Abstract
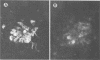
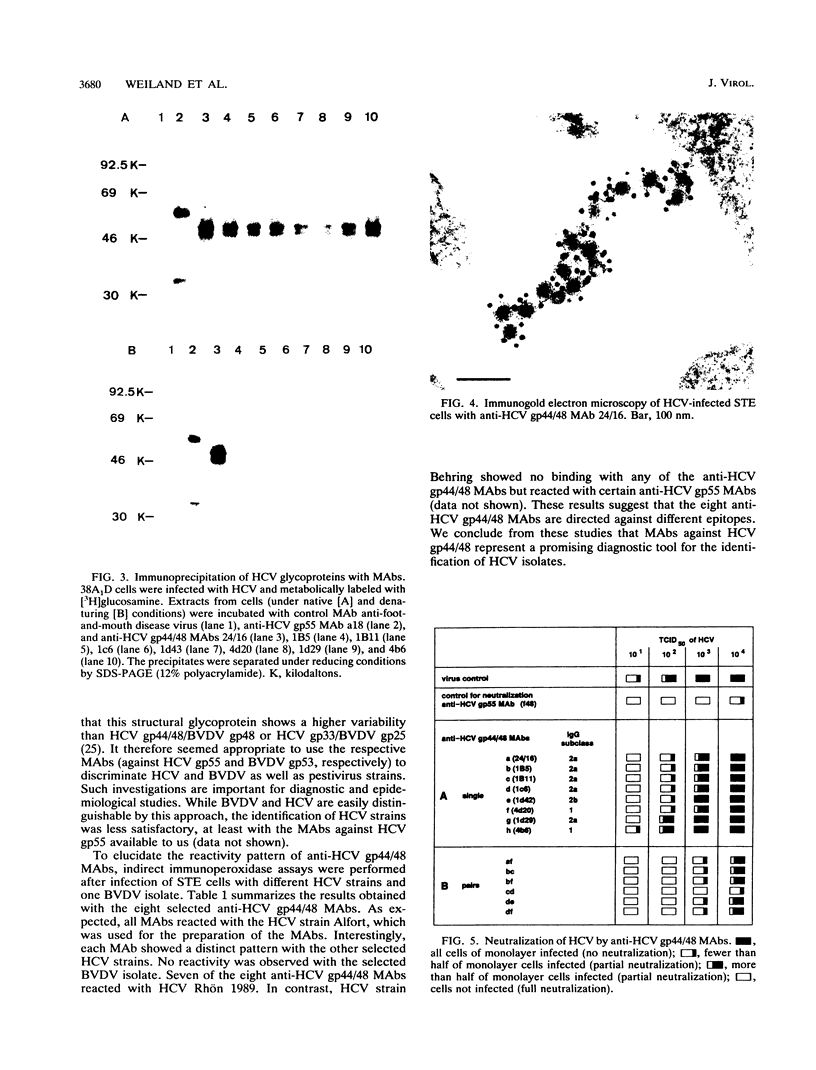
Several monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) raised against hog cholera virus (HCV) reacted with the HCV structural glycoprotein gp44/48 and neutralized the virus. The presence of HCV gp44/48 on the viral surface was directly demonstrated by immunogold electron microscopy. Eight anti-HCV gp44/48 MAbs were tested by immunoperoxidase assay against a panel of pestivirus strains. Each MAb showed a distinct pattern of reactivity with HCV strains. It is suggested that the MAbs are well suited for epidemiological investigations of HCV outbreaks.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson L. J., Bingham P., Hierholzer J. C. Neutralization of respiratory syncytial virus by individual and mixtures of F and G protein monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4232–4238. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4232-4238.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colett M. S., Larson R., Gold C., Strick D., Anderson D. K., Purchio A. F. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the pestivirus bovine viral diarrhea virus. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90672-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Larson R., Belzer S. K., Retzel E. Proteins encoded by bovine viral diarrhea virus: the genomic organization of a pestivirus. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):200–208. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90673-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis R. O., Corapi W., Dubovi E. J. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to bovine viral diarrhoea virus bind to the 56K to 58K glycoprotein. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):77–86. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucet J. P., Trifaró J. M. A discontinuous and highly porous sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide slab gel system of high resolution. Anal Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;168(2):265–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90317-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubuisson J., Guillaume J., Boulanger D., Thiry E., Bublot M., Pastoret P. P. Neutralization of bovine herpesvirus type 4 by pairs of monoclonal antibodies raised against two glycoproteins and identification of antigenic determinants involved in neutralization. J Gen Virol. 1990 Mar;71(Pt 3):647–653. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-3-647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Use of protein A-bearing staphylococci for the immunoprecipitation and isolation of antigens from cells. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):442–459. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsford L., Boucquey K. H. Monoclonal antibodies specific for the G1 glycoprotein of La Crosse virus that react with other California serogroup viruses. J Gen Virol. 1990 Mar;71(Pt 3):523–530. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-3-523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsford L. Enhanced neutralization of La Crosse virus by the binding of specific pairs of monoclonal antibodies to the G1 glycoprotein. Virology. 1984 Jul 30;136(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90163-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClurkin A. W., Norman J. O. Studies on transmissible gastroenteritis of swine. II. Selected characteristics of a cytopathogenic virus common to five isolates from transmissible gastroenteritis. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1966 Jul;30(7):190–198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCullough K. C. Monoclonal antibodies: implications for virology. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1986;87(1-2):1–36. doi: 10.1007/BF01310540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers G., Rümenapf T., Thiel H. J. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the genome of hog cholera virus. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):555–567. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90625-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moormann R. J., Warmerdam P. A., van der Meer B., Schaaper W. M., Wensvoort G., Hulst M. M. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of hog cholera virus strain Brescia and mapping of the genomic region encoding envelope protein E1. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):184–198. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90472-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rümenapf T., Meyers G., Stark R., Thiel H. J. Hog cholera virus--characterization of specific antiserum and identification of cDNA clones. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):18–27. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90506-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rümenapf T., Stark R., Meyers G., Thiel H. J. Structural proteins of hog cholera virus expressed by vaccinia virus: further characterization and induction of protective immunity. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):589–597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.589-597.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R., Rümenapf T., Meyers G., Thiel H. J. Genomic localization of hog cholera virus glycoproteins. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):286–289. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandström H., Veijalainen P., Moennig V., Hunsmann G., Schwarz H., Schäfer W. C-type particles produced by a permanent cell line from a leukemic pig. I. Origin and properties of the host cells and some evidence for the occurrence of C-type-like particles. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiel H. J., Stark R., Weiland E., Rümenapf T., Meyers G. Hog cholera virus: molecular composition of virions from a pestivirus. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4705–4712. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4705-4712.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland E., Stark R., Haas B., Rümenapf T., Meyers G., Thiel H. J. Pestivirus glycoprotein which induces neutralizing antibodies forms part of a disulfide-linked heterodimer. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3563–3569. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3563-3569.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensvoort G., Boonstra J., Bodzinga B. G. Immunoaffinity purification and characterization of the envelope protein E1 of hog cholera virus. J Gen Virol. 1990 Mar;71(Pt 3):531–540. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-3-531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zijl M., Wensvoort G., de Kluyver E., Hulst M., van der Gulden H., Gielkens A., Berns A., Moormann R. Live attenuated pseudorabies virus expressing envelope glycoprotein E1 of hog cholera virus protects swine against both pseudorabies and hog cholera. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2761–2765. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2761-2765.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]