Abstract
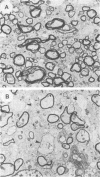
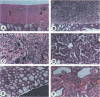
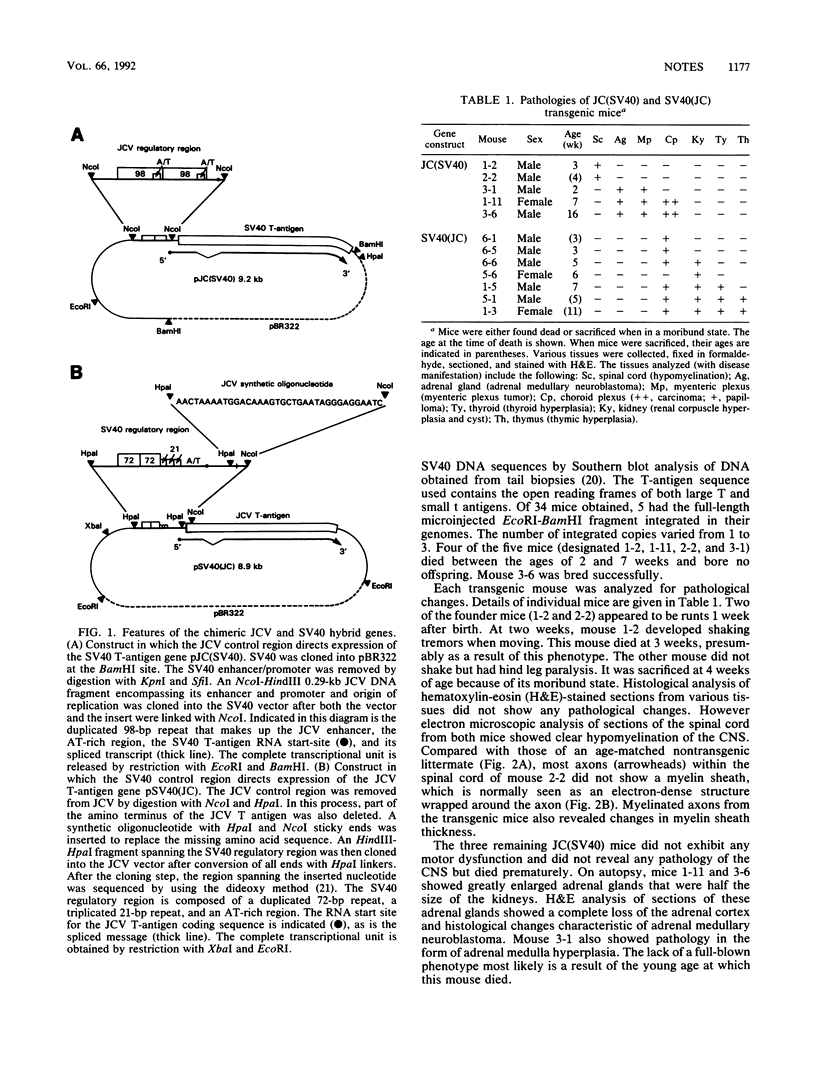
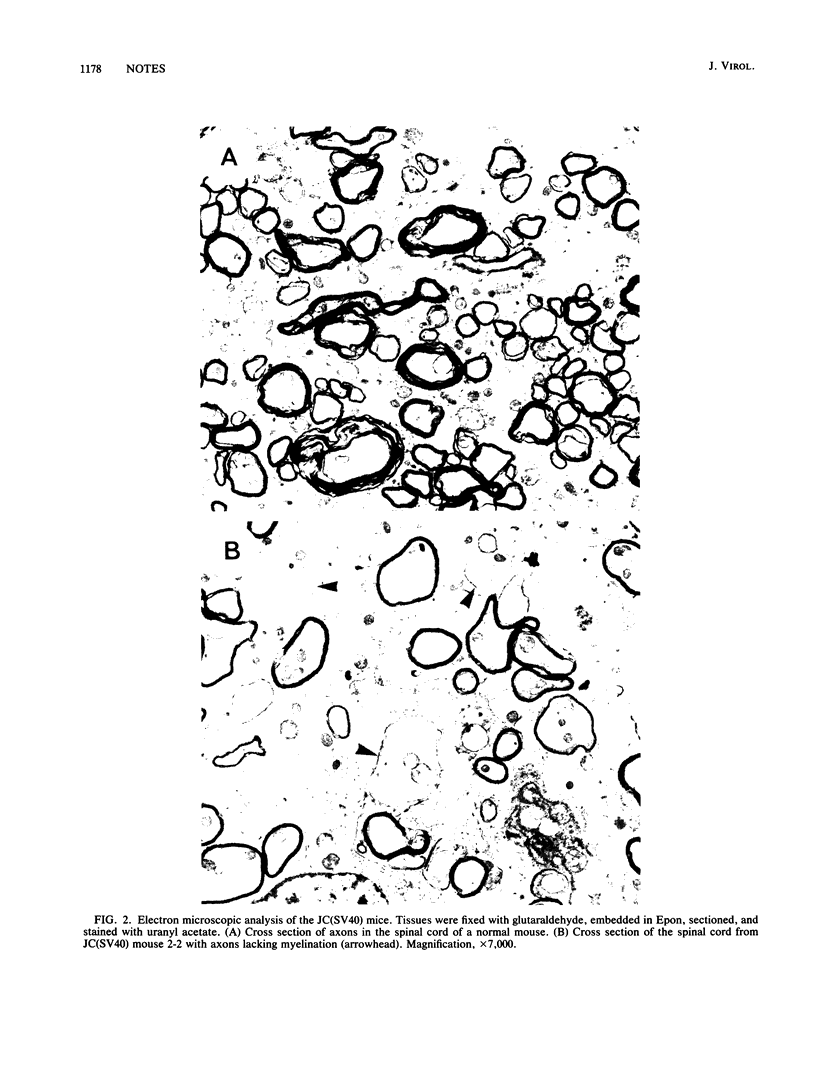
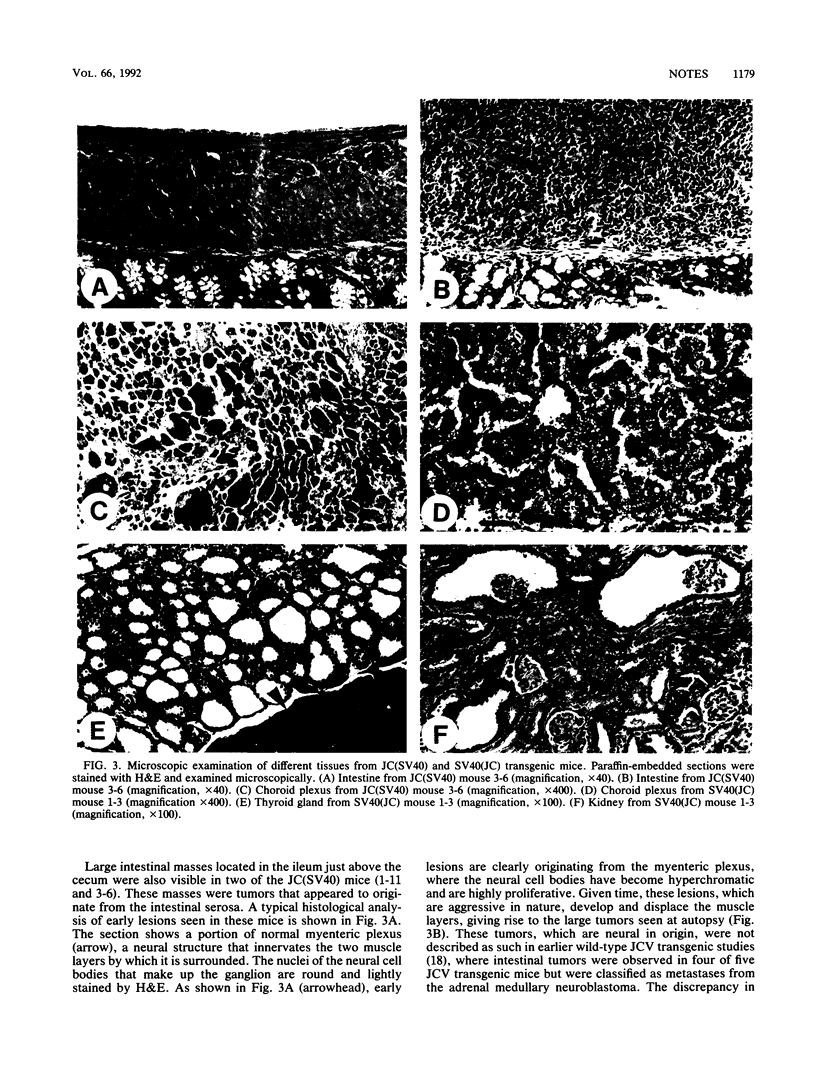
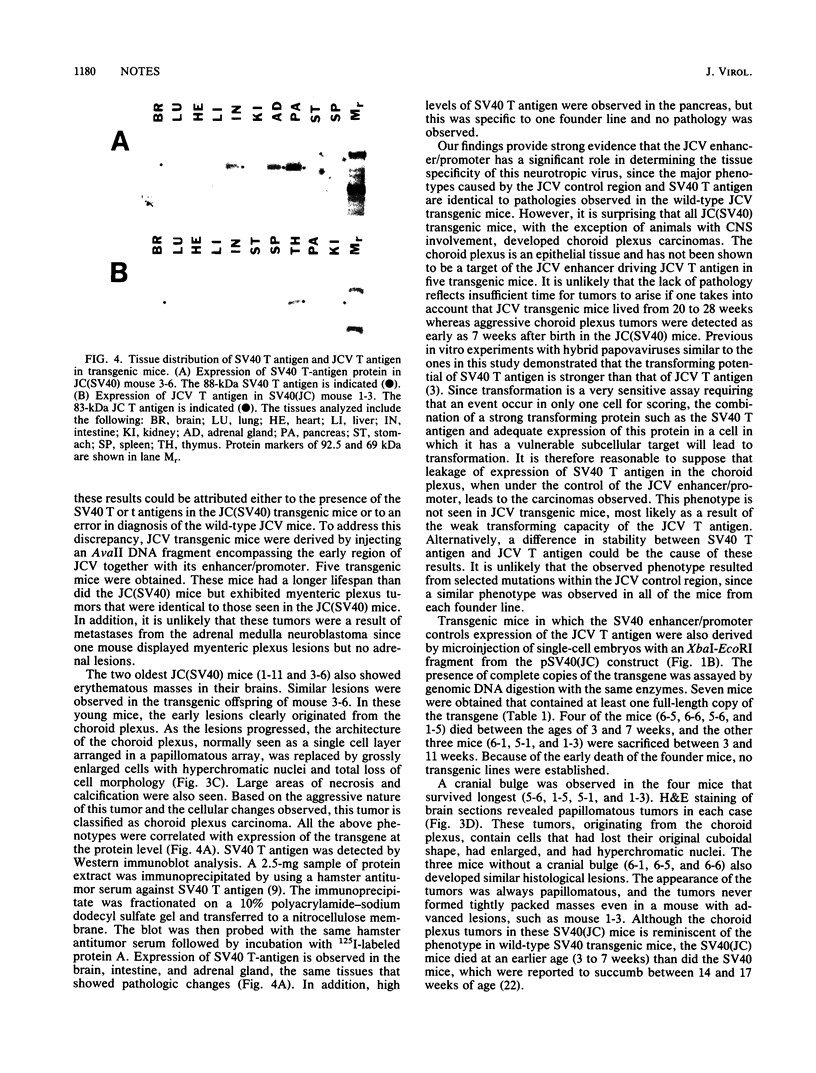
When introduced into the germ line of mice, the simian virus 40 (SV40) T antigen under the control of its own transcriptional enhancer and promoter selectively induced tumors in the choroid plexus as well as thymic hyperplasia and kidney pathology. In contrast, the JC virus (JCV) T antigen under the control of its own regulatory sequences induced hypomyelination of the central nervous system and tumors of neural origin. Since SV40 and JCV have extensive sequence homology, except for their transcriptional control regions, these observations suggest but do not prove that, although the diseases induced by the two viruses, are consequences of the transforming gene, they are determined predominantly by the respective viral enhancers and promoters. To test this hypothesis, the regulatory regions of the two viruses were exchanged, and transgenic mice were derived with either chimeric construct. Like wild-type JCV, the construct containing the SV40 T antigen under the control of the JCV regulatory region induced hypomyelination of the central nervous system and neural tumors. Surprisingly, mice with this construct also developed choroid plexus carcinomas. Like the wild-type SV40 transgenic mice, mice with the JCV T antigen under the control of the SV40 enhancer and promoter developed choroid plexus tumors and renal pathology. Unexpectedly, they also had hyperplasia of the thyroid follicular cells. These findings not only provide direct evidence for the specificity of the respective viral regulatory region but also, more importantly, show that the transforming genes play a critical role in determining viral pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed S., Rappaport J., Tada H., Kerr D., Khalili K. A nuclear protein derived from brain cells stimulates transcription of the human neurotropic virus promoter, JCVE, in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13899–13905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assouline J. G., Major E. O. Human fetal Schwann cells support JC virus multiplication. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):1002–1006. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.1002-1006.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag B., Chuke W. F., Frisque R. J. Hybrid genomes of the polyomaviruses JC virus, BK virus, and simian virus 40: identification of sequences important for efficient transformation. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):863–872. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.863-872.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Messing A., van Dyke T., Levine A. J., Palmiter R. D. Transgenic mice harboring SV40 T-antigen genes develop characteristic brain tumors. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):367–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90367-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigenbaum L., Khalili K., Major E., Khoury G. Regulation of the host range of human papovavirus JCV. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3695–3698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisque R. J., Bream G. L., Cannella M. T. Human polyomavirus JC virus genome. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):458–469. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.458-469.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Nomura S., Anderson C. W., Khoury G. Identification of the SV40 agnogene product: a DNA binding protein. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):346–349. doi: 10.1038/291346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Natarajan V., Strike D., Khoury G., Salzman N. P. JC virus enhancer-promoter active in human brain cells. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1337–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.6095453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalili K., Rappaport J., Khoury G. Nuclear factors in human brain cells bind specifically to the JCV regulatory region. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1205–1210. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02932.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeber G., Dörries K. DNA rearrangements in organ-specific variants of polyomavirus JC strain GS. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1730–1735. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1730-1735.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch K. J., Frisque R. J. Factors contributing to the restricted DNA replicating activity of JC virus. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):306–317. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90035-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay K., Striker L. J., Pinkert C. A., Brinster R. L., Striker G. E. Glomerulosclerosis and renal cysts in mice transgenic for the early region of SV40. Kidney Int. 1987 Dec;32(6):827–837. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. D. Regulatory sequences of SV40 variants isolated from patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Virus Res. 1989 Sep;14(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(89)90072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., ZuRhein G. M., Eckroade R. J., Dessel B. H. Cultivation of papova-like virus from human brain with progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy. Lancet. 1971 Jun 19;1(7712):1257–1260. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. A., Blair D. G., Showalter S. D., Scangos G. A. Analysis of a transgenic mouse containing simian virus 40 and v-myc sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):642–648. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. A., Khoury G., Jay G., Howley P. M., Scangos G. A. Early regions of JC virus and BK virus induce distinct and tissue-specific tumors in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8288–8292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. A., Scangos G. A., Cork L., Jay G., Khoury G. The early region of human papovavirus JC induces dysmyelination in transgenic mice. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90855-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Finlay C., Miller D., Marks J., Lozano G., Levine A. J. Relationship between simian virus 40 large tumor antigen expression and tumor formation in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):2029–2032. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.2029-2032.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]