Abstract
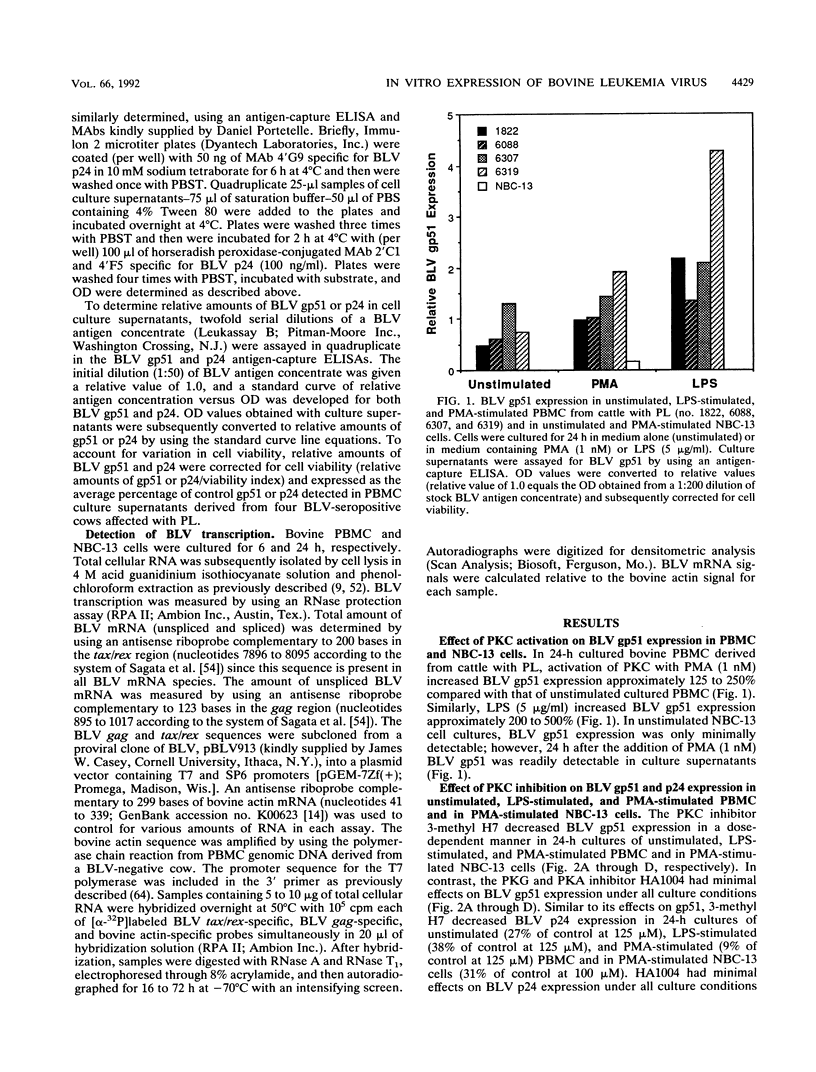
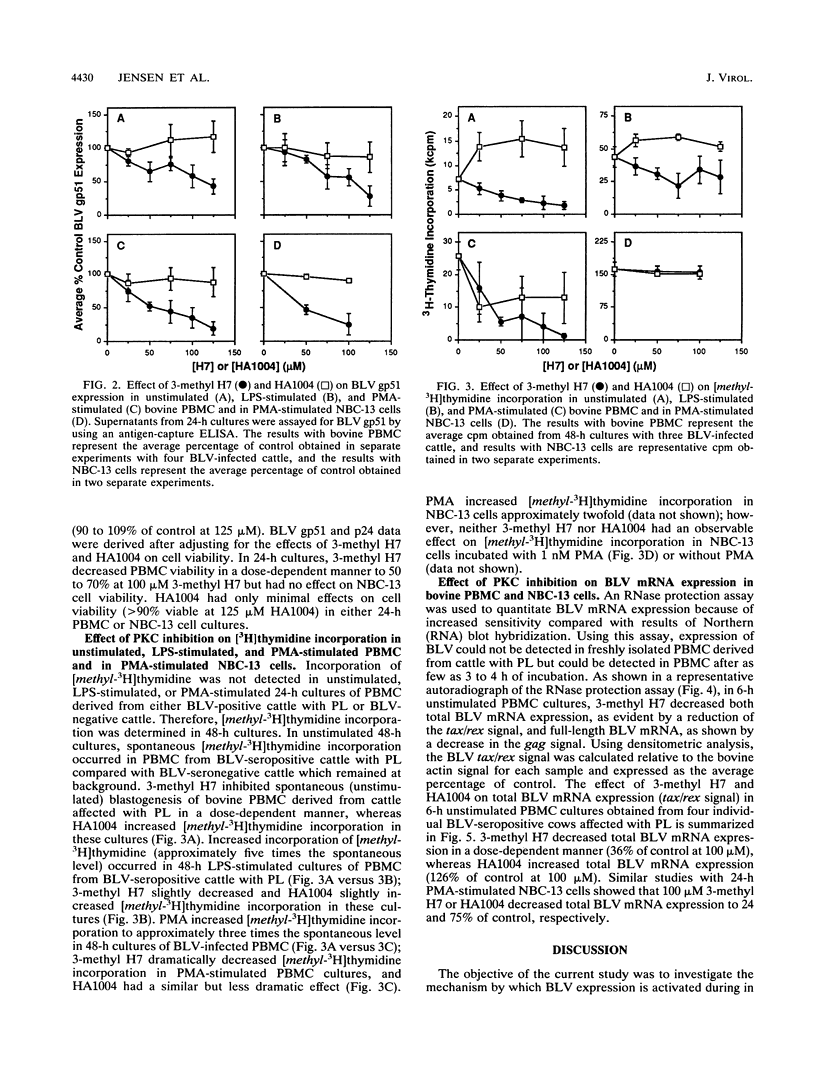
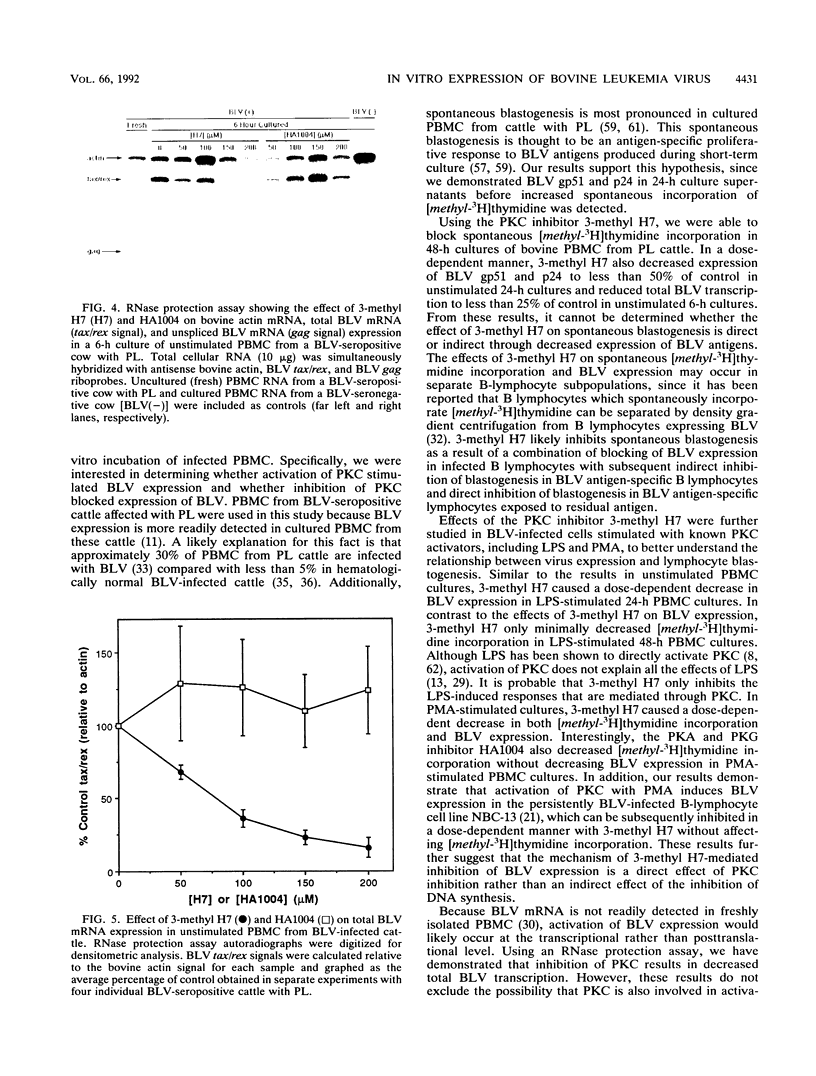
The in vitro expression of bovine leukemia virus (BLV) in short-term cultured bovine peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) is associated with increased spontaneous lymphocyte blastogenesis. The purpose of this study was to determine whether intracellular pathways responsible for antigen- or mitogen-induced lymphocyte blastogenesis were also responsible for induction of BLV expression. The protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor 1-(5-isoquinolinylsulfonyl)-3-methylpiperazine dihydrochloride (3-methyl H7) decreased blastogenesis in a dose-dependent manner, as measured by [3H]thymidine incorporation, in unstimulated, lipopolysaccharide-stimulated and phorbol ester (PMA)-stimulated BLV-infected PBMC. Similarly, 3-methyl H7 decreased BLV expression, as measured by production of gp51 envelope antigen or p24gag antigen, in BLV-infected PBMC under the same conditions. Using an RNase protection assay, the inhibition of BLV expression by 3-methyl H7 was shown to be due to decreased transcriptional activity. The cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor N-(2-guanidinoethyl)-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (HA1004) did not inhibit either BLV expression or blastogenesis of BLV-infected bovine PBMC. Additional evidence for the PKC-dependent expression of BLV was obtained by using a persistently BLV-infected B-lymphocyte cell line, NBC-13. Activation of PKC by PMA in NBC-13 cells increased BLV expression. 3-methyl H7 decreased the PMA-induced expression of BLV in NBC-13 cells in a dose-dependent manner, whereas HA1004 did not inhibit this expression. These results identify a mechanism for the induction of BLV expression through PKC activation and therefore indicate that latency and replication of BLV is controlled by normal B-lymphocyte intracellular signaling pathways.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi Y., Nosaka T., Hatanaka M. Protein kinase inhibitor H-7 blocks accumulation of unspliced mRNA of human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 15;169(2):469–475. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90355-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aida Y., Miyasaka M., Okada K., Onuma M., Kogure S., Suzuki M., Minoprio P., Levy D., Ikawa Y. Further phenotypic characterization of target cells for bovine leukemia virus experimental infection in sheep. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Nov;50(11):1946–1951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atluru D., Polam S., Atluru S., Woloschak G. E. Regulation of mitogen-stimulated human T-cell proliferation, interleukin-2 production, and interleukin-2 receptor expression by protein kinase C inhibitor, H-7. Cell Immunol. 1990 Sep;129(2):310–320. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90207-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atluru D., Polam S., Sarraju L., Blecha F., Minocha H. C., Atluru S. Inhibition of phytohemagglutinin-stimulated bovine mononuclear cell proliferation, interleukin-2 production and protein kinase C activity by a protein kinase C inhibitor, H-7. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 May;25(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(90)90111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baliga V., Ferrer J. F. Expression of the bovine leukemia virus and its internal antigen in blood lymphocytes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Nov;156(2):388–391. doi: 10.3181/00379727-156-39942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder S., Gallo R. C. Human T-cell leukemia viruses (HTLV): a unique family of pathogenic retroviruses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:321–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Ransom J. T. Molecular mechanisms of transmembrane signaling in B lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:175–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Z., Coggeshall K. M., Cambier J. C. Translocation of protein kinase C during membrane immunoglobulin-mediated transmembrane signaling in B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2300–2304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury I. H., Koyanagi Y., Kobayashi S., Hamamoto Y., Yoshiyama H., Yoshida T., Yamamoto N. The phorbol ester TPA strongly inhibits HIV-1-induced syncytia formation but enhances virus production: possible involvement of protein kinase C pathway. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):126–132. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90237-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerell G. L., Rovnak J. The correlation between the direct and indirect detection of bovine leukemia virus infection in cattle. Leuk Res. 1988;12(6):465–469. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(88)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornil I., Delon P., Parodi A. L., Levy D. T-B cell cooperation for bovine leukemia virus expression in ovine lymphocytes. Leukemia. 1988 May;2(5):313–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L. Molecular aspects of B-lymphocyte activation. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:143–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen J. L., Neubauer M. G., Degen S. J., Seyfried C. E., Morris D. R. Regulation of protein synthesis in mitogen-activated bovine lymphocytes. Analysis of actin-specific and total mRNA accumulation and utilization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12153–12162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D. Bovine leukemia virus transcription is controlled by a virus-encoded trans-acting factor and by cis-acting response elements. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2462–2471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2462-2471.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D. trans-acting regulation of bovine leukemia virus mRNA processing. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1115–1119. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1115-1119.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps J., Kettmann R., Burny A. Experiments with cloned complete tumor-derived bovine leukemia virus information prove that the virus is totally exogenous to its target animal species. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):605–609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.605-609.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshayes L., Levy D., Parodi A. L., Levy J. P. Spontaneous immune response of bovine leukemia-virus-infected cattle against five different viral proteins. Int J Cancer. 1980 Apr 15;25(4):503–508. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910250412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djilali S., Parodi A. L., Levy D. Bovine leukemia virus replicates in sheep B lymphocytes under a T cell released factor. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1987 Jan;23(1):81–85. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(87)90423-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. M., Baumgartener L. E., Olson C. Concanavalin A and the production of bovine leukemia virus antigen in short-term lymphocyte cultures. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 May;58(5):1513–1514. doi: 10.1093/jnci/58.5.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer J. F., Stock N. D., Lin P. Detection of replicating C-type viruses in continuous cell cultures established from cows with leukemia: effect of the culture medium. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Sep;47(3):613–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossum C., Burny A., Portetelle D., Mammerickx M., Morein B. Detection of B and T cells, with lectins or antibodies, in healthy and bovine leukemia virus-infected cattle. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Apr;18(3):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grupp S. A., Harmony J. A. Increased phosphatidylinositol metabolism is an important but not an obligatory early event in B lymphocyte activation. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4087–4094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P., Kashmiri S. V., Ferrer J. F. Transcriptional control of the bovine leukemia virus genome: role and characterization of a non-immunoglobulin plasma protein from bovine leukemia virus-infected cattle. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):267–270. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.267-270.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamamoto Y., Matsuyama T., Yamamoto N., Kobayashi N. Augmentation of cytotoxic effect of tumor necrosis factor on human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells by staurosporine, a potent protein kinase C inhibitor. Cancer Res. 1990 Sep 1;50(17):5287–5290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. B., Nielsen S. E., Berg K. Re-examination and further development of a precise and rapid dye method for measuring cell growth/cell kill. J Immunol Methods. 1989 May 12;119(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90397-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits A., Rosenthal A., Capon D. J. Trans-activation of HIV-1 LTR-directed gene expression by tat requires protein kinase C. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1165–1170. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08223.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakway J. P., DeFranco A. L. Pertussis toxin inhibition of B cell and macrophage responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Science. 1986 Nov 7;234(4777):743–746. doi: 10.1126/science.3095921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen W. A., Rovnak J., Cockerell G. L. In vivo transcription of the bovine leukemia virus tax/rex region in normal and neoplastic lymphocytes of cattle and sheep. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2484–2490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2484-2490.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon S. J., Piper C. E. Cellular basis of persistent lymphocytosis in cattle infected with bovine leukemia virus. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):891–897. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.891-897.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon S. J., Piper C. E. Properties of density gradient-fractionated peripheral blood leukocytes from cattle infected with bovine leukemia virus. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):898–903. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.898-903.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettmann R., Cleuter Y., Mammerickx M., Meunier-Rotival M., Bernardi G., Burny A., Chantrenne H. Genomic integration of bovine leukemia provirus: comparison of persistent lymphocytosis with lymph node tumor form of enzootic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2577–2581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettmann R., Deschamps J., Cleuter Y., Couez D., Burny A., Marbaix G. Leukemogenesis by bovine leukemia virus: proviral DNA integration and lack of RNA expression of viral long terminal repeat and 3' proximate cellular sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2465–2469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettmann R., Marbaix G., Cleuter Y., Portetelle D., Mammerickx M., Burny A. Genomic integration of bovine leukemia provirus and lack of viral RNA expression in the target cells of cattle with different responses to BLV infection. Leuk Res. 1980;4(6):509–519. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(80)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinter A. L., Poli G., Maury W., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S. Direct and cytokine-mediated activation of protein kinase C induces human immunodeficiency virus expression in chronically infected promonocytic cells. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4306–4312. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4306-4312.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kischel T., Harbers M., Stabel S., Borowski P., Müller K., Hilz H. Tumor promotion and depletion of protein kinase C in epidermal JB6 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):981–987. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92699-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyokawa T., Seiki M., Iwashita S., Imagawa K., Shimizu F., Yoshida M. p27x-III and p21x-III, proteins encoded by the pX sequence of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8359–8363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemsz M. J., Justement L. B., Palmer E., Cambier J. C. Induction of c-fos and c-myc expression during B cell activation by IL-4 and immunoglobulin binding ligands. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):1032–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Coligan J. E., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A., Salahuddin S. Z., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Essex M. Antigens encoded by the 3'-terminal region of human T-cell leukemia virus: evidence for a functional gene. Science. 1984 Oct 5;226(4670):57–61. doi: 10.1126/science.6089350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévy D., Kettmann R., Marchand P., Djilali S., Parodi A. L. Selective tropism of bovine leukemia virus (BLV) for surface immunoglobulin-bearing ovine B lymphocytes. Leukemia. 1987 May;1(5):463–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. M., Miller L. D., Olson C., Gillette K. G. Virus-like particles in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated lymphocyte cultures with reference to bovine lymphosarcoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Dec;43(6):1297–1305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuguchi J., Tsang W., Morrison S. L., Beaven M. A., Paul W. E. Membrane IgM, IgD, and IgG act as signal transmission molecules in a series of B lymphomas. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2162–2167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscoplat C. C., Alhaji I., Johnson D. W., Pomeroy K. A., Olson J. M., Larson V. L., Stevens J. B., Sorensen D. K. Characteristics of lymphocyte responses to phytomitogens: comparison of responses of lymphocytes from normal and lymphocytotic cows. Am J Vet Res. 1974 Aug;35(8):1053–1055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul P. S., Pomeroy K. A., Castro A. E., Johnson D. W., Muscoplat C. C., Sorensen D. K. Detection of bovine leukemia virus in B-lymphocytes by the syncytia induction assay. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Oct;59(4):1269–1272. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.4.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul P. S., Pomeroy K. A., Johnson D. W., Muscoplat C. C., Handwerger B. S., Soper F. F., Sorensen D. K. Evidence for the replication of bovine leukemia virus in the B lymphocytes. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jun;38(6):873–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portetelle D., Bruck C., Burny A., Dekegel D., Mammerickx M., Urbain J. Detection of complement-dependent lytic antibodies in sera from bovine leukemia virus-infected animals. Ann Rech Vet. 1978;9(4):667–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portetelle D., Couez D., Bruck C., Kettmann R., Mammerickx M., Van der Maaten M., Brasseur R., Burny A. Antigenic variants of bovine leukemia virus (BLV) are defined by amino acid substitutions in the NH2 part of the envelope glycoprotein gp51. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portetelle D., Mammerickx M., Burny A. Use of two monoclonal antibodies in an ELISA test for the detection of antibodies to bovine leukaemia virus envelope protein gp51. J Virol Methods. 1989 Feb;23(2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(89)90135-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puissant C., Houdebine L. M. An improvement of the single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Biotechniques. 1990 Feb;8(2):148–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom J. T., Cambier J. C. B cell activation. VII. Independent and synergistic effects of mobilized calcium and diacylglycerol on membrane potential and I-A expression. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):66–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Yasunaga T., Tsuzuku-Kawamura J., Ohishi K., Ogawa Y., Ikawa Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of the genome of bovine leukemia virus: its evolutionary relationship to other retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):677–681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Shimotohno K., Cline M. J., Golde D. W., Chen I. S. Identification of the putative transforming protein of the human T-cell leukemia viruses HTLV-I and HTLV-II. Science. 1984 Oct 5;226(4670):61–65. doi: 10.1126/science.6089351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock N. D., Ferrer J. F. Replicating C-type virus in phytohemagglutinin-treated buffy-coat cultures of bovine origin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Apr;48(4):985–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima I., Olson C. Effect of mitogens and anti-bovine leukosis virus serums on DNA synthesis of lymphocytes from cattle. Eur J Cancer. 1980 May;16(5):639–645. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(80)90204-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan T. H., Jia R., Roeder R. G. Utilization of signal transduction pathway by the human T-cell leukemia virus type I transcriptional activator tax. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3761–3768. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3761-3768.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorn R. M., Gupta P., Kenyon S. J., Ferrer J. F. Evidence that the spontaneous blastogenesis of lymphocytes from bovine leukemia virus-infected cattle is viral antigen specific. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):84–89. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.84-89.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Broeke A., Cleuter Y., Chen G., Portetelle D., Mammerickx M., Zagury D., Fouchard M., Coulombel L., Kettmann R., Burny A. Even transcriptionally competent proviruses are silent in bovine leukemia virus-induced sheep tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9263–9267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villouta G., Botto G., Rudolph W. Spontaneous and mitogen-induced RNA synthesis by blood lymphocytes from bovine leukemia virus-infected and normal cows. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Apr;18(3):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(88)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wightman P. D., Raetz C. R. The activation of protein kinase C by biologically active lipid moieties of lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10048–10052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L., Amborski G. F., Davis W. C. Enumeration of T and B lymphocytes in bovine leukemia virus-infected cattle, using monoclonal antibodies. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jul;49(7):1098–1103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. D., Ailles L., Deugau K., Kisilevsky R. Transcription of cRNA for in situ hybridization from polymerase chain reaction-amplified DNA. Lab Invest. 1991 May;64(5):709–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



