Abstract
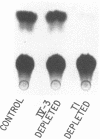
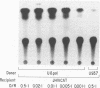
One of the unexplained aspects of the progression of AIDS is that immunological abnormalities are detectable before CD4+ T-helper cell depletion occurs (A.R. Gruters, F.G. Terpstra, R. De Jong, C.J.M. Van Noesel, R.A.W. Van Lier, and F. Miedema, Eur. J. Immunol. 20:1039-1044, 1990; F. Miedema, A.J. Chantal-Petit, F.G. Terpstra, J.K.M.E. Schattenkerk, F. de Wolf, B.J.M. Al, M. Roos, J.M.A. Lang, S.A. Danner, J. Goudsmit, and P.T.A. Schellekens, J. Clin. Invest. 82:1908-1914, 1988; G.M. Shearer, D.C. Bernstein, K.S. Tung, C.S. Via, R. Redfield, S.Z. Salahuddin, and R.C. Gallo, J. Immunol. 137:2514-2521, 1986). In this report, we describe a mechanism by which human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-infected cells can influence neighboring HIV-1-infected T lymphocytes and uninfected T cells as well. We have examined the interaction of T-cell and macrophage cell lines that are transfected with HIV-1 DNA by using cocultured lymphocytes. The HIV-1 constructs we used lack a functional pol gene and therefore do not produce infectious virus. Cocultivation results in the transcellular activation of the HIV long terminal repeat in the cocultured T cells. This transcellular activation is evident in as little as 3 h of cocultivation, at ratios of HIV-expressing cells to target cells as low as 1:1,000, and is dependent on the Tat-responsive element. The demonstration that a small number of HIV-expressing cells can affect a large number of uninfected bystander cells in a short period of time suggests a mechanism by which global immune dysfunction can precede the high prevalence of infected cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arya S. K., Guo C., Josephs S. F., Wong-Staal F. Trans-activator gene of human T-lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III). Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):69–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2990040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brake D. A., Debouck C., Biesecker G. Identification of an Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) cell adhesion site in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transactivation protein, tat. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1275–1281. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus occurs via a bimodal mechanism. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton A. I., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Goh W. C., Haseltine W. A. The trans-activator gene of the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III is required for replication. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):941–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond D. C., Sleckman B. P., Gregory T., Lasky L. A., Greenstein J. L., Burakoff S. J. Inhibition of CD4+ T cell function by the HIV envelope protein, gp120. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3715–3717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Barillari G., Salahuddin S. Z., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Tat protein of HIV-1 stimulates growth of cells derived from Kaposi's sarcoma lesions of AIDS patients. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):84–86. doi: 10.1038/345084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenow M., Huet T., Saurin W., Kwok S., Sninsky J., Wain-Hobson S. HIV-1 isolates are rapidly evolving quasispecies: evidence for viral mixtures and preferred nucleotide substitutions. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(4):344–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruters R. A., Terpstra F. G., De Jong R., Van Noesel C. J., Van Lier R. A., Miedema F. Selective loss of T cell functions in different stages of HIV infection. Early loss of anti-CD3-induced T cell proliferation followed by decreased anti-CD3-induced cytotoxic T lymphocyte generation in AIDS-related complex and AIDS. Eur J Immunol. 1990 May;20(5):1039–1044. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld H., Cruikshank W. W., Pyle S. W., Berman J. S., Center D. M. Lymphocyte activation by HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):445–448. doi: 10.1038/335445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Reyes G. R., McGrath M. S., Stein B. S., Engleman E. G. AIDS retrovirus induced cytopathology: giant cell formation and involvement of CD4 antigen. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1123–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.3010463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. A., Frankel A. D. Endocytosis and targeting of exogenous HIV-1 Tat protein. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1733–1739. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07697.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. L., Gartner S., Le Sane F., Buchow H., Popovic M. HIV-1 transmission and function of virus-infected monocytes/macrophages. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2152–2158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. L., Lasane F., Popovic M., Arthur L. O., Robey W. G., Blattner W. A., Newman M. J. HTLV-III large envelope protein (gp120) suppresses PHA-induced lymphocyte blastogenesis. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2640–2644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhans A., Cheynier R., Albert J., Seth M., Kwok S., Sninsky J., Morfeldt-Månson L., Asjö B., Wain-Hobson S. Temporal fluctuations in HIV quasispecies in vivo are not reflected by sequential HIV isolations. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):901–910. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90942-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miedema F., Petit A. J., Terpstra F. G., Schattenkerk J. K., de Wolf F., Al B. J., Roos M., Lange J. M., Danner S. A., Goudsmit J. Immunological abnormalities in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected asymptomatic homosexual men. HIV affects the immune system before CD4+ T helper cell depletion occurs. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):1908–1914. doi: 10.1172/JCI113809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Capon D. J. Regulation of mRNA accumulation by a human immunodeficiency virus trans-activator protein. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):691–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newstein M., Stanbridge E. J., Casey G., Shank P. R. Human chromosome 12 encodes a species-specific factor which increases human immunodeficiency virus type 1 tat-mediated trans activation in rodent cells. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4565–4567. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4565-4567.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Benter T., Josephs S. F., Sadaie M. R., Wong-Staal F. Transcriptional activation from the long-terminal repeat of human immunodeficiency virus in vitro. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):606–614. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90526-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyaizu N., Chirmule N., Kalyanaraman V. S., Hall W. W., Pahwa R., Shuster M., Pahwa S. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein gp120 produces immune defects in CD4+ T lymphocytes by inhibiting interleukin 2 mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2379–2383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):813–823. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S. M., Psallidopoulos M. C., Lane H. C., Thompson L., Baseler M., Massari F., Fox C. H., Salzman N. P., Fauci A. S. The reservoir for HIV-1 in human peripheral blood is a T cell that maintains expression of CD4. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):305–308. doi: 10.1126/science.2665081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer G. M., Bernstein D. C., Tung K. S., Via C. S., Redfield R., Salahuddin S. Z., Gallo R. C. A model for the selective loss of major histocompatibility complex self-restricted T cell immune responses during the development of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2514–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Campbell K., Haseltine W. A. Role of the HTLV-III/LAV envelope in syncytium formation and cytopathicity. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):470–474. doi: 10.1038/322470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Patarca R., Rosen C., Wong-Staal F., Haseltine W. Location of the trans-activating region on the genome of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):74–77. doi: 10.1126/science.2990041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viscidi R. P., Mayur K., Lederman H. M., Frankel A. D. Inhibition of antigen-induced lymphocyte proliferation by Tat protein from HIV-1. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1606–1608. doi: 10.1126/science.2556795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl L. M., Corcoran M. L., Pyle S. W., Arthur L. O., Harel-Bellan A., Farrar W. L. Human immunodeficiency virus glycoprotein (gp120) induction of monocyte arachidonic acid metabolites and interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):621–625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]