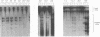Abstract
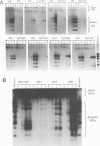
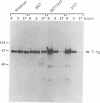
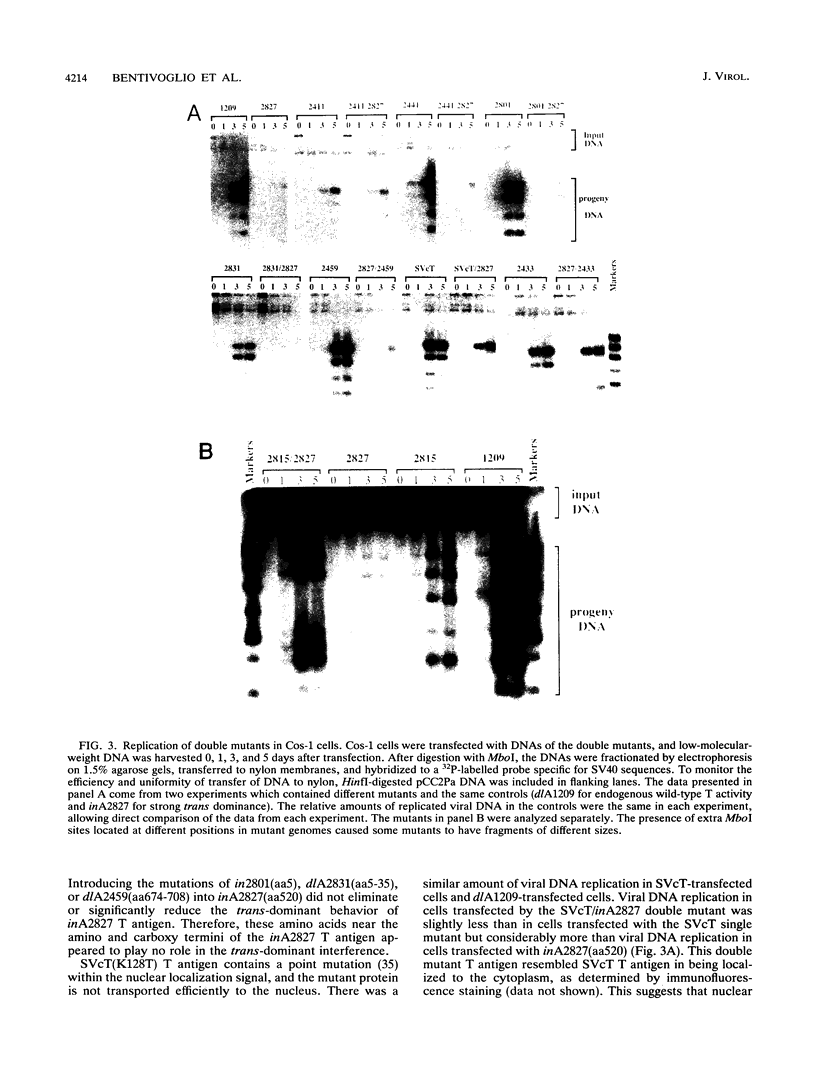
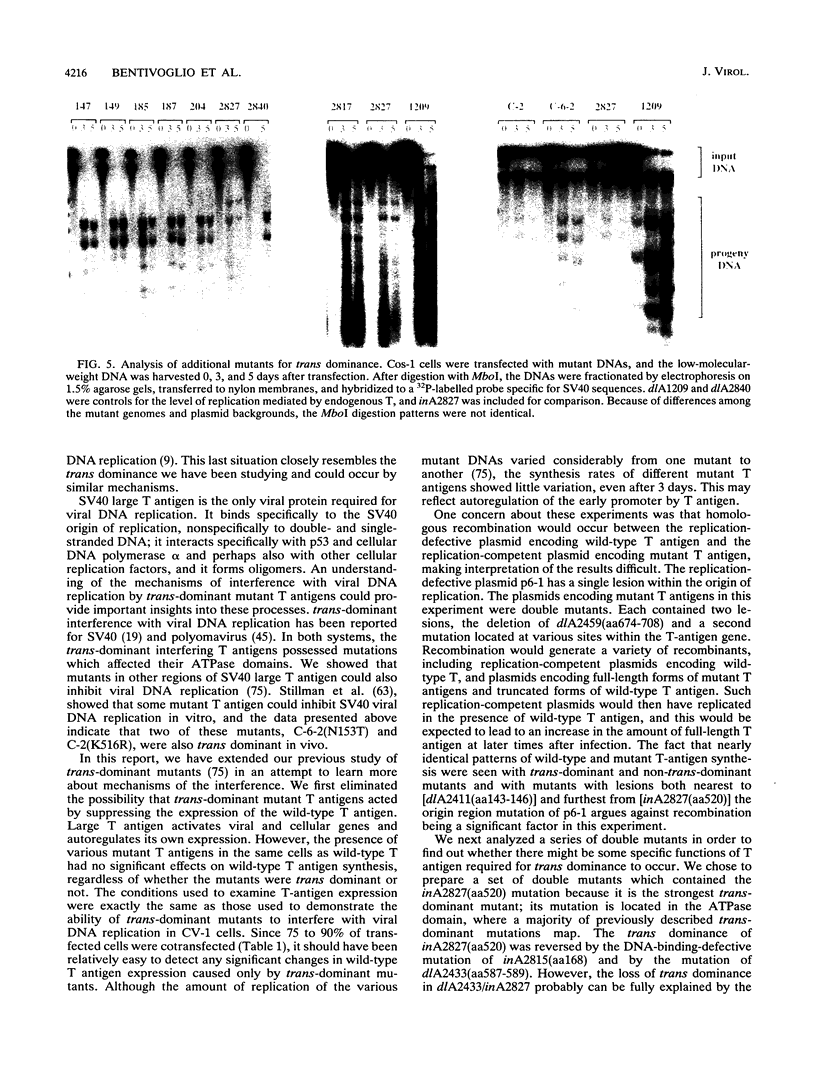
Mutations at multiple sites within the simian virus 40 (SV40) early region yield large T antigens which interfere trans dominantly with the replicative activities of wild-type T antigen. A series of experiments were conducted to study possible mechanisms of interference with SV40 DNA replication caused by these mutant T antigens. First, the levels of wild-type T antigen expression in cells cotransfected with wild-type and mutant SV40 DNAs were examined; approximately equal levels of wild-type T antigen were seen, regardless of whether the cotransfected mutant was trans dominant or not. Second, double mutants that contained the mutation of inA2827, a strong trans-dominant mutation with a 12-bp linker inserted at the position encoding amino acid 520, and various mutations in other parts of the large-T-antigen coding region were constructed. The trans-dominant interference of inA2827 was not affected by second mutations within the p105Rb binding site or the amino or carboxy terminus of large T antigen. Mutation of the nuclear localization signal partially reduced the trans dominance of inA2827. The large T antigen of mutant inA2815 contains an insertion of 4 amino acids at position 168 of large T; this T antigen fails to bind SV40 DNA but is not trans dominant for DNA replication. The double mutant containing the mutations of both inA2815 and in A2827 was not trans dominant. The large T antigen of dlA2433 lacks amino acids 587 to 589, was unstable, and failed to bind p53. Combining the dlA2433 mutation with the inA2827 mutation also reversed the trans dominance completely, but the effect of the dlA2433 mutation on trans dominance can be explained by the instability of this double mutant protein. In addition, we examined several mutants with conservative point mutations in the DNA binding domain and found that most of them were not trans dominant. The implications of the results of these experiments on possible mechanisms of trans dominance are discussed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auborn K., Guo M., Prives C. Helicase, DNA-binding, and immunological properties of replication-defective simian virus 40 mutant T antigens. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):912–918. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.912-918.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Dean F. B., Bullock P. A., Hurwitz J. Binding and unwinding--how T antigen engages the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90730-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley M. K. Activation of ATPase activity of simian virus 40 large T antigen by the covalent affinity analog of ATP, fluorosulfonylbenzoyl 5'-adenosine. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4939–4947. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4939-4947.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley M. K., Griffin J. D., Livingston D. M. Relationship of oligomerization to enzymatic and DNA-binding properties of the SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90382-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley M. K., Smith T. F., Lathrop R. H., Livingston D. M., Webster T. A. Consensus topography in the ATP binding site of the simian virus 40 and polyomavirus large tumor antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4026–4030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Bolen J. B., Radonovich M., Salzman N., Khoury G. Stimulation of simian virus 40 late gene expression by simian virus 40 tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2040–2044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. B., Hager L., Dulbecco R. Simian virus 40 T antigen binds to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3754–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chejanovsky N., Carter B. J. Mutation of a consensus purine nucleotide binding site in the adeno-associated virus rep gene generates a dominant negative phenotype for DNA replication. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1764–1770. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1764-1770.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y., Martin R. G. DNA infectivity and the induction of host DNA synthesis with temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):145–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.145-150.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Crawford L. V., Berg P. Simian virus 40 mutants with deletions at the 3' end of the early region are defective in adenovirus helper function. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):683–691. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.683-691.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Landers T., Goff S. P., Manteuil-Brutlag S., Berg P. Physical and genetic characterization of deletion mutants of simian virus 40 constructed in vitro. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):277–294. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.277-294.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Stacy T. P. Biological properties of simian virus 40 host range mutants lacking the COOH-terminus of large T antigen. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):170–180. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Tornow J., Clark R., Tjian R. Properties of the simian virus 40 (SV40) large T antigens encoded by SV40 mutants with deletions in gene A. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):539–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.539-546.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornreiter I., Höss A., Arthur A. K., Fanning E. SV40 T antigen binds directly to the large subunit of purified DNA polymerase alpha. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3329–3336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07533.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Ludlow J. W., Marsilio E., DeCaprio J. A., Millikan R. C., Cheng S. H., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. An N-terminal transformation-governing sequence of SV40 large T antigen contributes to the binding of both p110Rb and a second cellular protein, p120. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90840-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. M., Peden K. W., Nathans D. trans-dominant defective mutants of simian virus 40 T antigen. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):436–445. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.436-445.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Triezenberg S. J., McKnight S. L. Expression of a truncated viral trans-activator selectively impedes lytic infection by its cognate virus. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):452–454. doi: 10.1038/335452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 and DNA polymerase alpha compete for binding to SV40 T antigen. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):456–458. doi: 10.1038/329456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Davison J., Oren M., Winocour E. Properties of permissive monkey cells transformed by UV-irradiated simian virus 40. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):256–266. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.256-266.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Frisque R. J., Sambrook J. Origin-defective mutants of SV40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):293–300. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman N., Brown M., Khoury G. Modification of SV40 T antigen by poly ADP-ribosylation. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):567–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90347-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Ishino M., Loewenstein P. M. Mutational analysis of HIV-1 Tat minimal domain peptides: identification of trans-dominant mutants that suppress HIV-LTR-driven gene expression. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90417-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P., Zervos P., Raducha M., Harris H., Kadesch T. Expression of a human placental alkaline phosphatase gene in transfected cells: use as a reporter for studies of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6342–6346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwabuchi M., Shibata T., Ohtani T., Natori M., Ando T. ATP-dependent unwinding of the double helix and extensive supercoiling by Escherichia coli recA protein in the presence of topoisomerase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12394–12404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENSEN F. C., GIRARDI A. J., GILDEN R. V., KOPROWSKI H. INFECTION OF HUMAN AND SIMIAN TISSUE CULTURES WITH ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:53–59. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis D. L., Butel J. S. Modification of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen by glycosylation. Virology. 1985 Mar;141(2):173–189. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90250-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Activation of the SV40 late promoter: direct effects of T antigen in the absence of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura G., Dulbecco R. A temperature-sensitive mutant of simian virus 40 affecting transforming ability. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):529–534. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90348-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Butel J. S. Construction and characterization of an SV40 mutant defective in nuclear transport of T antigen. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):801–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90415-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6973–6977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Böhnlein S., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Functional dissection of the HIV-1 Rev trans-activator--derivation of a trans-dominant repressor of Rev function. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manos M. M., Gluzman Y. Genetic and biochemical analysis of transformation-competent, replication-defective simian virus 40 large T antigen mutants. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):120–127. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.120-127.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastrangelo I. A., Hough P. V., Wall J. S., Dodson M., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. ATP-dependent assembly of double hexamers of SV40 T antigen at the viral origin of DNA replication. Nature. 1989 Apr 20;338(6217):658–662. doi: 10.1038/338658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McVey D., Brizuela L., Mohr I., Marshak D. R., Gluzman Y., Beach D. Phosphorylation of large tumour antigen by cdc2 stimulates SV40 DNA replication. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):503–507. doi: 10.1038/341503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson S. V., Magnusson G. Activities of polyomavirus large-T-antigen proteins expressed by mutant genes. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):768–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.768-775.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. E., Stenger J. E., Ray S., Welker R., Anderson M. E., Tegtmeyer P. Cooperative assembly of simian virus 40 T-antigen hexamers on functional halves of the replication origin. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2798–2806. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2798-2806.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Stillman B. Coordinated leading and lagging strand synthesis during SV40 DNA replication in vitro requires PCNA. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90493-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransone L. J., Visvader J., Wamsley P., Verma I. M. Trans-dominant negative mutants of Fos and Jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimsky L., Dodon M. D., Dixon E. P., Greene W. C. Trans-dominant inactivation of HTLV-I and HIV-1 gene expression by mutation of the HTLV-I Rex transactivator. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):453–456. doi: 10.1038/341453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C., Tjian R. SV40 T antigen binding site mutations that affect autoregulation. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1227–1240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawai E. T., Butel J. S. Association of a cellular heat shock protein with simian virus 40 large T antigen in transformed cells. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3961–3973. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3961-3973.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Echle B., Walter G. Simian virus 40 large T antigen is phosphorylated at multiple sites clustered in two separate regions. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):116–133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.116-133.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J., Schindewolf C., van Zee K., Fanning E. A mutant SV40 large T antigen interferes with nuclear localization of a heterologous protein. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard A. A., Tolentino P., DeLuca N. A. trans-dominant inhibition of herpes simplex virus transcriptional regulatory protein ICP4 by heterodimer formation. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3916–3926. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3916-3926.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Loeber G., Tegtmeyer P. Four major sequence elements of simian virus 40 large T antigen coordinate its specific and nonspecific DNA binding. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):1973–1983. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.1973-1983.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Wun-Kim K., Young W. Identification of simian virus 40 T-antigen residues important for specific and nonspecific binding to DNA and for helicase activity. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4858–4865. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4858-4865.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Tjian R. T-antigen-DNA polymerase alpha complex implicated in simian virus 40 DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4077–4087. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprano K. J., Dev V. G., Croce C. M., Baserga R. Reactivation of silent rRNA genes by simian virus 40 in human-mouse hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3885–3889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprano K. J., Galanti N., Jonak G. J., McKercher S., Pipas J. M., Peden K. W., Baserga R. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 T antigen: stimulation of cellular DNA synthesis and activation of rRNA genes by mutants with deletions in the T-antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):214–219. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Dröge P., Knippers R. DNA helicase activity of SV40 large tumor antigen. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1939–1944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B., Gerard R. D., Guggenheimer R. A., Gluzman Y. T antigen and template requirements for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2933–2939. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Function of simian virus 40 gene A in transforming infection. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):613–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.613-618.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia M. J. Immortalization of primary mouse embryo fibroblasts with SV40 virions, viral DNA, and a subgenomic DNA fragment in a quantitative assay. Virology. 1984 Sep;137(2):414–421. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia M. J., Pipas J. M., Kierstead T., Cole C. Requirements for immortalization of primary mouse embryo fibroblasts probed with mutants bearing deletions in the 3' end of SV40 gene A. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):76–89. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90396-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornow J., Cole C. N. Intracistronic complementation in the simian virus 40 A gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6312–6316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornow J., Cole C. N. Nonviable mutants of simian virus 40 with deletions near the 3' end of gene A define a function for large T antigen required after onset of viral DNA replication. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):487–494. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.487-494.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornow J., Polvino-Bodnar M., Santangelo G., Cole C. N. Two separable functional domains of simian virus 40 large T antigen: carboxyl-terminal region of simian virus 40 large T antigen is required for efficient capsid protein synthesis. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):415–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.415-424.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J. Y., Cole C. N. Linker insertion mutants of simian virus 40 large T antigen that show trans-dominant interference with wild-type large T antigen map to multiple sites within the T-antigen gene. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4777–4786. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4777-4786.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J. Y., Rice P. W., Chamberlain M., Cole C. N. Mapping the transcriptional transactivation function of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2778–2790. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2778-2790.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J., Rice P. W., Gorsch L., Abate M., Cole C. N. Transformation of a continuous rat embryo fibroblast cell line requires three separate domains of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2780–2791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2780-2791.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]