Abstract
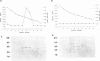
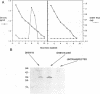
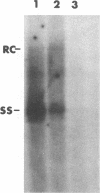
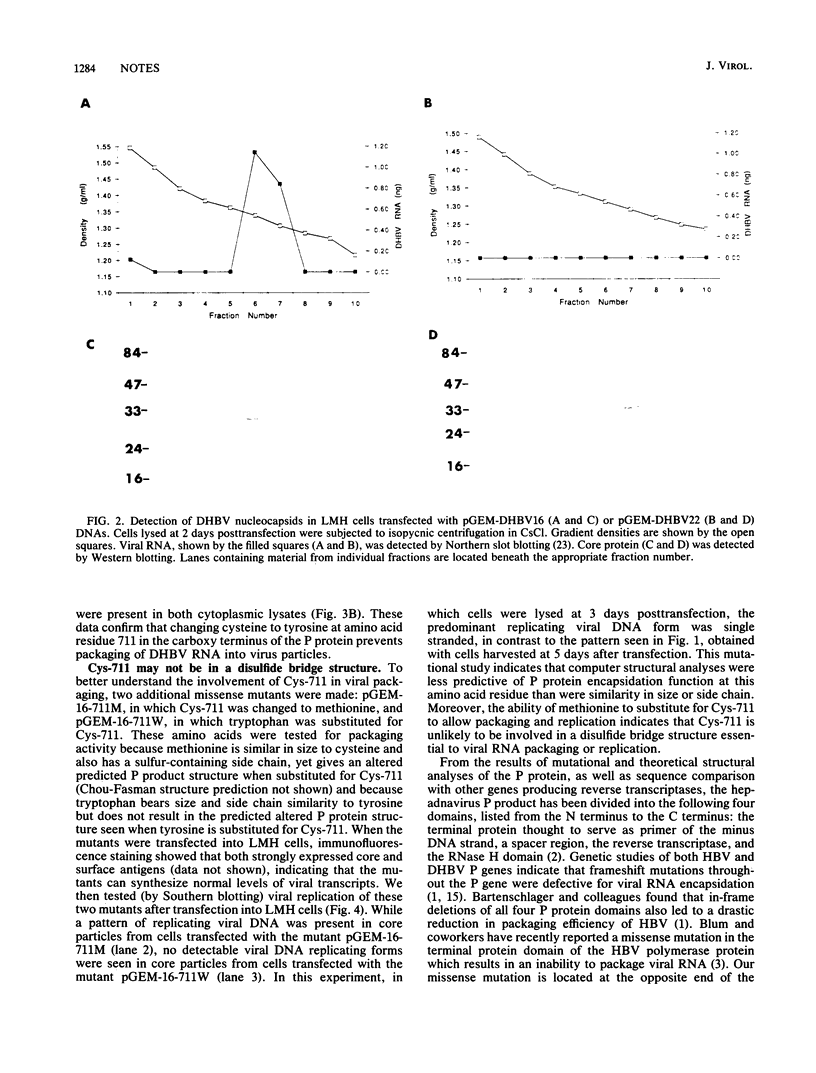
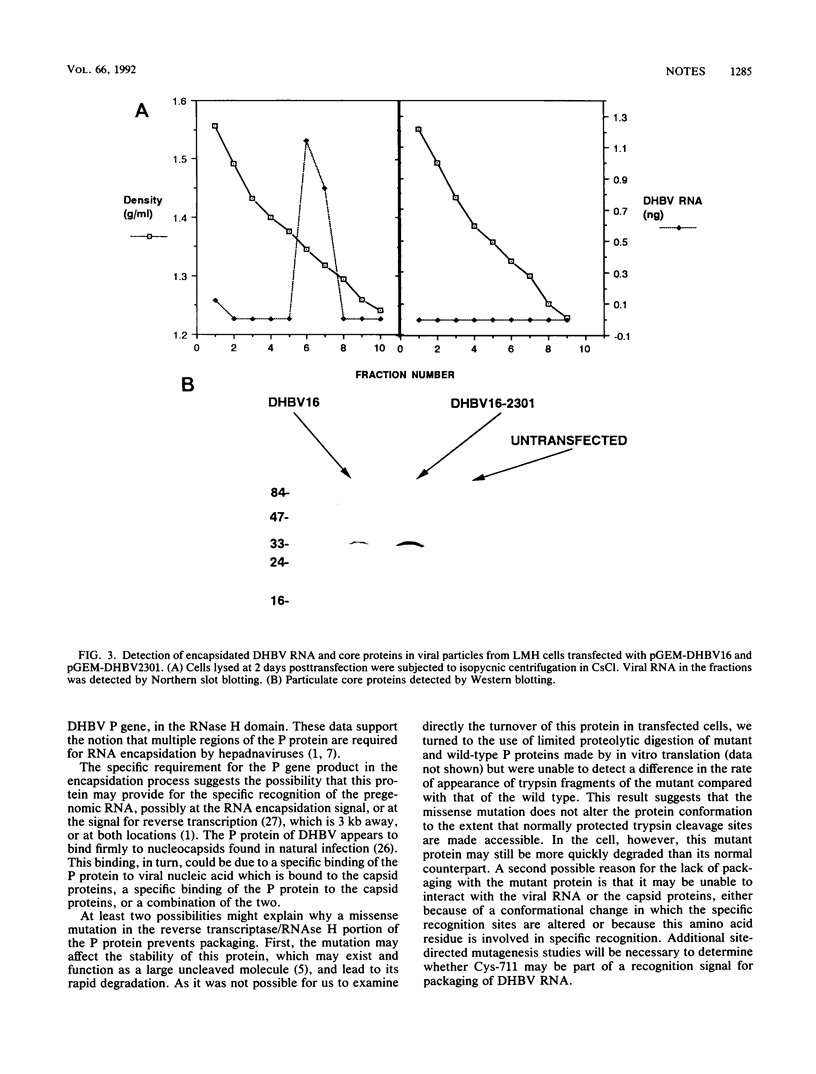
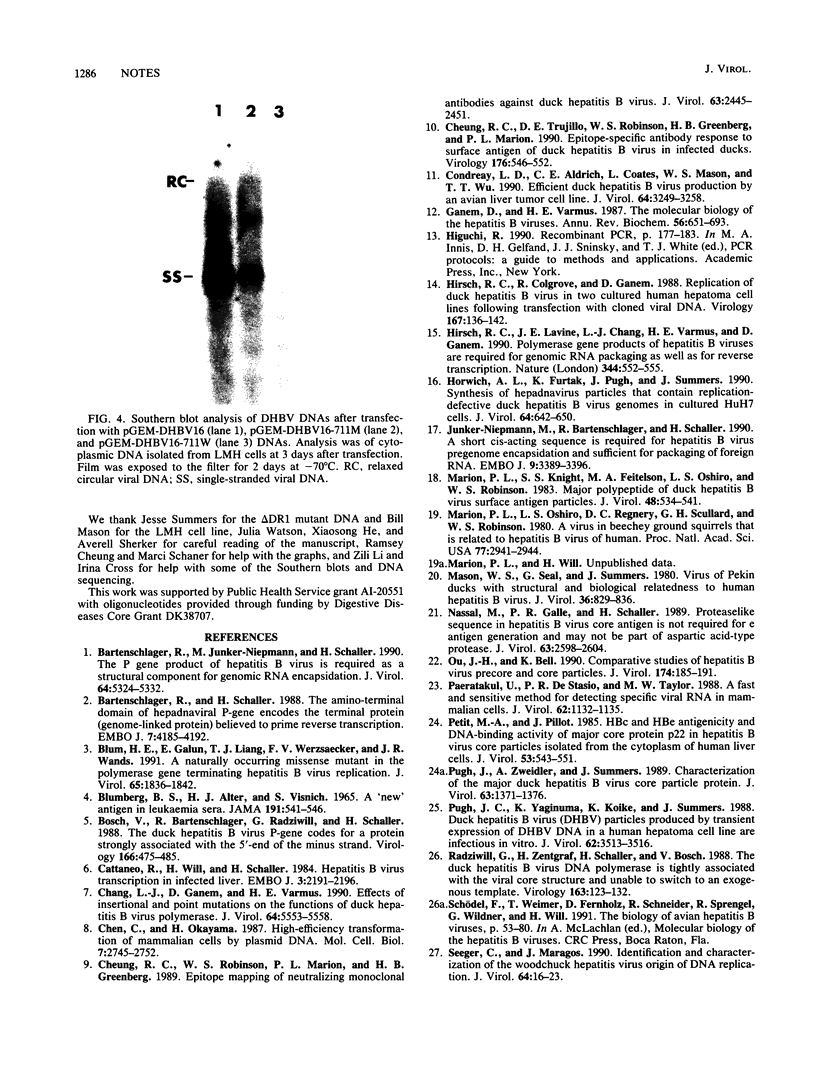
A duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) genome cloned from a domestic duck from the People's Republic of China has been sequenced and exhibits no variation in sequences known to be important in viral replication or generation of gene products. Intrahepatic transfection of a dimer of this viral genome into ducklings did not result in viremia or any sign of virus infection, indicating that the genome was defective. Functional analysis of this mutant genome, performed by transfecting the DNA into a chicken hepatoma cell line capable of replicating wild-type virus, indicated that viral RNA is not encapsidated. However, virus core protein is made and can assemble into particles in the absence of encapsidation of viral nucleic acid. Using genetic approaches, it was determined that a change of cysteine to tyrosine in position 711 in the polymerase (P) gene C terminus led to this RNA-packaging defect. By site-directed mutagenesis, it was found that while substitution of Cys-711 with tryptophan also abolished packaging, substitution with methionine did not affect packaging or viral replication. Therefore, Cys-711, which is conserved in all published sequences of DHBV, may not be involved in a disulfide bridge structure essential to viral RNA packaging or replication. Our results, showing that a missense mutation in the region of the DHBV polymerase protein thought to be primarily the RNase H domain results in packaging deficiency, support the previous findings that multiple regions of the complex hepadnaviral polymerase protein may be required for viral RNA packaging.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLUMBERG B. S., ALTER H. J., VISNICH S. A "NEW" ANTIGEN IN LEUKEMIA SERA. JAMA. 1965 Feb 15;191:541–546. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080070025007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartenschlager R., Junker-Niepmann M., Schaller H. The P gene product of hepatitis B virus is required as a structural component for genomic RNA encapsidation. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5324–5332. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5324-5332.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartenschlager R., Schaller H. The amino-terminal domain of the hepadnaviral P-gene encodes the terminal protein (genome-linked protein) believed to prime reverse transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4185–4192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03315.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum H. E., Galun E., Liang T. J., von Weizsäcker F., Wands J. R. Naturally occurring missense mutation in the polymerase gene terminating hepatitis B virus replication. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1836–1842. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1836-1842.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch V., Bartenschlager R., Radziwill G., Schaller H. The duck hepatitis B virus P-gene codes for protein strongly associated with the 5'-end of the viral DNA minus strand. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):475–485. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90518-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Will H., Schaller H. Hepatitis B virus transcription in the infected liver. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2191–2196. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. J., Hirsch R. C., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Effects of insertional and point mutations on the functions of the duck hepatitis B virus polymerase. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5553–5558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5553-5558.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung R. C., Robinson W. S., Marion P. L., Greenberg H. B. Epitope mapping of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against duck hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2445–2451. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2445-2451.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung R. C., Trujillo D. E., Robinson W. S., Greenberg H. B., Marion P. L. Epitope-specific antibody response to the surface antigen of duck hepatitis B virus in infected ducks. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):546–552. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90025-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condreay L. D., Aldrich C. E., Coates L., Mason W. S., Wu T. T. Efficient duck hepatitis B virus production by an avian liver tumor cell line. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3249–3258. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3249-3258.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R. C., Lavine J. E., Chang L. J., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Polymerase gene products of hepatitis B viruses are required for genomic RNA packaging as wel as for reverse transcription. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):552–555. doi: 10.1038/344552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R., Colgrove R., Ganem D. Replication of duck hepatitis B virus in two differentiated human hepatoma cell lines after transfection with cloned viral DNA. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A. L., Furtak K., Pugh J., Summers J. Synthesis of hepadnavirus particles that contain replication-defective duck hepatitis B virus genomes in cultured HuH7 cells. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):642–650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.642-650.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junker-Niepmann M., Bartenschlager R., Schaller H. A short cis-acting sequence is required for hepatitis B virus pregenome encapsidation and sufficient for packaging of foreign RNA. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3389–3396. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L., Knight S. S., Feitelson M. A., Oshiro L. S., Robinson W. S. Major polypeptide of duck hepatitis B surface antigen particles. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):534–541. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.534-541.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L., Oshiro L. S., Regnery D. C., Scullard G. H., Robinson W. S. A virus in Beechey ground squirrels that is related to hepatitis B virus of humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2941–2945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Seal G., Summers J. Virus of Pekin ducks with structural and biological relatedness to human hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):829–836. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.829-836.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassal M., Galle P. R., Schaller H. Proteaselike sequence in hepatitis B virus core antigen is not required for e antigen generation and may not be part of an aspartic acid-type protease. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2598–2604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2598-2604.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Bell K. D. Comparative studies of hepatitis B virus precore and core particles. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paeratakul U., De Stasio P. R., Taylor M. W. A fast and sensitive method for detecting specific viral RNA in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1132–1135. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1132-1135.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit M. A., Pillot J. HBc and HBe antigenicity and DNA-binding activity of major core protein P22 in hepatitis B virus core particles isolated from the cytoplasm of human liver cells. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):543–551. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.543-551.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh J. C., Yaginuma K., Koike K., Summers J. Duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) particles produced by transient expression of DHBV DNA in a human hepatoma cell line are infectious in vitro. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3513–3516. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3513-3516.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh J., Zweidler A., Summers J. Characterization of the major duck hepatitis B virus core particle protein. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1371–1376. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1371-1376.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziwill G., Zentgraf H., Schaller H., Bosch V. The duck hepatitis B virus DNA polymerase is tightly associated with the viral core structure and unable to switch to an exogenous template. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90239-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger C., Maragos J. Identification and characterization of the woodchuck hepatitis virus origin of DNA replication. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):16–23. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.16-23.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel R., Kaleta E. F., Will H. Isolation and characterization of a hepatitis B virus endemic in herons. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3832–3839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3832-3839.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel R., Schneider R., Marion P. L., Fernholz D., Wildner G., Will H. Comparative sequence analysis of defective and infectious avian hepadnaviruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4289–4289. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smith P. M., Horwich A. L. Hepadnavirus envelope proteins regulate covalently closed circular DNA amplification. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2819–2824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2819-2824.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smolec J. M., Snyder R. A virus similar to human hepatitis B virus associated with hepatitis and hepatoma in woodchucks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4533–4537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sureau C., Romet-Lemonne J. L., Mullins J. I., Essex M. Production of hepatitis B virus by a differentiated human hepatoma cell line after transfection with cloned circular HBV DNA. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90364-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagawa M., Robinson W. S., Marion P. L. Duck hepatitis B virus replicates in the yolk sac of developing embryos. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2273–2279. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2273-2279.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]