Abstract
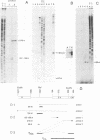
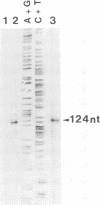
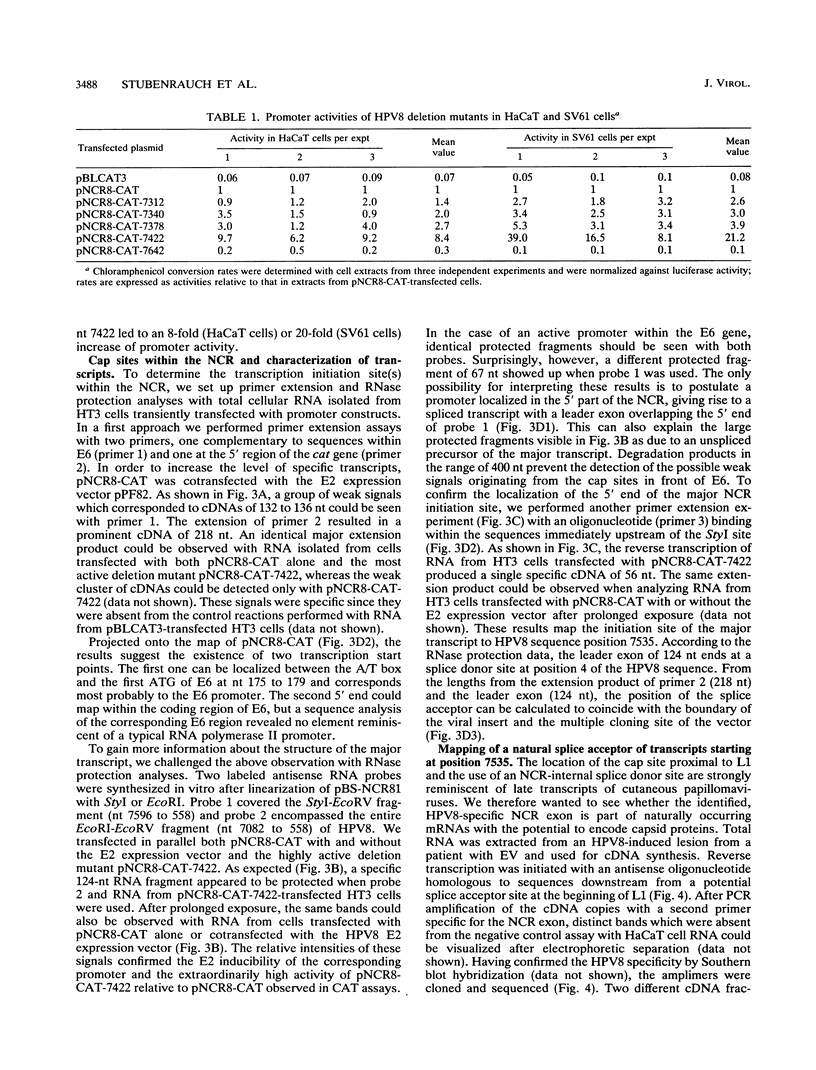
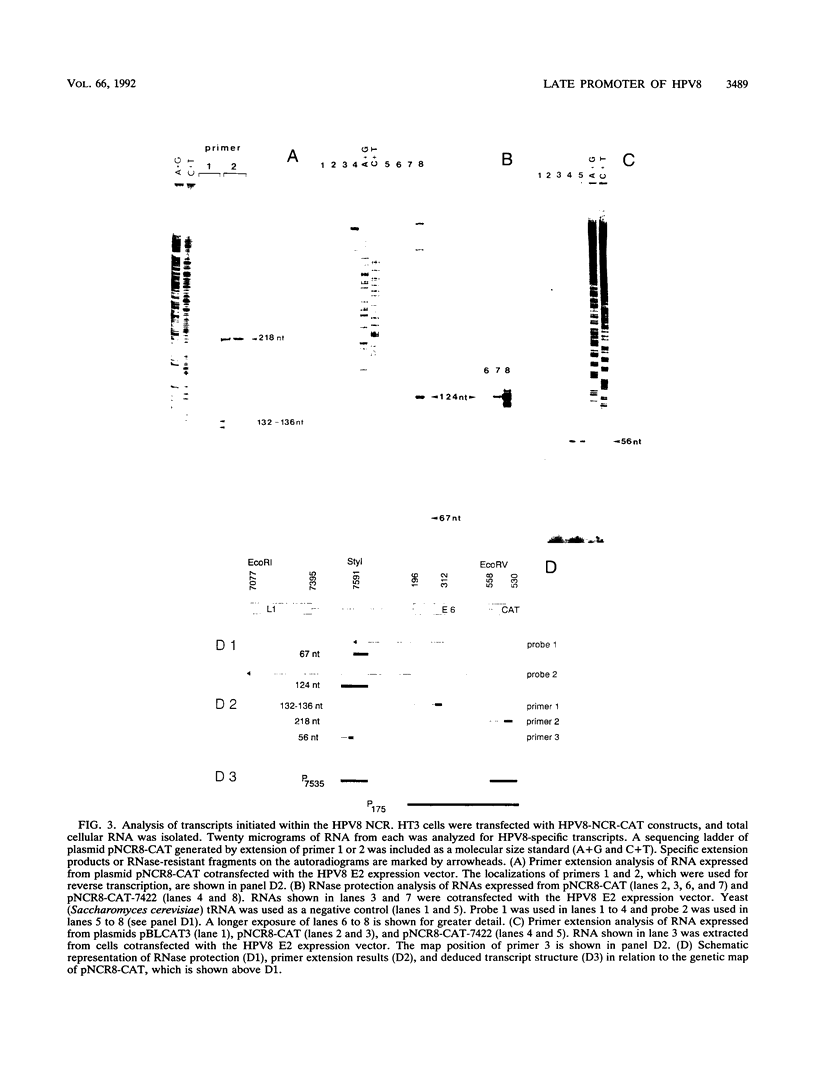
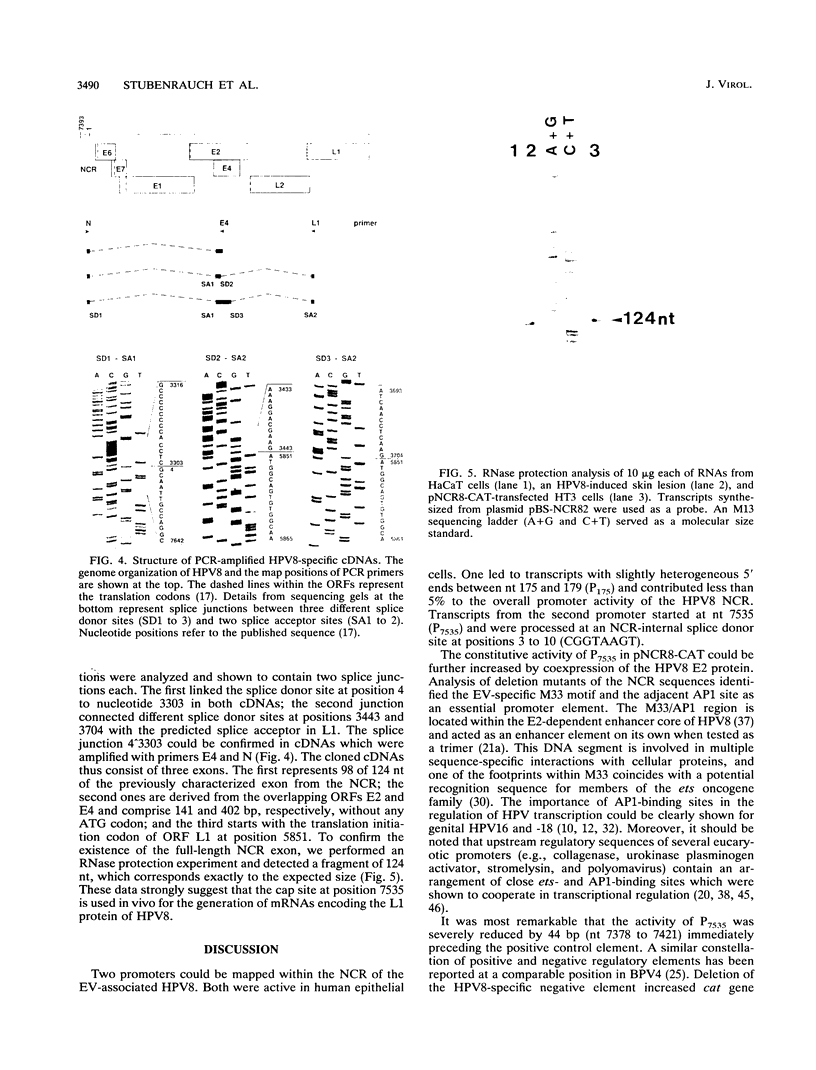
Human papillomavirus type 8 (HPV8) belongs to the HPV types associated with skin carcinomas of patients with epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EV). Its noncoding regulatory sequences (NCR) were shown to drive the expression of the reporter gene chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (cat) in transient assays with human epithelial cells (HT3 cells). This constitutive activity could be enhanced by coexpression of the HPV8 transactivator protein E2. The analysis of 5' deletions of the NCR showed that the EV-specific sequence motif M33 and the neighboring AP1 site are essential for the promoter activity, whereas 44 nucleotides located immediately upstream of M33 are strongly inhibitory. The same effects were observed in simian virus 40-immortalized fetal keratinocytes (SV61 cells) and spontaneously immortalized skin keratinocytes (HaCaT cells). By using primer extension and RNase protection analyses two promoters could be identified within the HPV8 NCR. A nested set of weak signals, corresponding to start sites between positions 175 to 179, represented the previously described E6 promoter. The vast majority of transcripts was initiated at position 7535 and shown to undergo processing at an NCR-internal splice donor (positions 1 to 8). The promoter P7535 is similar to late promoters of other skin-associated papillomaviruses as far as localization, transcript structure, and sequence characteristics are concerned. To confirm that P7535-initiated transcripts proceed indeed to the L1 gene for the major capsid protein, viral mRNAs from an HPV8-induced lesion of a patient with EV were characterized by RNase protection and sequence analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified cDNAs. The NCR leader (positions 7535 to 4) appeared in two messages with three exons each. The third exon started with the second ATG codon of L1 in both cases; the short central exons from the 3' part of the early coding region were defined by a common splice acceptor site (position 3303) and different splice donor sites (positions 3443 and 3704).
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. C., Howley P. M. Differential promoter utilization by the bovine papillomavirus in transformed cells and productively infected wart tissues. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1027–1035. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boukamp P., Petrussevska R. T., Breitkreutz D., Hornung J., Markham A., Fusenig N. E. Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):761–771. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Radonovich M., Vodkin M., Natarajan V., Thoren M., Das G., Janik J., Salzman N. P. Site-specific base substitution and deletion mutations that enhance or suppress transcription of the SV40 major late RNA. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):625–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90318-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Howley P. M., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H. The primary structure and genetic organization of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 genome. Nature. 1982 Oct 7;299(5883):529–534. doi: 10.1038/299529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong T., Chan W. K., Bernard H. U. Transcriptional activation of human papillomavirus 16 by nuclear factor I, AP1, steroid receptors and a possibly novel transcription factor, PVF: a model for the composition of genital papillomavirus enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):465–470. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Reilly S. S., Broker T. R., Taichman L. B. Identification and mapping of human papillomavirus type 1 RNA transcripts recovered from plantar warts and infected epithelial cell cultures. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1913–1918. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1913-1918.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripe T. P., Alderborn A., Anderson R. D., Parkkinen S., Bergman P., Haugen T. H., Pettersson U., Turek L. P. Transcriptional activation of the human papillomavirus-16 P97 promoter by an 88-nucleotide enhancer containing distinct cell-dependent and AP-1-responsive modules. New Biol. 1990 May;2(5):450–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danos O., Katinka M., Yaniv M. Human papillomavirus 1a complete DNA sequence: a novel type of genome organization among papovaviridae. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):231–236. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01152.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensser A., Pfister H. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis associated human papillomaviruses present a subgenus-specific organization of the regulatory genome region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3919–3922. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. G., Iftner T., Weninger J., Pfister H. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis-associated human papillomavirus 8: genomic sequence and comparative analysis. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):626–634. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.626-634.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth P. A., Baker C. C. An element in the bovine papillomavirus late 3' untranslated region reduces polyadenylated cytoplasmic RNA levels. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5806–5812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5806-5812.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giri I., Danos O., Yaniv M. Genomic structure of the cottontail rabbit (Shope) papillomavirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1580–1584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Wasylyk B. The collagenase gene promoter contains a TPA and oncogene-responsive unit encompassing the PEA3 and AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2241–2246. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iftner T., Fuchs P. G., Pfister H. Two independently transforming functions of human papillomavirus 8. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;144:167–173. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74578-2_20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iftner T., Sagner G., Pfister H., Wettstein F. O. The E7 protein of human papillomavirus 8 is a nonphosphorylated protein of 17 kDa and can be generated by two different mechanisms. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):428–436. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90311-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. E., Campo M. S. Positive and negative E2-independent regulatory elements in the long control region of bovine papillomavirus type 4. J Gen Virol. 1991 Apr;72(Pt 4):877–883. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-4-877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy I. M., Haddow J. K., Clements J. B. A negative regulatory element in the human papillomavirus type 16 genome acts at the level of late mRNA stability. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):2093–2097. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.2093-2097.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyono T., Nagashima K., Ishibashi M. The primary structure of major viral RNA in a rat cell line transfected with type 47 human papillomavirus DNA and the transforming activity of its cDNA and E6 gene. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):551–565. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90567-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krubke J., Kraus J., Delius H., Chow L., Broker T., Iftner T., Pfister H. Genetic relationship among human papillomaviruses associated with benign and malignant tumours of patients with epidermodysplasia verruciformis. J Gen Virol. 1987 Dec;68(Pt 12):3091–3103. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-12-3091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May M., Helbl V., Pfister H., Fuchs P. G. Unique topography of DNA-protein interactions in the non-coding region of epidermodysplasia verruciformis-associated human papillomaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1991 Dec;72(Pt 12):2989–2997. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-12-2989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tilly K., Maniatis T. Fine structure genetic analysis of a beta-globin promoter. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):613–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3457470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offord E. A., Beard P. A member of the activator protein 1 family found in keratinocytes but not in fibroblasts required for transcription from a human papillomavirus type 18 promoter. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4792–4798. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4792-4798.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palermo-Dilts D. A., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Human papillomavirus type 1 produces redundant as well as polycistronic mRNAs in plantar warts. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3144–3149. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3144-3149.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson E. K., Grabham P., Emmerson A. A subpopulation of cultured human keratinocytes which is resistant to the induction of terminal differentiation-related changes by phorbol, 12-myristate, 13-acetate: evidence for an increase in the resistant population following transformation. Carcinogenesis. 1983;4(7):857–861. doi: 10.1093/carcin/4.7.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister H. Biology and biochemistry of papillomaviruses. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1984;99:111–181. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reh H., Pfister H. Human papillomavirus type 8 contains cis-active positive and negative transcriptional control sequences. J Gen Virol. 1990 Oct;71(Pt 10):2457–2462. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-10-2457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiter M., van Mullem P. J. Behavior of virus in malignant degeneration of skin lesion in epidermodysplasia verruciformis. J Invest Dermatol. 1970 Apr;54(4):324–331. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12258641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rørth P., Nerlov C., Blasi F., Johnsen M. Transcription factor PEA3 participates in the induction of urokinase plasminogen activator transcription in murine keratinocytes stimulated with epidermal growth factor or phorbol-ester. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5009–5017. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Prokoph H., Wettstein F. O. Oncogenic and nononcogenic human genital papillomaviruses generate the E7 mRNA by different mechanisms. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1441–1447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1441-1447.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamminger T., Fickenscher H., Fleckenstein B. Cell type-specific induction of the major immediate early enhancer of human cytomegalovirus by cyclic AMP. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jan;71(Pt 1):105–113. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-1-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanssens P., Opsomer C., McKeown Y. M., Kramer W., Zabeau M., Fritz H. J. Efficient oligonucleotide-directed construction of mutations in expression vectors by the gapped duplex DNA method using alternating selectable markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4441–4454. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenlund A., Botchan M. R. The E2 trans-activator can act as a repressor by interfering with a cellular transcription factor. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):123–136. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vande Pol S. B., Howley P. M. A bovine papillomavirus constitutive enhancer is negatively regulated by the E2 repressor through competitive binding for a cellular factor. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5420–5429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5420-5429.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Flores P., Begue A., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The c-ets proto-oncogenes encode transcription factors that cooperate with c-Fos and c-Jun for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):191–193. doi: 10.1038/346191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Gutman A., Nicholson R., Wasylyk B. The c-Ets oncoprotein activates the stromelysin promoter through the same elements as several non-nuclear oncoproteins. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1127–1134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettstein F. O., Barbosa M. S., Nasseri M. Identification of the major cottontail rabbit papillomavirus late RNA cap site and mapping and quantitation of an E2 and minor E6 coding mRNA in papillomas and carcinomas. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):321–328. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90470-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe Y., Yasui M., Yoshino N., Fujiwara T., Ohkuma N., Nohara N. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis: viral particles in early malignant lesions. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Oct;71(4):225–228. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12515089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Human papillomaviruses and their possible role in squamous cell carcinomas. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1977;78:1–30. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66800-5_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]