Abstract
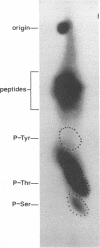
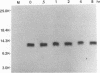
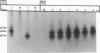
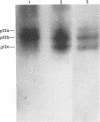
We have previously shown that the 12-kDa capsid protein (p12) of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) is a gamma 2 (true late) gene product encoded by the UL35 open reading frame (D. S. McNabb and R. J. Courtney, J. Virol. 66:2653-2663, 1992). To extend the characterization of p12, we have investigated the posttranslational modifications and intracellular localization of the 12-kDa polypeptide. These studies have demonstrated that p12 is modified by phosphorylation at serine and threonine residues. In addition, analysis of p12 by acid-urea gel electrophoresis has indicated that the protein can be resolved into three components, designated p12a, p12b, and p12c. Using isotopic-labeling and alkaline phosphatase digestion experiments, we have determined that p12a and p12b are phosphorylated forms of the protein, and p12c is likely to represent the unphosphorylated polypeptide. The kinetics of phosphorylation was examined by pulse-chase radiolabeling, and these studies indicated that p12c can be completely converted into p12a and p12b following a 4-h chase. All three species of p12 were found to be associated with purified HSV-1 virions; however, p12b and p12c represented the most abundant forms of the protein within viral particles. We have also examined the intracellular localization of p12 by cell fractionation and indirect immunofluorescence techniques. These results indicated that p12 is predominantly localized in the nucleus of HSV-1-infected cells and appears to be restricted to specific regions within the nucleus.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker T. S., Newcomb W. W., Booy F. P., Brown J. C., Steven A. C. Three-dimensional structures of maturable and abortive capsids of equine herpesvirus 1 from cryoelectron microscopy. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):563–573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.563-573.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone D. R., Courtney R. J. A temperature-sensitive mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1 defective in the synthesis of the major capsid polypeptide. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):17–27. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booy F. P., Newcomb W. W., Trus B. L., Brown J. C., Baker T. S., Steven A. C. Liquid-crystalline, phage-like packing of encapsidated DNA in herpes simplex virus. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90324-r. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun D. K., Batterson W., Roizman B. Identification and genetic mapping of a herpes simplex virus capsid protein that binds DNA. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):645–648. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.645-648.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun D. K., Roizman B., Pereira L. Characterization of post-translational products of herpes simplex virus gene 35 proteins binding to the surfaces of full capsids but not empty capsids. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):142–153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.142-153.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassai E. N., Sarmiento M., Spear P. G. Comparison of the virion proteins specified by herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1327–1331. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1327-1331.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Lawrence G. L., Barrell B. G. Alpha-, beta- and gammaherpesviruses encode a putative phosphotransferase. J Gen Virol. 1989 May;70(Pt 5):1151–1160. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-5-1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Ponce de Leon M., Diggelmann H., Lawrence W. C., Vernon S. K., Eisenberg R. J. Structural analysis of the capsid polypeptides of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):521–531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.521-531.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton T., Courtney R. J. Virus-specific glycoproteins associated with the nuclear fraction of herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):594–597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.594-597.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flannery V. L., Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A. Expression of an early, nonstructural antigen of herpes simplex virus in cell transformed in vitro by herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.284-291.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. 8. Characterization and composition of multiple capsid forms of subtypes 1 and 2. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1044–1052. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1044-1052.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. Structural and nonstructural proteins of strain Colburn cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1981 Jun;111(2):516–537. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90354-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich L. D., Schaffer P. A., Dorsky D. I., Crumpacker C. S., Parris D. S. Localization of the herpes simplex virus type 1 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein and DNA polymerase in the presence and absence of viral DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5738–5749. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5738-5749.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilman C. J., Jr, Zweig M., Stephenson J. R., Hampar B. Isolation of a nucleocapsid polypeptide of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 possessing immunologically type-specific and cross-reactive determinants. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):34–42. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.34-42.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Acid and base hydrolysis of phosphoproteins bound to immobilon facilitates analysis of phosphoamino acids in gel-fractionated proteins. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jan;176(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Senechek D., Rice S. A., Smith J. L. Stages in the nuclear association of the herpes simplex virus transcriptional activator protein ICP4. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):276–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.276-284.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Spang A. E. Definition of a series of stages in the association of two herpesviral proteins with the cell nucleus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):314–324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.314-324.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf K. W., Kaerner H. C. Virus-specific basic phosphoproteins associated with herpes simplex virus type a (HSV-1) particles and the chromatin of HSV-1-infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1980 Feb;46(2):405–414. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-46-2-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leader D. P., Deana A. D., Marchiori F., Purves F. C., Pinna L. A. Further definition of the substrate specificity of the alpha-herpesvirus protein kinase and comparison with protein kinases A and C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Feb 19;1091(3):426–431. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90210-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. Y., Irmiere A., Gibson W. Primate cytomegalovirus assembly: evidence that DNA packaging occurs subsequent to B capsid assembly. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Courtney R. J., Fowler G., Rouse B. T. Herpes simplex virus type 1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize virus nonstructural proteins. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2265–2273. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2265-2273.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNabb D. S., Courtney R. J. Identification and characterization of the herpes simplex virus type 1 virion protein encoded by the UL35 open reading frame. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2653–2663. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2653-2663.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb W. W., Brown J. C. Structure of the herpes simplex virus capsid: effects of extraction with guanidine hydrochloride and partial reconstitution of extracted capsids. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):613–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.613-620.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb W. W., Brown J. C. Use of Ar+ plasma etching to localize structural proteins in the capsid of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4697–4702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4697-4702.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Courtney R. J. Polypeptide synthesized in herpes simplex virus type 2-infected HEp-2 cells. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Watson D. H. Some structural antigens of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1975 Nov;29(2):167–178. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-29-2-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Coates J. A., Rixon F. J. Identification and characterization of a herpes simplex virus gene product required for encapsidation of virus DNA. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1056–1064. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1056-1064.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves F. C., Deana A. D., Marchiori F., Leader D. P., Pinna L. A. The substrate specificity of the protein kinase induced in cells infected with herpesviruses: studies with synthetic substrates [corrected] indicate structural requirements distinct from other protein kinases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 28;889(2):208–215. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves F. C., Spector D., Roizman B. The herpes simplex virus 1 protein kinase encoded by the US3 gene mediates posttranslational modification of the phosphoprotein encoded by the UL34 gene. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5757–5764. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5757-5764.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Chen L. B., Knipe D. M. The intranuclear location of a herpes simplex virus DNA-binding protein is determined by the status of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):857–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrag J. D., Prasad B. V., Rixon F. J., Chiu W. Three-dimensional structure of the HSV1 nucleocapsid. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):651–660. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90587-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman G., Bachenheimer S. L. Characterization of intranuclear capsids made by ts morphogenic mutants of HSV-1. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):471–480. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90288-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F., Smith T. F. Identification of new protein kinase-related genes in three herpesviruses, herpes simplex virus, varicella-zoster virus, and Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):450–455. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.450-455.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. V. Purification and structural proteins of the herpesvirion. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):143–159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.143-159.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon S. K., Ponce de Leon M., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J., Rubin B. A. Morphological components of herpesvirus. III. Localization of herpes simplex virus type 1 nucleocapsid polypeptides by immune electron microscopy. J Gen Virol. 1981 May;54(Pt 1):39–46. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox K. W., Kohn A., Sklyanskaya E., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus phosphoproteins. I. Phosphate cycles on and off some viral polypeptides and can alter their affinity for DNA. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):167–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.167-182.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao F., Courtney R. J. A major transcriptional regulatory protein (ICP4) of herpes simplex virus type 1 is associated with purified virions. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3338–3344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3338-3344.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweig M., Heilman C. J., Jr, Hampar B. Identification of disulfide-linked protein complexes in the nucleocapsids of herpes simplex virus type 2. Virology. 1979 Apr 30;94(2):442–450. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90474-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]