Abstract
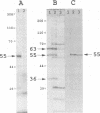
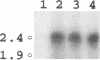
The small and middle T (tumor) antigens of polyomavirus have been shown previously to associate with the 36-kDa catalytic subunit and the 63-kDa regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase type 2A, apparently substituting for a normal third 55-kDa regulatory subunit (D.C. Pallas, L.K. Shahrik, B.L. Martin, S. Jaspers, T.B. Miller, D.L. Brautigan, and T.M. Roberts, Cell 60:167-176, 1990). To facilitate a comparison of the normal regulatory subunit and T antigens, we isolated a 2.14-kb cDNA clone encoding this 55-kDa subunit from a rat liver library. Using a probe from the coding region of this gene, we detected a major 2.4-kb mRNA transcript in liver and muscle RNAs. The 55-kDa protein phosphatase 2A subunit purified from rat skeletal muscle generates multiple species when analyzed on two-dimensional gels. Transcription and translation of the clone in vitro produced a full-length protein that comigrated precisely on two-dimensional gels with three of these species, indicating that the 55-kDa protein is apparently modified similarly in vivo and in reticulocyte lysates. Additional species in the purified preparation were not found in the translate, suggesting that there are probably two or more isoforms of this protein in rat muscle. Somewhat surprisingly, there was no clear homology with T-antigen amino acid sequences.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebersold R. H., Leavitt J., Saavedra R. A., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins separated by one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis after in situ protease digestion on nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6970–6974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arino J., Woon C. W., Brautigan D. L., Miller T. B., Jr, Johnson G. L. Human liver phosphatase 2A: cDNA and amino acid sequence of two catalytic subunit isotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4252–4256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Smith A. E. Polyoma virus transforming protein associates with the product of the c-src cellular gene. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):435–439. doi: 10.1038/303435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Lynch D., Furukawa Y., Griffin J., Piwnica-Worms H., Huang C. M., Livingston D. M. The product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene has properties of a cell cycle regulatory element. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1085–1095. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90507-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Woo S. L. Hybridization of genomic DNA to oligonucleotide probes in the presence of tetramethylammonium chloride. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:447–451. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Kaplan D. R., Kavanaugh W. M., Turck C. W., Williams L. T. A phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase binds to platelet-derived growth factor receptors through a specific receptor sequence containing phosphotyrosine. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1125–1132. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figge J., Smith T. F. Cell-division sequence motif. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):109–109. doi: 10.1038/334109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figge J., Webster T., Smith T. F., Paucha E. Prediction of similar transforming regions in simian virus 40 large T, adenovirus E1A, and myc oncoproteins. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1814–1818. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1814-1818.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Félix M. A., Cohen P., Karsenti E. Cdc2 H1 kinase is negatively regulated by a type 2A phosphatase in the Xenopus early embryonic cell cycle: evidence from the effects of okadaic acid. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):675–683. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08159.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Hermann J., Hendrix P., Ozon R., Merlevede W. Okadaic acid, a specific protein phosphatase inhibitor, induces maturation and MPF formation in Xenopus laevis oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):91–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80198-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. When the products of oncogenes and anti-oncogenes meet. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90975-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grussenmeyer T., Scheidtmann K. H., Hutchinson M. A., Eckhart W., Walter G. Complexes of polyoma virus medium T antigen and cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7952–7954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings B. A., Adams-Pearson C., Maurer F., Müller P., Goris J., Merlevede W., Hofsteenge J., Stone S. R. alpha- and beta-forms of the 65-kDa subunit of protein phosphatase 2A have a similar 39 amino acid repeating structure. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 3;29(13):3166–3173. doi: 10.1021/bi00465a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaoka T., Imazu M., Usui H., Kinohara N., Takeda M. Resolution and reassociation of three distinct components from pig heart phosphoprotein phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1526–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Stewart A. A., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 6. Measurement of type-1 and type-2 protein phosphatases in extracts of mammalian tissues; an assessment of their physiological roles. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):297–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaspers S. R., Miller T. B., Jr Purification and the immunological characterization of rat protein phosphatase 2A: enzyme levels in diabetic liver and heart. Mol Cell Biochem. 1991 Mar 13;101(2):167–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00229533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi B., Rundell K. Association of simian virus 40 small-t antigen with the 61-kilodalton component of a cellular protein complex. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5649–5651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5649-5651.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita N., Ohkura H., Yanagida M. Distinct, essential roles of type 1 and 2A protein phosphatases in the control of the fission yeast cell division cycle. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90173-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa Y., Tahira T., Ikeda I., Kikuchi K., Tsuiki S., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Molecular cloning of cDNA for the catalytic subunit of rat liver type 2A protein phosphatase, and detection of high levels of expression of the gene in normal and cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 10;951(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Solomon M. J., Mumby M. C., Kirschner M. W. INH, a negative regulator of MPF, is a form of protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):415–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90649-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer R. E., Hendrix P., Cron P., Matthies R., Stone S. R., Goris J., Merlevede W., Hofsteenge J., Hemmings B. A. Structure of the 55-kDa regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A: evidence for a neuronal-specific isoform. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 16;30(15):3589–3597. doi: 10.1021/bi00229a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda T., Satake M., Robins T., Ito Y. Isolation and characterization of NIH 3T3 cells expressing polyomavirus small T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):105–113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.105-113.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Cherington V., Morgan W., DeAnda J., Kaplan D., Schaffhausen B., Roberts T. M. Cellular proteins that associate with the middle and small T antigens of polyomavirus. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3934–3940. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3934-3940.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Schley C., Mahoney M., Harlow E., Schaffhausen B. S., Roberts T. M. Polyomavirus small t antigen: overproduction in bacteria, purification, and utilization for monoclonal and polyclonal antibody production. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1075–1084. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1075-1084.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Shahrik L. K., Martin B. L., Jaspers S., Miller T. B., Brautigan D. L., Roberts T. M. Polyoma small and middle T antigens and SV40 small t antigen form stable complexes with protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90726-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D., Solomon F. Cytoplasmic microtubule-associated proteins: phosphorylation at novel sites is correlated with their incorporation into assembled microtubules. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):407–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90238-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundell K. Complete interaction of cellular 56,000- and 32,000-Mr proteins with simian virus 40 small-t antigen in productively infected cells. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1240–1243. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1240-1243.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundell K., Major E. O., Lampert M. Association of cellular 56,000- and 32,000-molecular-weight protein with BK virus and polyoma virus t-antigens. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):1090–1093. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.1090-1093.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Bockus B. J., Berkner K. L., Kaplan D., Roberts T. M. Characterization of middle T antigen expressed by using an adenovirus expression system. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1221–1225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1221-1225.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Silver J. E., Benjamin T. L. Tumor antigen(s) in cell productively infected by wild-type polyoma virus and mutant NG-18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):79–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. Transforming genes and gene products of polyoma and SV40. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982;13(3):215–286. doi: 10.3109/10409238209114230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabel S., Argos P., Philipson L. The release of growth arrest by microinjection of adenovirus E1A DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2329–2336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virca G. D., Northemann W., Shiels B. R., Widera G., Broome S. Simplified northern blot hybridization using 5% sodium dodecyl sulfate. Biotechniques. 1990 Apr;8(4):370–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Carbone-Wiley A., Joshi B., Rundell K. Homologous cellular proteins associated with simian virus 40 small T antigen and polyomavirus medium T antigen. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4760–4762. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4760-4762.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Ferre F., Espiritu O., Carbone-Wiley A. Molecular cloning and sequence of cDNA encoding polyoma medium tumor antigen-associated 61-kDa protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8669–8672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Ruediger R., Slaughter C., Mumby M. Association of protein phosphatase 2A with polyoma virus medium tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2521–2525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Kaplan D. R., Schaffhausen B., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase activity with polyoma middle-T competent for transformation. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):239–242. doi: 10.1038/315239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. I., Lickteig R. L., Estes R., Rundell K., Walter G., Mumby M. C. Control of protein phosphatase 2A by simian virus 40 small-t antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1988–1995. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Hearing P., Rundell K. Cellular proteins associated with simian virus 40 early gene products in newly infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):147–154. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.147-154.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]