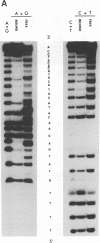
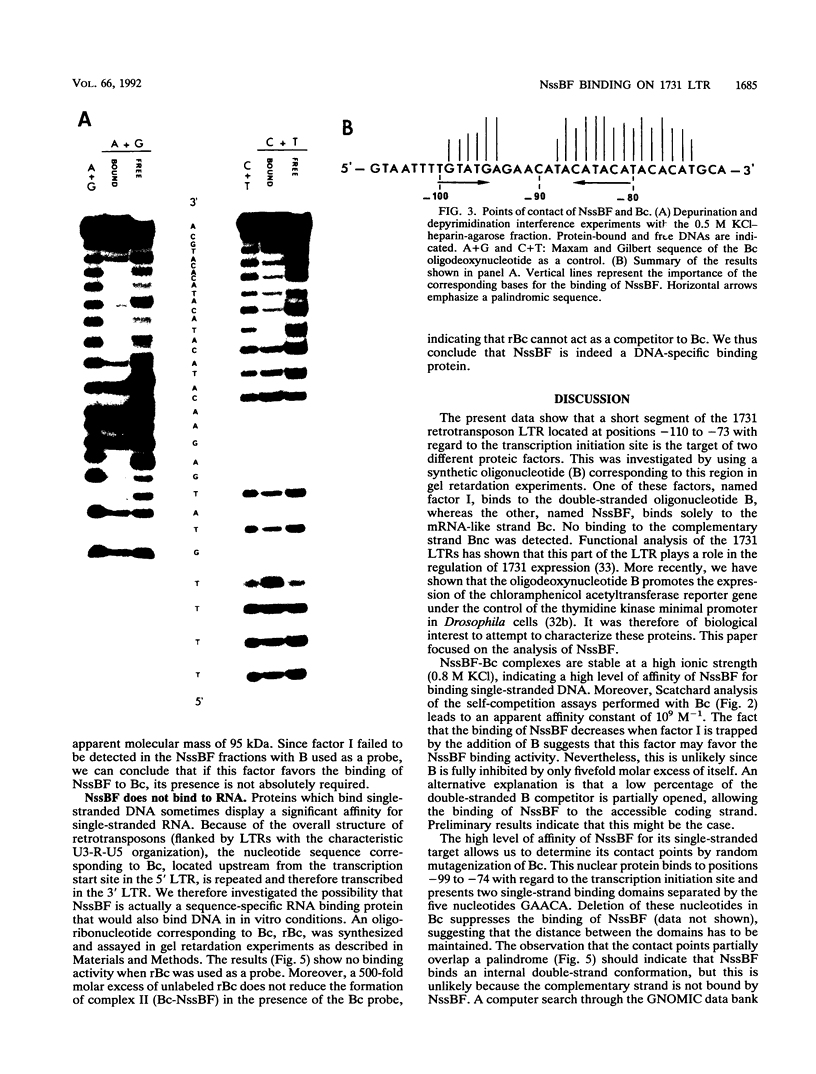
Abstract
Using gel mobility assays, we have detected two proteins that bind in the U3 region of the 1731 retrotransposon long terminal repeats (between positions -110 and -73) in nuclear extracts from Drosophila melanogaster cultured cells. The first one binds double-stranded DNA, whereas the other binds the mRNA-like strand in a sequence-specific manner. We report here the characterization of the latter protein, named NssBF for nuclear single-stranded-DNA binding factor. Gel filtration shows an apparent molecular mass of 95 kDa for NssBF. The points of contact between NssBF and its single-stranded DNA target were determined. This protein binds neither the complementary strand nor the corresponding RNA sequence. A possible role of NssBF in transcription is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. C., Smiley J. K., Campbell J. L. Purification of DNA polymerase II stimulatory factor I, a yeast single-stranded DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):677–681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunelle A., Schleif R. F. Missing contact probing of DNA-protein interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6673–6676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase J. W., Williams K. R. Single-stranded DNA binding proteins required for DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:103–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. M., Lehman I. R. Enzymes of general recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:229–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echalier G. Drosophila retrotransposons: interactions with genome. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:33–105. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60582-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echalier G., Ohanessian A. Isolement, en cultures in vitro, de lignées cellulaires diploïdes de Drosophila melanogaster. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1969 Mar 31;268(13):1771–1773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelmann W., Kröger B., Goller M., Horak I. A recombination hotspot in the LTR of a mouse retrotransposon identified in an in vitro system. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):937–946. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90332-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feavers I. M., McEwan I. J., Liang H., Jost J. P. An estradiol-dependent protein from chicken liver binds single-stranded DNA and RNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9114–9117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnegan D. J., Fawcett D. H. Transposable elements in Drosophila melanogaster. Oxf Surv Eukaryot Genes. 1986;3:1–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fourcade-Peronnet F., d'Auriol L., Becker J., Galibert F., Best-Belpomme M. Primary structure and functional organization of Drosophila 1731 retrotransposon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6113–6125. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry M., Perrino F. W., Levy A., Loeb L. A. Factor D is a selective single-stranded oligodeoxythymidine binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):199–211. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard C., Strauss F. Sequence-specific single-strand-binding protein for the simian virus 40 early promoter stimulates transcription in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1990 Sep 20;215(2):245–255. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80343-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard C., Weber M., Strauss F. A sequence-specific single-strand-binding protein for the late-coding strand of the simian virus 40 control region. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2380–2385. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2380-2385.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss P., Krassa K. B., McPheeters D. S., Nelson M. A., Gold L. Zinc (II) and the single-stranded DNA binding protein of bacteriophage T4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8515–8519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann O., Heidmann T. Retrotransposition of a mouse IAP sequence tagged with an indicator gene. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):159–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90217-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Saluz H., Jiricny J., Moncharmont B. Estradiol-dependent trans-acting factor binds preferentially to a dyad-symmetry structure within the third intron of the avian vitellogenin gene. J Cell Biochem. 1987 Sep;35(1):69–82. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240350106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny M. K., Schlegel U., Furneaux H., Hurwitz J. The role of human single-stranded DNA binding protein and its individual subunits in simian virus 40 DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7693–7700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Lueders K. K. The intracisternal A-particle gene family: structure and functional aspects. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;51:183–276. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lannigan D. A., Notides A. C. Estrogen receptor selectively binds the "coding strand" of an estrogen responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):863–867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinbach S. S., Heath L. S. Characterization of the single-stranded DNA-binding domain of the herpes simplex virus protein ICP8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 14;1008(3):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg G., Kowalczykowski S. C., Rist J. K., Sugino A., Rothman-Denes L. B. Purification and characterization of the coliphage N4-coded single-stranded DNA binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12700–12708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee R., Chambon P. A single-stranded DNA-binding protein promotes the binding of the purified oestrogen receptor to its responsive element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5713–5716. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor L. H., Clark E. M. d(TG)n.d(CA)n sequences upstream of the rat prolactin gene form Z-DNA and inhibit gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1595–1601. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peritz L. N., Fodor E. J., Silversides D. W., Cattini P. A., Baxter J. D., Eberhardt N. L. The human growth hormone gene contains both positive and negative control elements. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5005–5007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peronnet F., Becker J. L., Becker J., d'Auriol L., Galibert F., Best-Belpomme M. 1731, a new retrotransposon with hormone modulated expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9017–9033. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Homologous pairing and strand exchange in genetic recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:405–437. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., Nordheim A., Wang A. H. The chemistry and biology of left-handed Z-DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:791–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.004043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runkel L., Nordheim A. Chemical footprinting of the interaction between left-handed Z-DNA and anti-Z-DNA antibodies by diethylpyrocarbonate carbethoxylation. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jun 5;189(3):487–501. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90319-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traut W., Fanning E. Sequence-specific interactions between a cellular DNA-binding protein and the simian virus 40 origin of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):903–911. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziarczyk P., Best-Belpomme M. A short 5' region of the long terminal repeat is required for regulation by hormone and heat shock of Drosophila retrotransposon 1731. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5689–5693. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziarczyk P., Fourcade-Peronnet F., Simonart S., Maisonhaute C., Best-Belpomme M. Functional analysis of the long terminal repeats of Drosophila 1731 retrotransposon: promoter function and steroid regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8631–8644. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]