gene suppresses herpes simplex virus-induced DNA amplification. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3012–3018. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3012-3018.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilbronn R., Schlehofer J. R., zur Hausen H. Selective killing of carcinogen-treated SV40-transformed Chinese hamster cells by a defective parvovirus. Virology. 1984 Jul 30;136(2):439–441. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermonat P. L. The adeno-associated virus Rep78 gene inhibits cellular transformation induced by bovine papillomavirus. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khleif S. N., Myers T., Carter B. J., Trempe J. P. Inhibition of cellular transformation by the adeno-associated virus rep gene. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):738–741. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90909-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labow M. A., Berns K. I. The adeno-associated virus rep gene inhibits replication of an adeno-associated virus/simian virus 40 hybrid genome in cos-7 cells. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1705–1712. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1705-1712.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labow M. A., Graf L. H., Jr, Berns K. I. Adeno-associated virus gene expression inhibits cellular transformation by heterologous genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1320–1325. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzei D., Novi C., Bazzi C. Mitogenic action of trypsin and chymotrypsin. Lancet. 1966 Jul 23;2(7456):232–232. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92526-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson E., Smith M. G., Miller I. L., Carter B. J. Effect of a viral rep gene on transformation of cells by an adeno-associated virus vector. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):612–615. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90536-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen C. D., Means A. R. Calmodulin is required for cell-cycle progression during G1 and mitosis. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):73–82. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03350.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd Construction of a genetic switch for inducible trans-activation of gene expression in eucaryotic cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1448–1456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1448-1456.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd, Richard S. M. Characterization of the trans-activation-responsive element of the parvovirus H-1 P38 promoter. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2807–2815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2807-2815.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlehofer J. R., Heilbronn R., Georg-Fries B., zur Hausen H. Inhibition of initiator-induced SV40 gene amplification in SV40-transformed Chinese hamster cells by infection with a defective parvovirus. Int J Cancer. 1983 Nov 15;32(5):591–595. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910320512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt J., Schlehofer J. R., Mergener K., Gissmann L., zur Hausen H. Amplification of bovine papillomavirus DNA by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine, ultraviolet irradiation, or infection with herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoehr M., Gebhardt U., Goerttler K. Computer assistance in multiparameter flow microphotometry of mammalian cells. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1976 Aug;18(8):1057–1074. doi: 10.1002/bit.260180804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöhr M., Vogt-Schaden M., Knobloch M., Vogel R., Futterman G. Evaluation of eight fluorochrome combinations for simultaneous DNA-protein flow analyses. Stain Technol. 1978 Jul;53(4):205–215. doi: 10.3109/10520297809111467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan L. M., Quigley J. P. An anticatalytic monoclonal antibody to avian plasminogen activator: its effect on behavior of RSV-transformed chick fibroblasts. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):905–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90565-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao J., Chapman M. S., Agbandje M., Keller W., Smith K., Wu H., Luo M., Smith T. J., Rossmann M. G., Compans R. W. The three-dimensional structure of canine parvovirus and its functional implications. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1456–1464. doi: 10.1126/science.2006420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hille B., Duponchel N., Salomé N., Spruyt N., Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P., Cornelis J. J., Rommelaere J. Limitations to the expression of parvoviral nonstructural proteins may determine the extent of sensitization of EJ-ras-transformed rat cells to minute virus of mice. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90514-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veigl M. L., Sedwick W. D., Niedel J., Branch M. E. Induction of myeloid differentiation of HL-60 cells with naphthalene sulfonamide calmodulin antagonists. Cancer Res. 1986 May;46(5):2300–2305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winocour E., Callaham M. F., Huberman E. Perturbation of the cell cycle by adeno-associated virus. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):393–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakobson B., Koch T., Winocour E. Replication of adeno-associated virus in synchronized cells without the addition of a helper virus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):972–981. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.972-981.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalkinoglu A. O., Heilbronn R., Bürkle A., Schlehofer J. R., zur Hausen H. DNA amplification of adeno-associated virus as a response to cellular genotoxic stress. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 1;48(11):3123–3129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetter B. R., Chen L. B., Buchanan J. M. Effects of protease treatment on growth, morphology, adhesion, and cell surface proteins of secondary chick embryo fibroblasts. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90170-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




