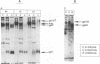Abstract
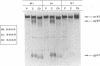
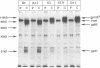
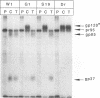
We investigated the amino acid sequence requirements for intracellular cleavage of the Rous sarcoma virus glycoprotein precursor by introducing mutations into the region encoding the cleavage recognition site (Arg-Arg-Lys-Arg). In addition to mutants G1 (Arg-Arg-Glu-Arg) and Dr1 (deletion of all four codons) that we have reported on previously (L. G. Perez and E. Hunter, J. Virol. 61:1609-1614, 1987), we constructed two additional mutants, AR1 (Arg-Arg-Arg-Arg), in which the highly conserved lysine is replaced by an arginine, and S19 (Ser-Arg-Glu-Arg), in which no dibasic pairs remain. The results of these studies demonstrate that when the cleavage sequence is deleted (Dr1) or modified to contain unpaired basic residues (S19), intracellular cleavage of the glycoprotein precursor is completely blocked. This demonstrates that the cellular endopeptidase responsible for cleavage has a stringent requirement for the presence of a pair of basic residues (Arg-Arg or Lys-Arg). Furthermore, it implies that the cleavage enzyme is not trypsinlike, since it is unable to recognize arginine residues that are sensitive to trypsin action. Substitution of the mutated genes into a replication-competent avian retrovirus genome showed that cleavage of the glycoprotein precursor was not required for incorporation into virions but was necessary for infectivity. Treatment of BH-RCAN-S19-transfected turkey cells with low levels of trypsin resulted in the release of infectious virus, demonstrating that exogenous cleavage could generate a biologically active glycoprotein molecule.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosch V., Pawlita M. Mutational analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 env gene product proteolytic cleavage site. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2337–2344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2337-2344.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnahan P. A., Leduc R., Thomas L., Thorner J., Gibson H. L., Brake A. J., Barr P. J., Thomas G. Human fur gene encodes a yeast KEX2-like endoprotease that cleaves pro-beta-NGF in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2851–2859. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. L., Hunter E. A charged amino acid substitution within the transmembrane anchor of the Rous sarcoma virus envelope glycoprotein affects surface expression but not intracellular transport. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1191–1203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande K. L., Fried V. A., Ando M., Webster R. G. Glycosylation affects cleavage of an H5N2 influenza virus hemagglutinin and regulates virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einfeld D., Hunter E. Oligomeric structure of a prototype retrovirus glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8688–8692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E. O., Myers D. J., Risser R. Mutational analysis of the cleavage sequence of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein precursor gp160. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4670–4675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4670-4675.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Earl P. L., Moss B. Use of a hybrid vaccinia virus-T7 RNA polymerase system for expression of target genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2538–2544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Brake A. J., Thorner J. Intracellular targeting and structural conservation of a prohormone-processing endoprotease. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):482–486. doi: 10.1126/science.2683070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Brake A., Thorner J. Yeast prohormone processing enzyme (KEX2 gene product) is a Ca2+-dependent serine protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1434–1438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallaher W. R. Detection of a fusion peptide sequence in the transmembrane protein of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):327–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90485-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Stieneke A., Shaw E., Wikstrom P., Klenk H. D. Inhibition of proteolytic activation of influenza virus hemagglutinin by specific peptidyl chloroalkyl ketones. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90103-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain D., Zollinger L., Racine C., Gossard F., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y., Crine P., Boileau G. The yeast KEX-2-processing endoprotease is active in the Golgi apparatus of transfected NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1572–1579. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-10-1572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatsuzawa K., Hosaka M., Nakagawa T., Nagase M., Shoda A., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Structure and expression of mouse furin, a yeast Kex2-related protease. Lack of processing of coexpressed prorenin in GH4C1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22075–22078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosaka M., Nagahama M., Kim W. S., Watanabe T., Hatsuzawa K., Ikemizu J., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Arg-X-Lys/Arg-Arg motif as a signal for precursor cleavage catalyzed by furin within the constitutive secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12127–12130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S., Kosik E. Mutagenesis of the region between env and src of the SR-A strain of Rous sarcoma virus for the purpose of constructing helper-independent vectors. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90250-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E. Biological techniques for avian sarcoma viruses. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:379–393. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58153-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E., Hill E., Hardwick M., Bhown A., Schwartz D. E., Tizard R. Complete sequence of the Rous sarcoma virus env gene: identification of structural and functional regions of its product. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):920–936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.920-936.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaster K. R., Burgett S. G., Rao R. N., Ingolia T. D. Analysis of a bacterial hygromycin B resistance gene by transcriptional and translational fusions and by DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6895–6911. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Omer C. A., Weis J. H., Mitsialis S. A., Faras A. J., Guntaka R. V. Restriction endonuclease and nucleotide sequence analyses of molecularly cloned unintegrated avian tumor virus DNA: structure of large terminal repeats in circle junctions. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):346–351. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.346-351.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Hanafusa H. Isolation of defective mutant of avian sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3493–3497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Nishizawa M. New procedure for DNA transfection with polycation and dimethyl sulfoxide. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1172–1174. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaoka Y., Webster R. G. Sequence requirements for cleavage activation of influenza virus hemagglutinin expressed in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):324–328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Garten W., Rott R. Inhibition of proteolytic cleavage of the hemagglutinin of influenza virus by the calcium-specific ionophore A23187. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2911–2915. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02231.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leamnson R. N., Halpern M. S. Subunit structure of the glycoprotein complex of avian tumor virus. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):956–968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.956-968.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Fenno J., Burnette W. N., Rohrschneider L. Synthesis and processing of viral glycoproteins in two nonconditional mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):280–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.280-290.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Rabin L. B., Feinberg M. B., Lieberman M., Kosek J. C., Reyes G. R., Weissman I. L. Endoproteolytic cleavage of gp160 is required for the activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi Y., Sohda M., Ikehara Y. Sequence of the cDNA encoding rat furin, a possible propeptide-processing endoprotease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6719–6719. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Jimenez H., Lai M. M., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Continuous tissue culture cell lines derived from chemically induced tumors of Japanese quail. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohuchi M., Orlich M., Ohuchi R., Simpson B. E., Garten W., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Mutations at the cleavage site of the hemagglutinin after the pathogenicity of influenza virus A/chick/Penn/83 (H5N2). Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):274–280. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohuchi R., Ohuchi M., Garten W., Klenk H. D. Human influenza virus hemagglutinin with high sensitivity to proteolytic activation. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3530–3537. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3530-3537.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Shaughnessy M. A., Lamb R. A. Analysis of the relationship between cleavability of a paramyxovirus fusion protein and length of the connecting peptide. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1293–1301. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1293-1301.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez L. G., Davis G. L., Hunter E. Mutants of the Rous sarcoma virus envelope glycoprotein that lack the transmembrane anchor and cytoplasmic domains: analysis of intracellular transport and assembly into virions. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):2981–2988. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.2981-2988.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez L. G., Hunter E. Mutations within the proteolytic cleavage site of the Rous sarcoma virus glycoprotein that block processing to gp85 and gp37. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1609–1614. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1609-1614.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez L., Wills J. W., Hunter E. Expression of the Rous sarcoma virus env gene from a simian virus 40 late-region replacement vector: effects of upstream initiation codons. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1276–1281. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1276-1281.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petropoulos C. J., Hughes S. H. Replication-competent retrovirus vectors for the transfer and expression of gene cassettes in avian cells. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3728–3737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3728-3737.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. S., Hui H. X., Hunter E. Preassembled capsids of type D retroviruses contain a signal sufficient for targeting specifically to the plasma membrane. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3844–3852. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3844-3852.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rholam M., Nicolas P., Cohen P. Precursors for peptide hormones share common secondary structures forming features at the proteolytic processing sites. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele C. M., Hanafusa H. Proteins of helper-dependent RSV. Virology. 1971 Aug;45(2):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90341-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Identification of biological activities of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Activation of cell fusion, hemolysis, and infectivity of proteolytic cleavage of an inactive precursor protein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger R. W., Bradshaw G. L., Barbone F., Reinacher M., Rott R., Husak P. Role of hemagglutinin cleavage and expression of M1 protein in replication of A/WS/33, A/PR/8/34, and WSN influenza viruses in mouse brain. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1695–1703. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1695-1703.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C., Schwarz R. T., Keil W., Klenk H. D. A mutant of fowl plague virus (influenza A) with an altered glycosylation pattern in its hemagglutinin. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Gaspar L., Mion P., Marcinkiewicz M., Mbikay M., Chrétien M. cDNA sequence of two distinct pituitary proteins homologous to Kex2 and furin gene products: tissue-specific mRNAs encoding candidates for pro-hormone processing proteinases. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Jul-Aug;9(6):415–424. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Marcinkiewicz M., Benjannet S., Gaspar L., Beaubien G., Mattei M. G., Lazure C., Mbikay M., Chrétien M. Cloning and primary sequence of a mouse candidate prohormone convertase PC1 homologous to PC2, Furin, and Kex2: distinct chromosomal localization and messenger RNA distribution in brain and pituitary compared to PC2. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;5(1):111–122. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Avruch A. S., LaMendola J., Chan S. J., Steiner D. F. Identification of a cDNA encoding a second putative prohormone convertase related to PC2 in AtT20 cells and islets of Langerhans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):340–344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F. Identification of a human insulinoma cDNA encoding a novel mammalian protein structurally related to the yeast dibasic processing protease Kex2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):2997–3000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoller T. J., Shields D. The role of paired basic amino acids in mediating proteolytic cleavage of prosomatostatin. Analysis using site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6922–6928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai W. P., Oroszlan S. Novel glycosylation pathways of retroviral envelope proteins identified with avian reticuloendotheliosis virus. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3167–3174. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3167-3174.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weldon R. A., Jr, Erdie C. R., Oliver M. G., Wills J. W. Incorporation of chimeric gag protein into retroviral particles. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4169–4179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4169-4179.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Srinivas R. V., Hunter E. Mutations of the Rous sarcoma virus env gene that affect the transport and subcellular location of the glycoprotein products. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2011–2023. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. J., Barr P. J., Wong P. A., Kiefer M. C., Brake A. J., Kaufman R. J. Expression of a human proprotein processing enzyme: correct cleavage of the von Willebrand factor precursor at a paired basic amino acid site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9378–9382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Giuli C., Kawai S., Dales S., Hanafusa H. Absence of surface projections of some noninfectious forms of RSV. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Ven W. J., Voorberg J., Fontijn R., Pannekoek H., van den Ouweland A. M., van Duijnhoven H. L., Roebroek A. J., Siezen R. J. Furin is a subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme in higher eukaryotes. Mol Biol Rep. 1990 Nov;14(4):265–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00429896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]