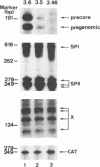
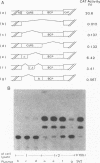
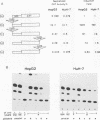
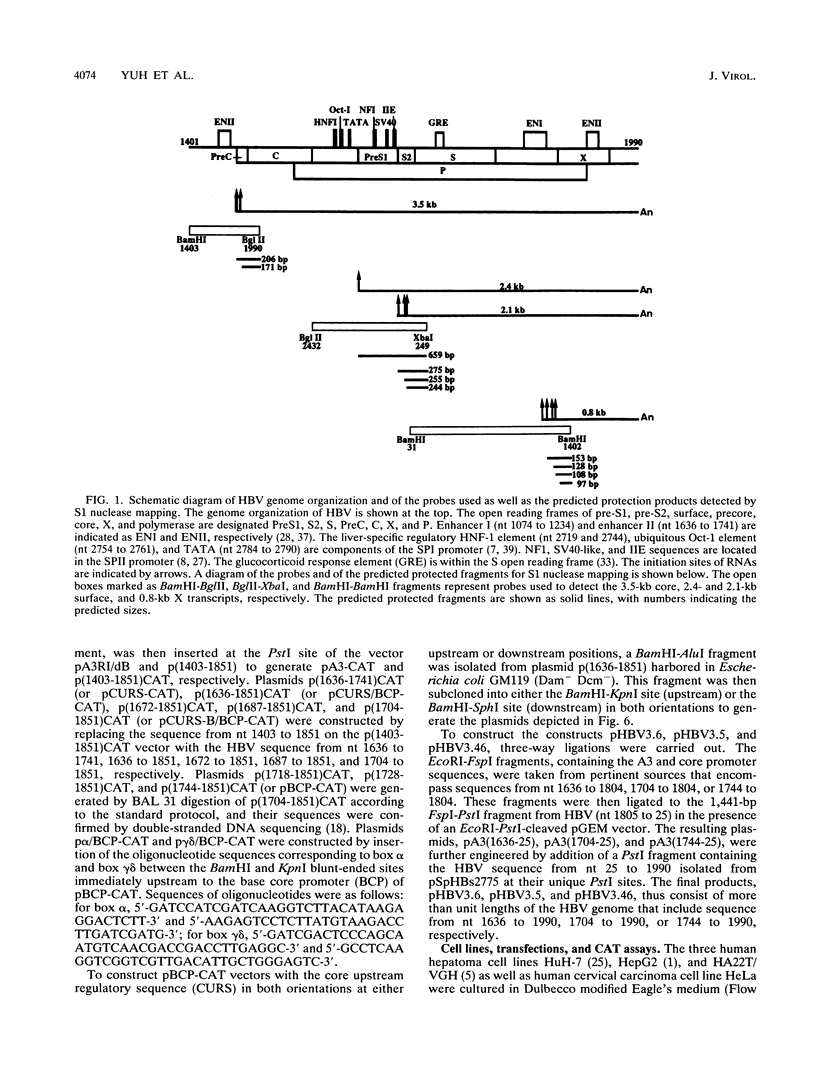
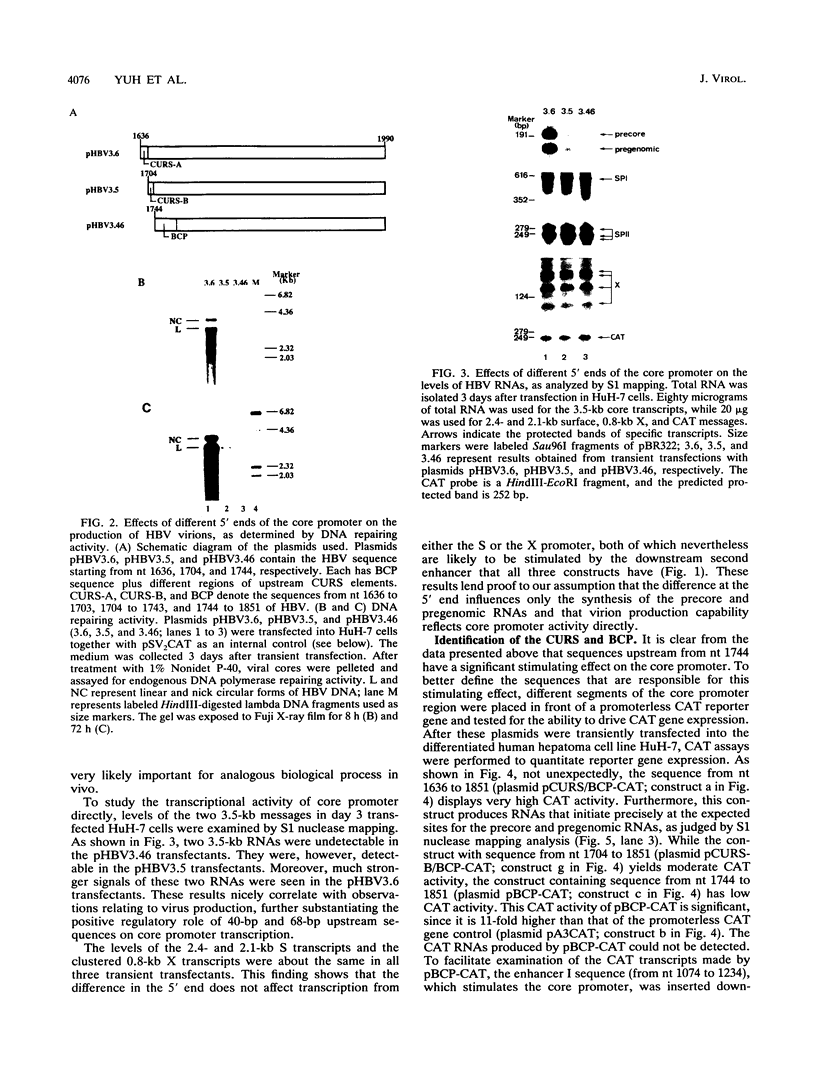
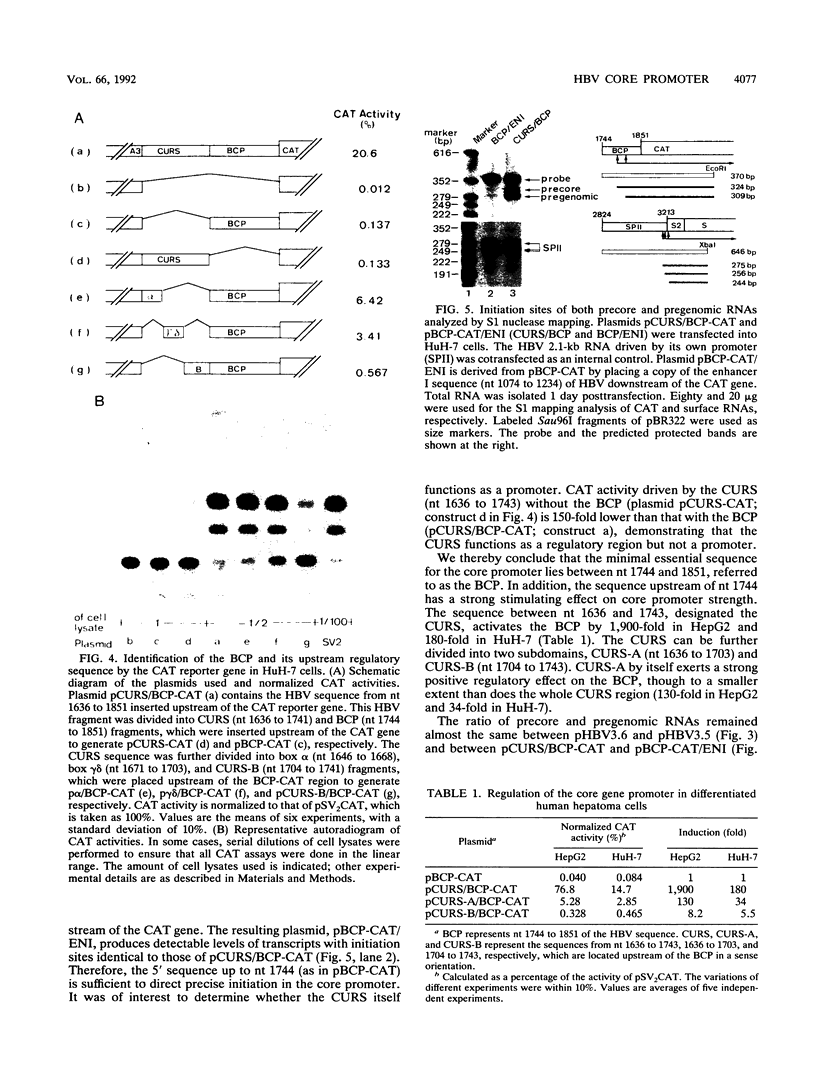
Abstract
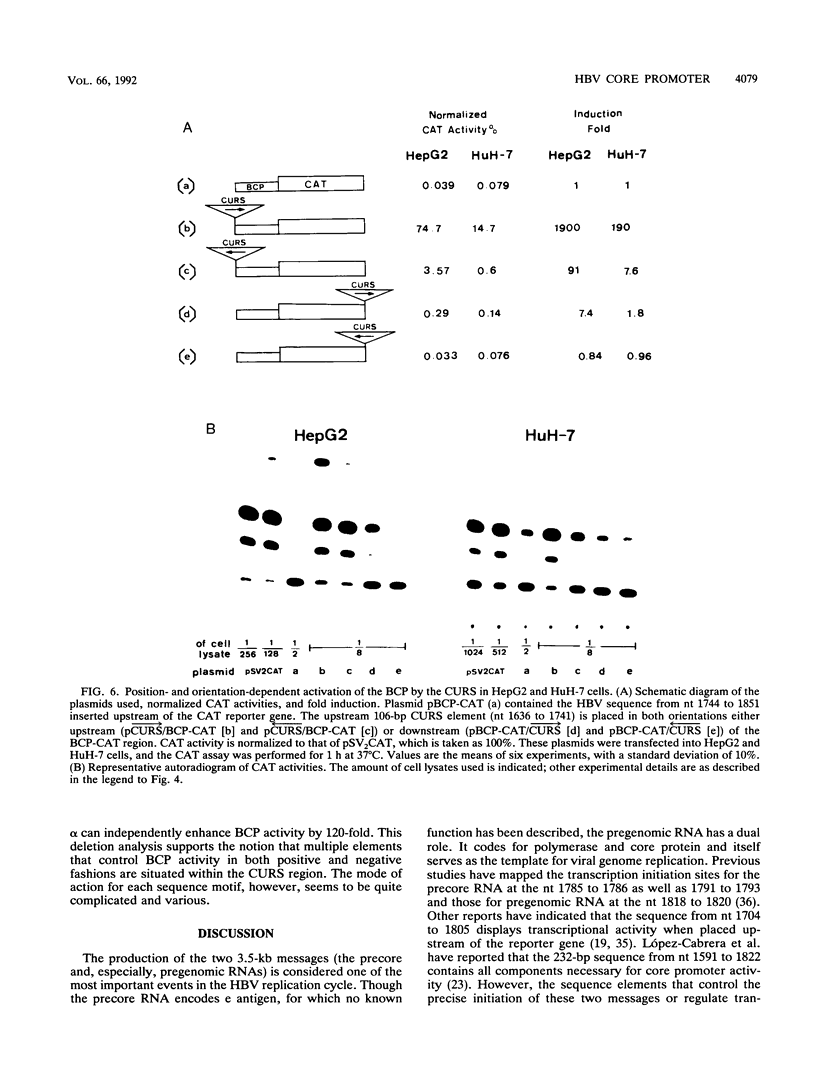
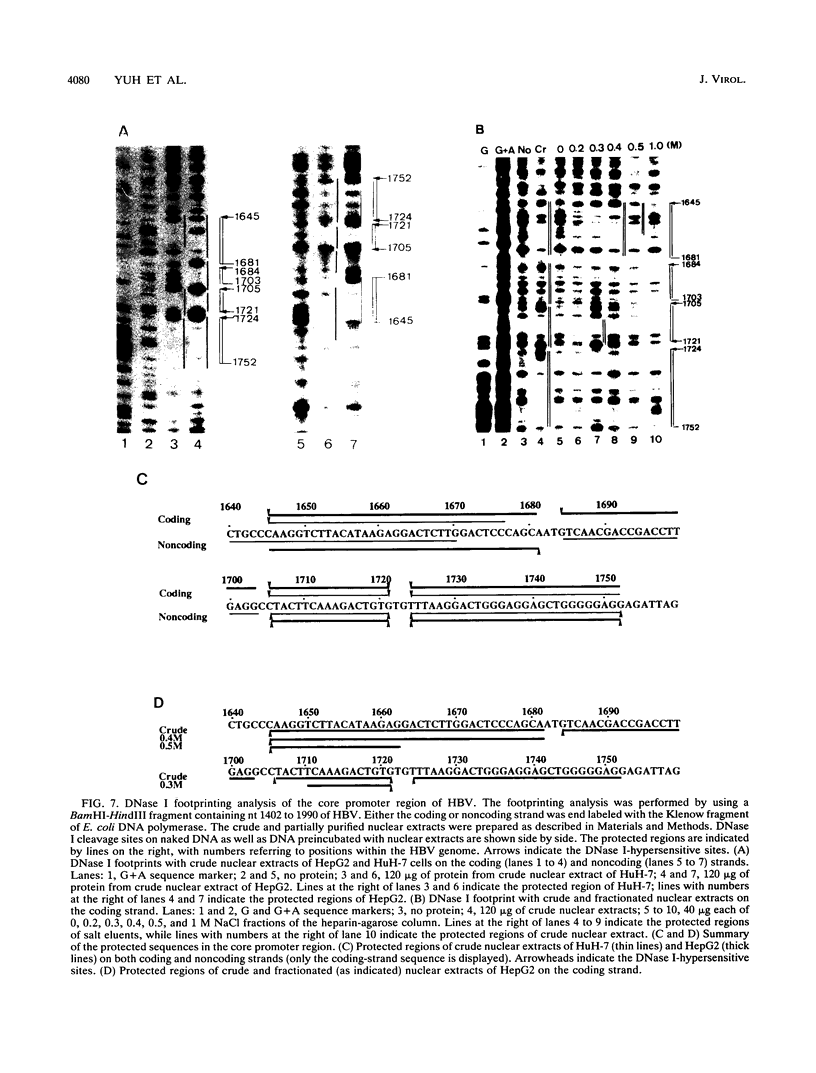
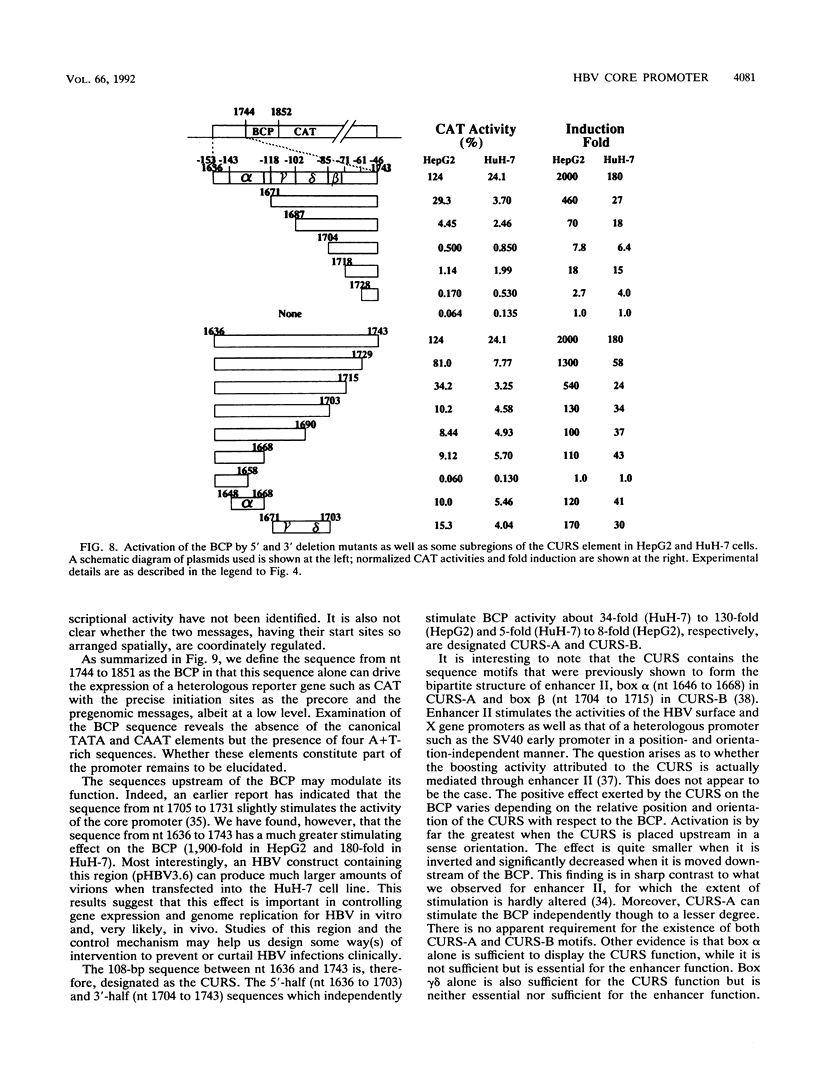
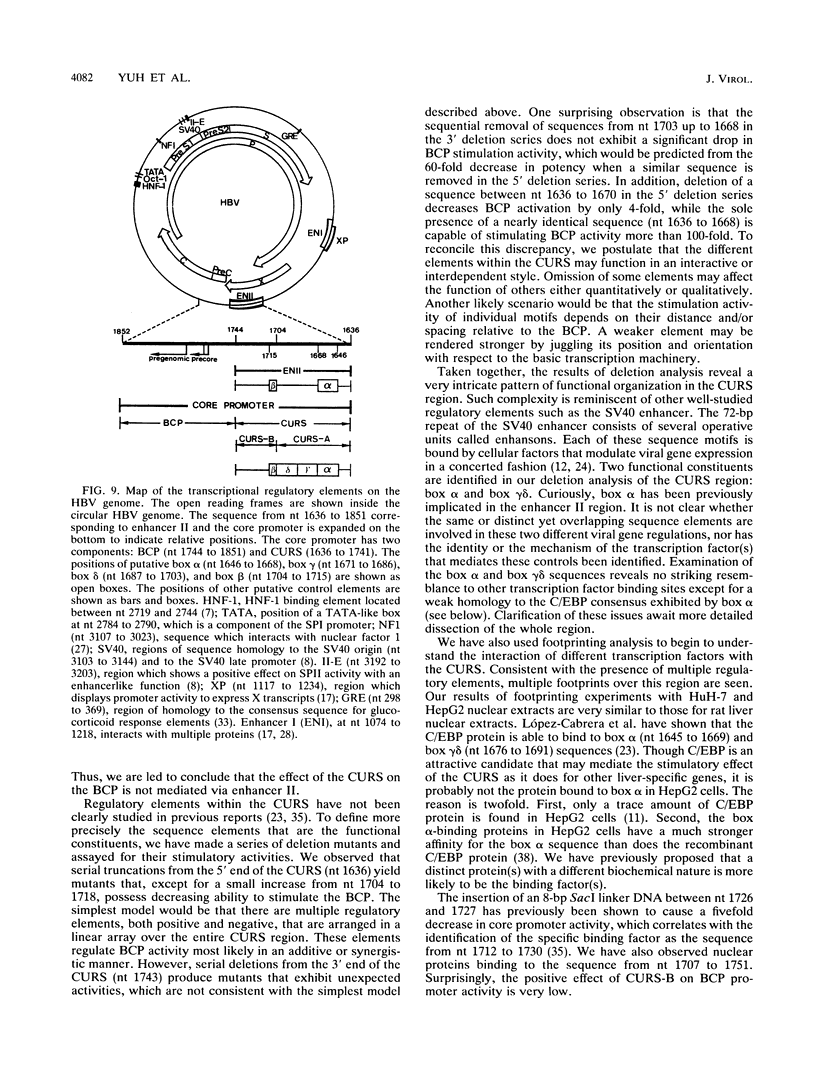
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, either acute or chronic, has been one of the leading health problems in the world. To understand the HBV life cycle and disease process, we set out to study the regulation of viral gene expression. In this paper, we report the characterization of the HBV core promoter: two 3.5-kb transcripts, precore and pregenomic, are made from it. The latter is itself a template for viral genome replication and also encodes viral proteins essential for both viral replication and virion assembly. We identify a short sequence (from nucleotides [nt] 1744 to 1851, referred to as the basic core promoter [BCP]) that is sufficient to direct correct initiation of both precore and pregenomic messages. In addition, the two appear to be regulated in a coordinate manner. Sequences upstream of the BCP (from nt 1636 to 1744, referred to as the core upstream regulatory sequence [CURS]), have a strong stimulating effect on the BCP. Addition of the CURS to the BCP leads to a dramatic increase in both the transcription of two 3.5-kb messages and the production of 42-nm virions from transiently transfected hepatoma cells. The CURS stimulates the BCP in a position- and orientation-dependent manner. Therefore, it is unlikely that the effect is mediated through enhancer II, which has been localized to the same sequence. Deletion analysis of the CURS suggests that it contains multiple regulatory elements that control the BCP in an interactive manner. In accord with this hypothesis, the CURS is found to be bound with many distinct protein factors in footprinting experiments. Among these elements, box alpha (from nt 1646 to 1668) and box gamma delta (from nt 1671 to 1703) are two regulatory elements which individually stimulate promoter activity more than 100-fold.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aden D. P., Fogel A., Plotkin S., Damjanov I., Knowles B. B. Controlled synthesis of HBsAg in a differentiated human liver carcinoma-derived cell line. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):615–616. doi: 10.1038/282615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley R. P., Hwang L. Y., Lin C. C., Chien C. S. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study of 22 707 men in Taiwan. Lancet. 1981 Nov 21;2(8256):1129–1133. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90585-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. M., Jeng K. S., Hu C. P., Lo S. J., Su T. S., Ting L. P., Chou C. K., Han S. H., Pfaff E., Salfeld J. Production of hepatitis B virus in vitro by transient expression of cloned HBV DNA in a hepatoma cell line. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):675–680. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04807.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Lin Y., O-Lee T. W., Chou C. K., Lee T. S., Liu T. J., P'eng F. K., Chen T. Y., Hu C. P. Induction of plasma protein secretion in a newly established human hepatoma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1133–1137. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. K., Ting L. P. The surface gene promoter of the human hepatitis B virus displays a preference for differentiated hepatocytes. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):176–183. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90364-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. K., Wang B. Y., Yuh C. H., Wei C. L., Ting L. P. A liver-specific nuclear factor interacts with the promoter region of the large surface protein gene of human hepatitis B virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5189–5197. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De-Medina T., Faktor O., Shaul Y. The S promoter of hepatitis B virus is regulated by positive and negative elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2449–2455. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders G. H., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. 5'-terminal sequences influence the segregation of ground squirrel hepatitis virus RNAs into polyribosomes and viral core particles. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):35–41. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.35-41.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farza H., Hadchouel M., Scotto J., Tiollais P., Babinet C., Pourcel C. Replication and gene expression of hepatitis B virus in a transgenic mouse that contains the complete viral genome. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4144–4152. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4144-4152.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein activates the promoter of the serum albumin gene in cultured hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1314–1322. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromental C., Kanno M., Nomiyama H., Chambon P. Cooperativity and hierarchical levels of functional organization in the SV40 enhancer. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):943–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo W. T., Bell K. D., Ou J. H. Characterization of the hepatitis B virus EnhI enhancer and X promoter complex. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6686–6692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6686-6692.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honigwachs J., Faktor O., Dikstein R., Shaul Y., Laub O. Liver-specific expression of hepatitis B virus is determined by the combined action of the core gene promoter and the enhancer. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):919–924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.919-924.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junker M., Galle P., Schaller H. Expression and replication of the hepatitis B virus genome under foreign promoter control. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10117–10132. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. M., Greenman R. L., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Robinson W. S. DNA polymerase associated with human hepatitis B antigen. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):995–1005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.995-1005.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Cabrera M., Letovsky J., Hu K. Q., Siddiqui A. Multiple liver-specific factors bind to the hepatitis B virus core/pregenomic promoter: trans-activation and repression by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5069–5073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi H., Taketa K., Miyano K., Yamane T., Sato J. Growth of human hepatoma cells lines with differentiated functions in chemically defined medium. Cancer Res. 1982 Sep;42(9):3858–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Gloss L., Herr W. The SV40 enhancer contains two distinct levels of organization. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):40–45. doi: 10.1038/333040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger C., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Biochemical and genetic evidence for the hepatitis B virus replication strategy. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):477–484. doi: 10.1126/science.3961490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Ben-Levy R., De-Medina T. High affinity binding site for nuclear factor I next to the hepatitis B virus S gene promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1967–1971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Rutter W. J., Laub O. A human hepatitis B viral enhancer element. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):427–430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Mason W. S. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B--like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):403–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sureau C., Romet-Lemonne J. L., Mullins J. I., Essex M. Production of hepatitis B virus by a differentiated human hepatoma cell line after transfection with cloned circular HBV DNA. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90364-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Pourcel C., Dejean A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):489–495. doi: 10.1038/317489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tur-Kaspa R., Shaul Y., Moore D. D., Burk R. D., Okret S., Poellinger L., Shafritz D. A. The glucocorticoid receptor recognizes a specific nucleotide sequence in hepatitis B virus DNA causing increased activity of the HBV enhancer. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):630–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will H., Reiser W., Weimer T., Pfaff E., Büscher M., Sprengel R., Cattaneo R., Schaller H. Replication strategy of human hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):904–911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.904-911.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma K., Koike K. Identification of a promoter region for 3.6-kilobase mRNA of hepatitis B virus and specific cellular binding protein. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2914–2920. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2914-2920.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma K., Shirakata Y., Kobayashi M., Koike K. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) particles are produced in a cell culture system by transient expression of transfected HBV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2678–2682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuh C. H., Ting L. P. C/EBP-like proteins binding to the functional box-alpha and box-beta of the second enhancer of hepatitis B virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5044–5052. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuh C. H., Ting L. P. The genome of hepatitis B virus contains a second enhancer: cooperation of two elements within this enhancer is required for its function. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4281–4287. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4281-4287.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D. X., Yen T. S. The ubiquitous transcription factor Oct-1 and the liver-specific factor HNF-1 are both required to activate transcription of a hepatitis B virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1353–1359. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]