Abstract
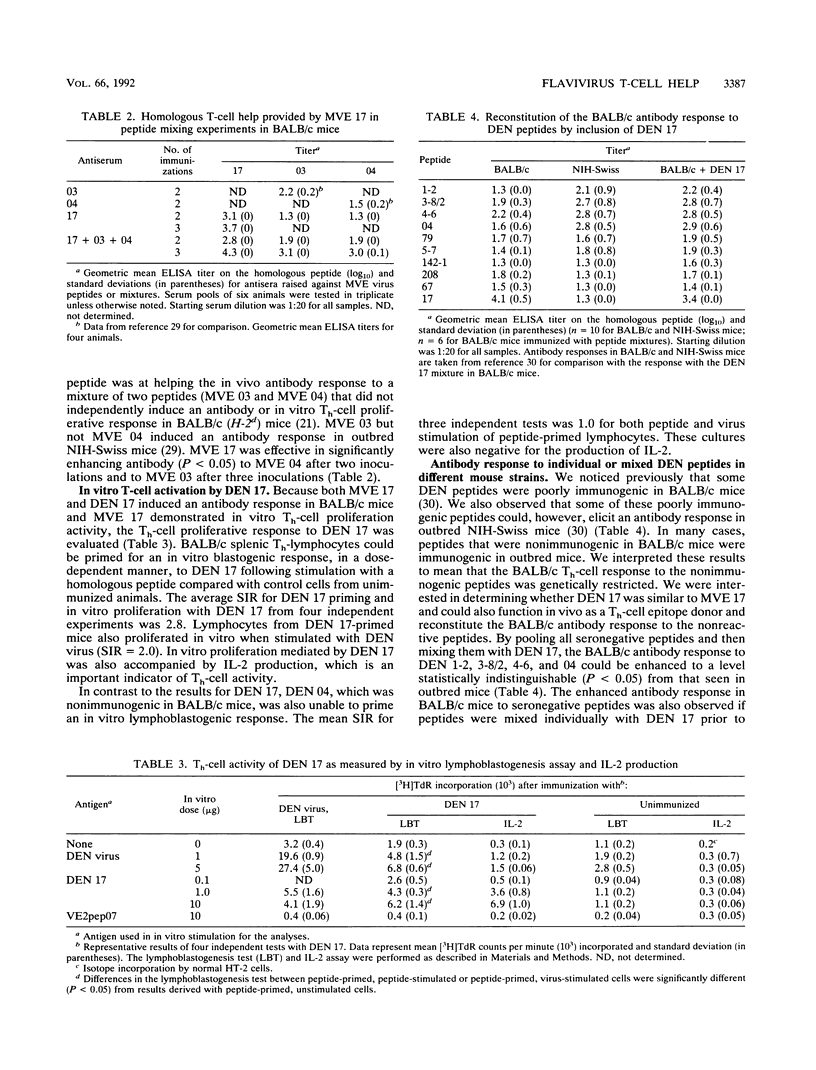
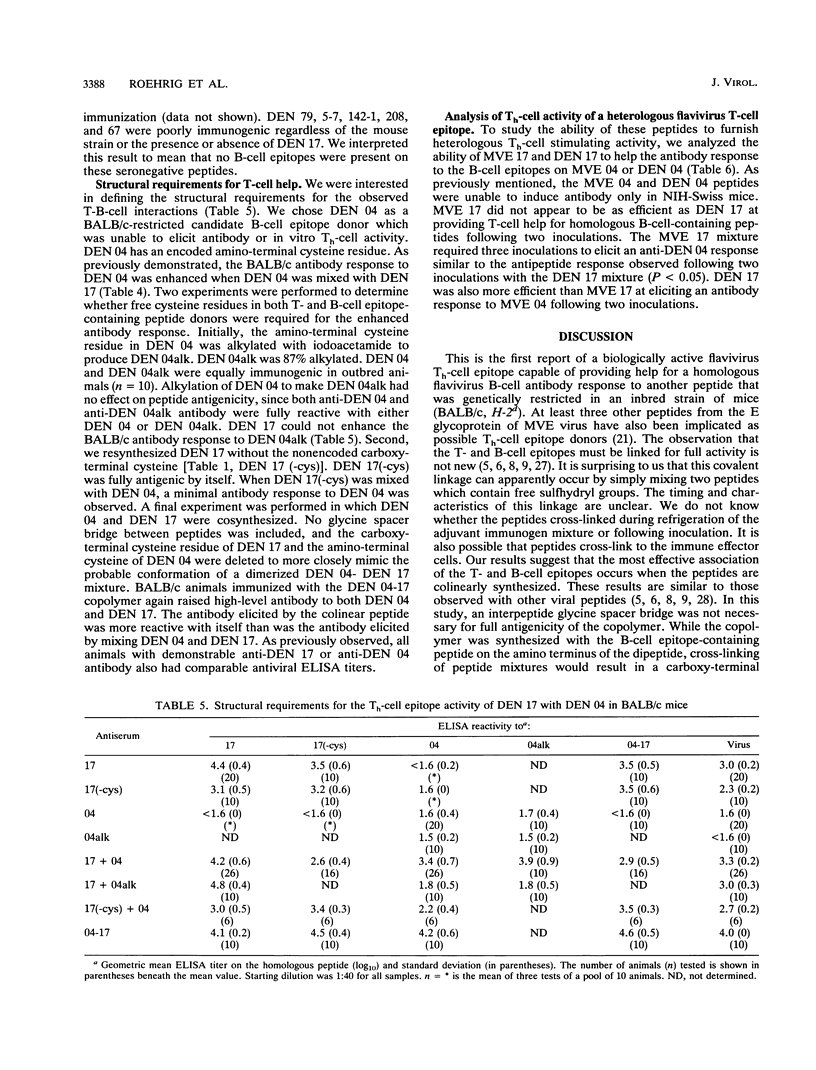
We have been investigating the T-helper (Th)-cell response to the flavivirus envelope (E) glycoprotein. In our studies with Murray Valley encephalitis (MVE) virus, we previously identified synthetic peptides capable of priming Th lymphocytes for an in vitro antivirus proliferative response (J. H. Mathews, J. E. Allan, J. T. Roehrig, J. R. Brubaker, and A. R. Hunt, J. Virol. 65:5141-5148, 1991). We have now characterized in vivo Th-cell priming activity of one of these peptides (MVE 17, amino acids 356 to 376) and an analogous peptide derived from the E-glycoprotein sequence of the dengue (DEN) 2, Jamaica strain (DEN 17, amino acids 352 to 368). This DEN peptide also primed the Th-cell compartment in BALB/c mice, as measured by in vitro proliferation and interleukin production. The failure of some MVE and DEN virus synthetic peptides to elicit an antibody response in BALB/c mice could be overcome if a Th-cell epitope-containing peptide was included in the immunization mixture. A more detailed analysis of the structural interactions between Th-cell and B-cell epitope donor peptides revealed that the peptides must be linked to observe the enhanced antibody response. Blockage or deletion of the free cysteine residue on either peptide abrogated the antibody response. The most efficient T-B-cell epitope interaction occurred when the peptides were colinearly synthesized. These Th-cell-stimulating peptides were also functional with the heterologous B-cell epitope-containing peptides. The Th-cell epitope on DEN 17 was more potent than the Th-cell epitope on MVE 17.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J. E., Doherty P. C. Stimulation of helper/delayed-type hypersensitivity T cells by flavivirus infection: determination by macrophage procoagulant assay. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jan;67(Pt 1):39–46. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett B. C., Graham C. M., Burt D. S., Skehel J. J., Thomas D. B. The immune response of BALB/c mice to influenza hemagglutinin: commonality of the B cell and T cell repertoires and their relevance to antigenic drift. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Mar;19(3):515–521. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borras-Cuesta F., Petit-Camurdan A., Fedon Y. Engineering of immunogenic peptides by co-linear synthesis of determinants recognized by B and T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Aug;17(8):1213–1215. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt W. E. From the World Health Organization. Development of dengue and Japanese encephalitis vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;162(3):577–583. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.3.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. H., Ivanyi J., Young D. B., Lamb J. R., Syred A. D., Francis M. J. Orientation of epitopes influences the immunogenicity of synthetic peptide dimers. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Dec;18(12):2015–2019. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertl H. C., Dietzschold B., Gore M., Otvos L., Jr, Larson J. K., Wunner W. H., Koprowski H. Induction of rabies virus-specific T-helper cells by synthetic peptides that carry dominant T-helper cell epitopes of the viral ribonucleoprotein. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2885–2892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2885-2892.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis M. J., Hastings G. Z., Clarke B. E., Brown A. L., Beddell C. R., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Neutralizing antibodies to all seven serotypes of foot-and-mouth disease virus elicited by synthetic peptides. Immunology. 1990 Feb;69(2):171–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis M. J., Hastings G. Z., Syred A. D., McGinn B., Brown F., Rowlands D. J. Non-responsiveness to a foot-and-mouth disease virus peptide overcome by addition of foreign helper T-cell determinants. Nature. 1987 Nov 12;330(6144):168–170. doi: 10.1038/330168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao X. M., Liew F. Y., Tite J. P. A dominant Th epitope in influenza nucleoprotein. Analysis of the fine specificity and functional repertoire of T cells recognizing a single determinant. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2730–2737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao X. M., Liew F. Y., Tite J. P. Identification and characterization of T helper epitopes in the nucleoprotein of influenza A virus. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):3007–3014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. Long term culture of tumour-specific cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):154–156. doi: 10.1038/268154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heber-Katz E., Valentine S., Dietzschold B., Burns-Purzycki C. Overlapping T cell antigenic sites on a synthetic peptide fragment from herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D, the degenerate MHC restriction elicited, and functional evidence for antigen-Ia interaction. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):275–287. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. J., Brubaker J. R., Roehrig J. T., Trent D. W. Variants of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus that resist neutralization define a domain of the E2 glycoprotein. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):676–683. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90533-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurane I., Innis B. L., Nisalak A., Hoke C., Nimmannitya S., Meager A., Ennis F. A. Human T cell responses to dengue virus antigens. Proliferative responses and interferon gamma production. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):506–513. doi: 10.1172/JCI113911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurane I., Meager A., Ennis F. A. Dengue virus-specific human T cell clones. Serotype crossreactive proliferation, interferon gamma production, and cytotoxic activity. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):763–775. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurata A., Palker T. J., Streilein R. D., Scearce R. M., Haynes B. F., Berzofsky J. A. Immunodominant sites of human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1 envelope protein for murine helper T cells. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):2024–2030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutubuddin M., Kolaskar A. S., Galande S., Gore M. M., Ghosh S. N., Banerjee K. Recognition of helper T cell epitopes in envelope (E) glycoprotein of Japanese encephalitis, west Nile and Dengue viruses. Mol Immunol. 1991 Jan-Feb;28(1-2):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margalit H., Spouge J. L., Cornette J. L., Cease K. B., Delisi C., Berzofsky J. A. Prediction of immunodominant helper T cell antigenic sites from the primary sequence. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2213–2229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews J. H., Allan J. E., Roehrig J. T., Brubaker J. R., Uren M. F., Hunt A. R. T-helper cell and associated antibody response to synthetic peptides of the E glycoprotein of Murray Valley encephalitis virus. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5141–5148. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5141-5148.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews J. H., Roehrig J. T. Specificity of the murine T helper cell immune response to various alphaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1989 Nov;70(Pt 11):2877–2886. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-11-2877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., McLachlan A., Moriarty A., Thornton G. B. A single 10-residue pre-S(1) peptide can prime T cell help for antibody production to multiple epitopes within the pre-S(1), pre-S(2), and S regions of HBsAg. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4457–4465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., McLachlan A., Thornton G. B., Hughes J. L. Antibody production to the nucleocapsid and envelope of the hepatitis B virus primed by a single synthetic T cell site. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):547–549. doi: 10.1038/329547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R. Synthetic T and B cell recognition sites: implications for vaccine development. Adv Immunol. 1989;45:195–282. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60694-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas J. A., Levely M. E., Mitchell M. A., Smith C. W. A 16-amino acid peptide of respiratory syncytial virus 1A protein contains two overlapping T cell-stimulating sites distinguishable by class II MHC restriction elements. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2790–2796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partidos C. D., Stanley C. M., Steward M. W. Immune responses in mice following immunization with chimeric synthetic peptides representing B and T cell epitopes of measles virus proteins. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jun;72(Pt 6):1293–1299. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-6-1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partidos C. D., Steward M. W. Prediction and identification of a T cell epitope in the fusion protein of measles virus immunodominant in mice and humans. J Gen Virol. 1990 Sep;71(Pt 9):2099–2105. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-9-2099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehrig J. T., Hunt A. R., Johnson A. J., Hawkes R. A. Synthetic peptides derived from the deduced amino acid sequence of the E-glycoprotein of Murray Valley encephalitis virus elicit antiviral antibody. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90509-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehrig J. T., Johnson A. J., Hunt A. R., Bolin R. A., Chu M. C. Antibodies to dengue 2 virus E-glycoprotein synthetic peptides identify antigenic conformation. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):668–675. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90532-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. B., Lechler R. I., Howland K., Bal V., Eckels D. D., Sekaly R., Long E. O., Taylor W. R., Lamb J. R. Structural model of HLA-DR1 restricted T cell antigen recognition. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):515–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90464-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman A. L., Kurane I., Zhang Y. M., Lai C. J., Ennis F. A. Dengue virus-specific murine T-lymphocyte proliferation: serotype specificity and response to recombinant viral proteins. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2486–2491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2486-2491.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin V. K., Kent S. B., Tam J. P., Merrifield R. B. Quantitative monitoring of solid-phase peptide synthesis by the ninhydrin reaction. Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90704-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherle P. A., Gerhard W. Functional analysis of influenza-specific helper T cell clones in vivo. T cells specific for internal viral proteins provide cognate help for B cell responses to hemagglutinin. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1114–1128. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uren M. F., Doherty P. C., Allan J. E. Flavivirus-specific murine L3T4+ T cell clones: induction, characterization and cross-reactivity. J Gen Virol. 1987 Oct;68(Pt 10):2655–2663. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-10-2655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


